(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 22, 2014—If future generations were to live and work on the moon or on a distant asteroid, they would probably want a broadband connection to communicate with home bases back on Earth. They may even want to watch their favorite Earth-based TV show. That may now be possible thanks to a team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory who, working with NASA last fall, demonstrated for the first time that a data communication technology exists that can provide space dwellers with the connectivity we all enjoy here on Earth, enabling large data transfers and even high-definition video streaming.
At CLEO: 2014, being held June 8-13 in San Jose, California, USA, the team will present new details and the first comprehensive overview of the on-orbit performance of their record-shattering laser-based communication uplink between the moon and Earth, which beat the previous record transmission speed last fall by a factor of 4,800. Earlier reports have stated what the team accomplished, but have not provided the details of the implementation.
"This will be the first time that we present both the implementation overview and how well it actually worked," says Mark Stevens of MIT Lincoln Laboratory. "The on-orbit performance was excellent and close to what we'd predicted, giving us confidence that we have a good understanding of the underlying physics," Stevens says.
The team made history last year when their Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration (LLCD) transmitted data over the 384,633 kilometers between the moon and Earth at a download rate of 622 megabits per second, faster than any radio frequency (RF) system. They also transmitted data from the Earth to the moon at 19.44 megabits per second, a factor of 4,800 times faster than the best RF uplink ever used.
"Communicating at high data rates from Earth to the moon with laser beams is challenging because of the 400,000-kilometer distance spreading out the light beam," Stevens says. "It's doubly difficult going through the atmosphere, because turbulence can bend light—causing rapid fading or dropouts of the signal at the receiver."
To outmaneuver problems with fading of the signal over such a distance, the demonstration uses several techniques to achieve error-free performance over a wide range of optically challenging atmospheric conditions in both darkness and bright sunlight. A ground terminal at White Sands, New Mexico, uses four separate telescopes to send the uplink signal to the moon. Each telescope is about 6 inches in diameter and fed by a laser transmitter that sends information coded as pulses of invisible infrared light. The total transmitter power is the sum of the four separate transmitters, which results in 40 watts of power.
The reason for the four telescopes is that each one transmits light through a different column of air that experiences different bending effects from the atmosphere, Stevens says. This increases the chance that at least one of the laser beams will interact with the receiver, which is mounted on a satellite orbiting the moon. This receiver uses a slightly narrower telescope to collect the light, which is then focused into an optical fiber similar to fibers used in terrestrial fiber optic networks.
From there, the signal in the fiber is amplified about 30,000 times. A photodetector converts the pulses of light into electrical pulses that are in turn converted into data bit patterns that carry the transmitted message. Of the 40-watt signals sent by the transmitter, less than a billionth of a watt is received at the satellite—but that's still about 10 times the signal necessary to achieve error-free communication, Stevens says.
Their CLEO: 2014 presentation will also describe how the large margins in received signal level can allow the system to operate through partly transparent thin clouds in the Earth's atmosphere, which the team views as a big bonus.
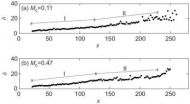
"We demonstrated tolerance to medium-size cloud attenuations, as well as large atmospheric-turbulence-induced signal power variations, or fading, allowing error-free performance even with very small signal margins," Stevens says.
While the LLCD design is directly relevant for near-Earth missions and those out to Lagrange points – areas where the forces between rotating celestial bodies are balanced, making them a popular destination for satellites -- the team predicts that it's also extendable to deep-space missions to Mars and the outer planets.
Presentation SM4J.1, titled "Overview and On-orbit Performance of the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration Uplink," will take place Monday, June 9, at 4:00 p.m. in Meeting Room 212 A/C of the San Jose Convention Center.
INFORMATION:
PRESS REGISTRATION: A press room for credentialed press and analysts will be located in the San Jose Convention Center, Sunday through Thursday, June 8-12. Those interested in obtaining a press badge for CLEO: 2014 should contact Lyndsay Meyer at 202.416.1435 or lmeyer@osa.org.
About CLEO
With a distinguished history as the industry's leading event on laser science, the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) is the premier international forum for scientific and technical optics, uniting the fields of lasers and opto-electronics by bringing together all aspects of laser technology, from basic research to industry applications. CLEO: Expo showcases the latest products and applications from more than 300 participating companies from around the world, providing hands-on demonstrations of the latest market innovations and applications. The Expo also offers valuable on-floor programming, including Market Focus and the Technology Transfer program.
Sponsored by the American Physical Society's (APS) Laser Science Division, IEEE Photonics Society and The Optical Society (OSA), CLEO provides the full range of critical developments in the field, showcasing the most significant milestones from laboratory to marketplace. With an unparalleled breadth and depth of coverage, CLEO connects all of the critical vertical markets in lasers and electro-optics. For more information, visit http://www.cleoconference.org. CLEO: 2014 takes place June 8 - 13 at the San Jose Convention Center.
First broadband wireless connection ... to the moon?!
MIT/NASA lunar laser communication team to present first report on record-shattering Earth-to-Moon uplink and its on-orbit performance
2014-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
On quantification of the growth of compressible mixing layer
2014-05-22
CML has been a research topic for more than five decades, due to its wide applications in propulsion design. Mixing in CML is controlled by the compressibility effects of velocity and density variations over the mixing layer, and quantified by the growth rate of CML. However, the lack of understanding of various definitions of mixing thicknesses has yielded scatter in analyzing experimental data. Prof. SHE ZhenSu and his colleagues at the State Key Laboratory for Turbulence and Complex Systems, Peking University investigated the growth of compressible mixing layer by introducing ...
Nanoshell-emitters hybrid nanoobject was proposed as promising 2-photon fluorescence probe
2014-05-22
Two-photon excitation fluorescence is growing in popularity in the bioimaging field but is limited by fluorophores' extremely low two-photon absorption cross-section. The researcher Dr. Guowei Lu and co-workers from State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Department of Physics, Peking University, are endeavoring to develop efficient fluorescent probes with improved two-photon fluorescence (TPF) performance. They theoretically present a promising bright probe using gold nanoshell to improve the TPF performances of fluorescent emitters. Their work, entitled "Plasmonic-Enhanced ...
Stanford research shows importance of European farmers adapting to climate change
2014-05-22
A new Stanford study finds that due to an average 3.5 degrees Fahrenheit of warming expected by 2040, yields of wheat and barley across Europe will drop more than 20 percent.
New Stanford research reveals that farmers in Europe will see crop yields affected as global temperatures rise, but that adaptation can help slow the decline for some crops.
For corn, the anticipated loss is roughly 10 percent, the research shows. Farmers of these crops have already seen yield growth slow down since 1980 as temperatures have risen, though other policy and economic factors have ...
Symbiosis or capitalism? A new view of forest fungi
2014-05-22
The so-called symbiotic relationship between trees and the fungus that grow on their roots may actually work more like a capitalist market relationship between buyers and sellers, according to the new study published in the journal New Phytologist.
Recent experiments in the forests of Sweden had brought into a question a long-held theory of biology: that the fungi or mycorrhizae that grow on tree roots work with trees in a symbiotic relationship that is beneficial for both the fungi and the trees, providing needed nutrients to both parties. These fungi, including many ...
Stanford, MIT scientists find new way to harness waste heat
2014-05-22
Vast amounts of excess heat are generated by industrial processes and by electric power plants. Researchers around the world have spent decades seeking ways to harness some of this wasted energy. Most such efforts have focused on thermoelectric devices – solid-state materials that can produce electricity from a temperature gradient – but the efficiency of such devices is limited by the availability of materials.
Now researchers at Stanford University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have found a new alternative for low-temperature waste-heat conversion into ...
A new target for alcoholism treatment: Kappa opioid receptors
2014-05-22
Philadelphia, PA, May 22, 2014 – The list of brain receptor targets for opiates reads like a fraternity: Mu Delta Kappa. The mu opioid receptor is the primary target for morphine and endogenous opioids like endorphin, whereas the delta opioid receptor shows the highest affinity for endogenous enkephalins. The kappa opioid receptor (KOR) is very interesting, but the least understood of the opiate receptor family.
Until now, the mu opioid receptor received the most attention in alcoholism research. Naltrexone, a drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for ...
Higher discharge rate for BPD in children and adolescents in the US compared to UK
2014-05-22
Washington D.C., May 22, 2014 – A study published in the June 2014 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry found a very much higher discharge rate for pediatric bipolar (PBD) in children and adolescents aged 1-19 years in the US compared to England between the years 2000-2010.
Using the English NHS Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) dataset and the US National Hospital Discharge Survey (NHDS) to compare US and English discharge rates for PBD over the period 2000-2010, the authors found a 72.1-fold higher discharge rate for pediatric ...
Liquid crystal as lubricant
2014-05-22
Lubricants are used in motors, axels, ventilators and manufacturing machines. Although lubricants are widely used, there have been almost no fundamental innovations for this product in the last twenty years. Together with a consortium, the Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM in Freiburg has developed an entirely new class of substance that could change everything: liquid crystalline lubricant. Its chemical makeup sets it apart; although it is a liquid, the molecules display directional properties like crystals do. When two surfaces move in opposite directions, ...
Fossil avatars are transforming palaeontology
2014-05-22
Palaeontology has traditionally proceeded slowly, with individual scientists labouring for years or even decades over the interpretation of single fossils which they have gradually recovered from entombing rock, sand grain by sand grain, using all manner of dental drills and needles.
The introduction of X-ray tomography has revolutionized the way that fossils are studied, allowing them to be virtually extracted from the rock in a fraction of the time necessary to prepare specimens by hand and without the risk of damaging the fossil.
The resulting fossil avatars not ...
Drug-target database lets researchers match old drugs to new uses
2014-05-22
There are thousands of drugs that silence many thousands of cancer-causing genetic abnormalities. Some of these drugs are in use now, but many of these drugs are sitting on shelves or could be used beyond the disease for which they were originally approved. Repurposing these drugs depends on matching drugs to targets. A study recently published in the journal Bioinformatics describes a new database and pattern-matching algorithm that allows researchers to evaluate rational drugs and drug combinations, and also recommends a new drug combination to treat drug-resistant non-small ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
[Press-News.org] First broadband wireless connection ... to the moon?!MIT/NASA lunar laser communication team to present first report on record-shattering Earth-to-Moon uplink and its on-orbit performance