(Press-News.org) Last month WHO issued a report that warned of an increase of antimicrobial-resistance and the renewed threat of bacterial infections world-wide and called for a concerted effort to develop new and better antimicrobial drugs. A study published on May 22nd in PLOS Pathogens reveals how a new type of anti-microbial substance interferes with biofilms formed by several dangerous bacteria.
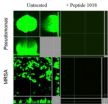
When growing on surfaces (including human skin, lung, heart, or bladder) many bacteria form so-called biofilms that consist of structured communities of identical bacteria. 65% of human infections are caused by biofilms, and in this configuration bacteria are much more resistant to standard antibiotics. Bob Hancock, from the University of British Columbia, Canada, and colleagues, are working on antimicrobials that inhibit bacterial biofilms. At the center of this study is "1018", a small protein (or peptide) with anti-biofilm activity against a range of different bacteria.
At concentrations that did not affect the "planktonic growth" of free-swimming bacteria, 1018 treatment completely prevented biofilm formation and eradicated mature biofilms in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, including the major resistant pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (or MRSA).
In their quest to understand the mechanism by which 1018 kills bacteria, and specifically those in biofilms, the researchers reasoned that it had to interfere with a process that was common to different bacterial species. One such process is the wide-spread "stringent stress response" that uses specific mediators called (p)ppGpp to orchestrate the expression of a plethora of genes that help bacteria to cope with changing environments. The scientists hypothesized that 1018 (and possibly other anti-biofilm factors) acted by blocking the stringent response.
They went on to test this by over-producing the mediator (p)ppGpp in biofilm-forming bacteria, and the fact that this made the bacteria more resistant to 1018 suggested that they were on the right track. They then went on to demonstrate that 1018 directly and specifically interacts with (p)ppGpp, triggers the destruction of the mediator, and thereby prevents its role in biofilm formation and maintenance.
The researchers conclude that "the strategy presented here represents a significant advance in the search for new agents that specifically target bacterial biofilms". On this basis, they are working to "take advantage of the opportunity to now develop more active peptides that have even more potent anti-biofilm activity".
INFORMATION:
Biofilm defense: Mechanisms and actions of a new class of broad-spectrum antimicrobials
2014-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients with a certain form of kidney disease may have a reduced risk of cancer
2014-05-23
Washington, DC (May 22, 2014) — Patients with a certain form of kidney disease may have a reduced risk of cancer compared with patients with other kidney diseases, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN).
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a kidney disorder passed down through families in which many cysts form in the kidneys, causing them to become enlarged. It's thought to have cancer-like features, but cancer risk has never been compared between PKD patients and others with kidney disease. Cancer ...
Kidney transplantation found superior to intensive home hemodialysis
2014-05-23
Washington, DC (May 22, 2014) — Compared with long and frequent home hemodialysis, kidney transplantation may allow kidney failure patients to be successfully treated and to live longer, but it may also increase their risk of being hospitalized within the first year. Those are the findings of study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The results support the need to encourage transplantation for potential candidates who are receiving home hemodialysis, but they also indicate that long and frequent home hemodialysis ...
Kidney transplant patients live longer than those in intensive home hemodialysis
2014-05-23
(TORONTO, Canada – May 22, 2014) – A first-ever study from a large Canadian centre found that kidney transplant recipients lived longer and had better treatment success than patients on intensive home hemodialysis, but also had an increased risk of being hospitalized within the first year.
These findings were reported in a study entitled, "Survival and hospitalization for intensive home hemodialysis and kidney transplantation", by lead author Dr. Karthik Tennankore, nephrologist at Dalhousie University, and Drs. Chris Chan and Joseph Kim, nephrologists at Toronto General ...
Promising discovery in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria
2014-05-23
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have identified a small molecule that prevents bacteria from forming into biofilms, a frequent cause of infections. The anti-biofilm peptide works on a range of bacteria including many that cannot be treated by antibiotics.
"Currently there is a severe problem with antibiotic-resistant organisms," says Bob Hancock, a professor in UBC's Dept. of Microbiology and Immunology and lead author of the study published today in PLOS Pathogens. "Our entire arsenal of antibiotics is gradually losing effectiveness."
Many bacteria ...
Children with cochlear implants at risk for deficits in executive function
2014-05-22
Children who receive cochlear implants (CI) to help alleviate severe to profound hearing loss are at greater risk of having deficiencies in executive functioning (EF), which are the skills to organize, control and process information in a goal-directed manner.
Permanent hearing loss is a common condition of early childhood, occurring in about 1.5 of every 1,000 births. Cochlear implants help children to achieve spoken language because the devices help them perceive sound. Still, children with cochlear implants can struggle with reading and writing skills and other ...
IU researchers identify pattern of cognitive risks in some children with cochlear implants
2014-05-22
INDIANAPOLIS -- Children with profound deafness who receive a cochlear implant had as much as five times the risk of having delays in areas of working memory, controlled attention, planning and conceptual learning as children with normal hearing, according to Indiana University research published May 22 in the Journal of the American Medical Association Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery.
The authors evaluated 73 children implanted before age 7 and 78 children with normal hearing to determine the risk of deficits in executive functioning behaviors in everyday life.
Executive ...
One-third of all brain aneurysms rupture: the size is not a significant risk factor
2014-05-22
VIDEO:
This video depicts microneurosurgical clipping of an unruptured intracranial aneurysm,
which is arising from the bifurcation i.e. branching point of two right
middle cerebral arteries.
In brief, the aneurysm locates in this...
Click here for more information.
The lifetime risk for rupture of a brain aneurysm depends heavily on the patient's overall load of risk factors. However, a recent study by researchers from the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University ...
Clinical trials designed to block autophagy in multiple cancers show promise
2014-05-22
PHILADELPHIA— In the largest group of results to date, researchers from Penn Medicine's Abramson Cancer Center and other institutions have shown in clinical trials that the malaria drug hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) blocked autophagy in a host of aggressive cancers—glioblastoma, melanoma, lymphoma and myeloma, renal and colon cancers—and in some cases helped stabilize disease. Autophagy—an essential process cancer cells need to fuel their growth—is a key troublemaker spurring tumor growth. Block this pathway, many preclinical studies suggest, and anti-cancer agents such as chemotherapy ...
Yale Cancer Center studies find lifestyle changes improve biomarkers for breast cancer recurrence and mortality
2014-05-22
New Haven, CT – A pair of Yale Cancer Center interventional studies involving breast cancer survivors found that lifestyle changes in the form of healthy eating and regular exercise can decrease biomarkers related to breast cancer recurrence and mortality. The abstracts are scheduled to be presented at the 2014 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology in Chicago May 30-June 3rd.
"The findings of both studies support a growing body of research that suggests lifestyle interventions lower biomarkers associated with breast cancer recurrence and mortality, ...
Repeated sexual assault victims report more psychological problems than previously thought
2014-05-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – According to recent studies, one in five adult women and one in 100 adult men have reported being raped. The prevalence increases to two in five among women and one in five among men who report experiencing other forms of sexual violence, such as repeated unwanted sexual contact and sexual coercion. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that those victims who are repeatedly assaulted, but not necessarily violently raped, show greater levels of psycho-behavioral consequences than earlier thought. The researchers suggest that understanding ...