(Press-News.org) This news release is available in French.
A signal that promotes insulin secretion and reduces hyperglycemia in a type 2 diabetes animal model is enhanced by the inhibition of a novel enzyme discovered by CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM) and University of Montreal researchers. The team is part of the Montreal Diabetes Research Center and their study, published recently in Cell Metabolism, was directed by researchers Marc Prentki and Murthy Madiraju.
Insulin is an important hormone in our body that controls glucose and fat utilization. Insufficient insulin release by the beta-cells of the pancreas and interference with the action of insulin lead to type 2 diabetes. The secretion in the blood of insulin is dependent upon the utilization of glucose and fat by the beta-cells and the production of a novel signal that they discovered named monoacylglycerol.
"Despite significant research on the mechanisms implicated in insulin secretion, the signal molecules involved in this process remained enigmatic; the identification of these signals is necessary to develop better therapeutics against diabetes," explains Marc Prentki, Director of the Montreal Diabetes Research Centre and Professor at the University of Montreal. Marc Prentki holds the Canada Research Chair in Diabetes and Metabolism.
"When sugar is being used by the insulin secreting pancreatic beta-cell, it produces monoacylglycerol, a fat-like signal and this is associated with insulin release into blood; we found that the production of monoacylglycerol is essential for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by the beta-cell," says Murthy Madiraju, Researcher at the CRCHUM.
Importantly, the research team discovered that an enzyme called alpha/beta hydrolase domain-6 (in short ABHD6) breaks down monoacylglycerol and thus negatively controls insulin release.
These researchers said that "an ideal drug for type-2 diabetes would increase insulin levels in blood by enhancing the beta cells response to glucose only when it is elevated and also increase the sensitivity of body tissues to insulin; this is precisely what ABHD6 inhibition does and thus we have identified a unique new target for type 2 diabetes."
The research team is currently in the process of discovering new and potent blockers of ABHD6 that do not show any unwanted toxicity and which can be developed as potential drugs for type 2 diabetes. These studies are being done in collaboration with AmorChem Financial, Inc., and its subsidiary NuChem Therapeutics, Montreal.
INFORMATION:
About the research project
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The Montreal research team directed by Marc Prentki and Murthy Madiraju consisted of Shangang Zhao, Yves Mugabo, Jose Iglesias, who are first authors of the study and performed most of the experimental work, and Viviane Delghingaro-Augusto, Roxane Lussier, Marie-Line Peyot, Erik Joly, and Bouchra Taïb, who also contributed. The study was conducted in collaboration with Dr Herbert Gaisano and Li Xie (Toronto), J. Mark Brown and Matthew A. Davis (Winston-Salem, NC), and Abdelkarim Abousalham (France). For more information, please visit the journal page at: http://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(14)00166-1
Novel drug target linked to insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes treatment
2014-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising approach to slow brain degeneration in a model of Huntington's disease uncovered
2014-05-26
This news release is available in French. Research presented by Dr. Lynn Raymond, from the University of British Columbia, shows that blocking a specific class of glutamate receptors, called extrasynaptic NMDA receptors, can improve motor learning and coordination, and prevent cell death in animal models of Huntington disease. As Huntington disease is an inherited condition that can be detected decades before any clinical symptoms are seen in humans, a better understanding of the earliest changes in brain cell (neuronal) function, and the molecular pathways underlying ...
The Lancet Oncology: UN officials warn refugees are struggling to access cancer treatment
2014-05-26
A study published in The Lancet Oncology journal reveals a high demand for costly cancer treatment among refugees from the recent conflicts in Iraq and Syria, with host countries struggling to find the money and the medicine to treat their new patients. The findings have prompted calls from lead author Dr Paul Spiegel, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) Chief Medical Expert, for innovative financing schemes to improve access to affordable high-quality cancer care for refugees.
In the first study of its kind, Spiegel and colleagues examined data ...
A new molecule for high-resolution cell imaging
2014-05-25
Like our own bodies, cells have their own skeletons called 'cytoskeletons' and are made of proteins instead of bones. These network-like structures maintain the cell's shape, provide mechanical support, and are involved in critical processes of the cell's lifecycle. The cytoskeleton is an object of intense scientific and medical research, which often requires being able to observe it directly in cells. Ideally, this would involve highly-fluorescent molecules that can bind cytoskeletal proteins with high specificity without being toxic to the cell. Publishing in Nature Methods, ...
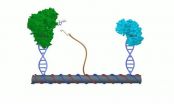
DNA nanotechnology places enzyme catalysis within an arm's length
2014-05-25
VIDEO:
In the middle of a DNA scaffold is affixed a single strand of DNA, with NAD+ tethered to the end like a ball and string. ASU Professor Han Yan refers...
Click here for more information.
Using molecules of DNA like an architectural scaffold, Arizona State University scientists, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Michigan, have developed a 3-D artificial enzyme cascade that mimics an important biochemical pathway that could prove important for future biomedical ...
Gene mutation found for aggressive form of pancreatic cancer
2014-05-25
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a mutated gene common to adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC) tumors – the first known unique molecular signature for this rare, but particularly virulent, form of pancreatic cancer.
The findings are published in the May 25 advance online issue of Nature Medicine.
Pancreatic cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States, with roughly 45,220 new cases diagnosed and more than 38,400 deaths annually. Both numbers are rising. ASC cases are infrequent, but ...
Mice with 'mohawks' help scientists link autism to 2 biological pathways in brain
2014-05-25
"Aha" moments are rare in medical research, scientists say. As rare, they add, as finding mice with Mohawk-like hairstyles.
But both events happened in a lab at NYU Langone Medical Center, months after an international team of neuroscientists bred hundreds of mice with a suspect genetic mutation tied to autism spectrum disorders.
Almost all the grown mice, the NYU Langone team observed, had sideways,"overgroomed" hair with a highly stylized center hairline between their ears and hardly a tuft elsewhere. Mice typically groom each other's hair.
Researchers say they ...
Buried fossil soils found to be awash in carbon
2014-05-25
MADISON, Wis. — Soils that formed on the Earth's surface thousands of years ago and that are now deeply buried features of vanished landscapes have been found to be rich in carbon, adding a new dimension to our planet's carbon cycle.
The finding, reported today (May 25, 2014) in the journal Nature Geoscience, is significant as it suggests that deep soils can contain long-buried stocks of organic carbon which could, through erosion, agriculture, deforestation, mining and other human activities, contribute to global climate change.
"There is a lot of carbon at depths ...
Study identifies how signals trigger cancer cells to spread
2014-05-25
May 25, 2014 — (Bronx, NY) — Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University have discovered a signaling pathway in cancer cells that controls their ability to invade nearby tissues in a finely orchestrated manner. The findings offer insights into the early molecular events involved in metastasis, the deadly spread of cancer cells from primary tumor to other parts of the body. The study was published today in the online edition of Nature Cell Biology.
To migrate from a primary tumor, a cancer cell must first break through surrounding connective ...
Scientists discover potential new target for cancer immunotherapy
2014-05-25
HOUSTON -- Scientists have found a way to target elusive cells that suppress immune response, depleting them with peptides that spare other important cells and shrink tumors in preclinical experiments, according to a paper published online by Nature Medicine.
"We've known about these cells blocking immune response for a decade, but haven't been able to shut them down for lack of an identified target," said the paper's senior author, Larry Kwak, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Lymphoma/Myeloma and director of the Center for Cancer Immunology Research at The University of Texas MD ...
Researchers map the epic evolution of a 'ring species'
2014-05-25
The Greenish Warbler, long considered an idealized example of a single species that diverged into two as it expanded its range, has a much more checkered family history than biologists previously realized.
Ring species are a continuous loop of related populations, each adapted to its local environment, with two terminal populations in the loop meeting but now unable to mate. But an in-depth genomic analysis published today in Nature by University of British Columbia researchers reveals that the Greenish Warbler's genetic migration through central Asia involved periods ...