(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC - Researchers have documented the longest-known terrestrial migration of wildlife in Africa – up to several thousand zebra covering a distance of 500km (more than 300 miles) – according to World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
Using GPS collars on eight adult Plains zebra (Equus quagga), WWF and Namibia's Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET), in collaboration with Elephants Without Borders (EWB) and Botswana's Department of Wildlife and National Parks, tracked two consecutive years of movement back and forth between the Chobe River in Namibia and Botswana's Nxai Pan National Park, a straight-line distance of 250km (500km round-trip). The findings are detailed in a new study published in the journal, Oryx.
The discovery comes at a time when migrations of a diverse range of species around the world are increasingly imperiled, and zebra migrations in other parts of Africa have been disrupted by physical barriers such as fences.
"This unexpected discovery of endurance in an age dominated by humans, where we think we know most everything about the natural world, underscores the importance of continued science and research for conservation" said Dr. Robin Naidoo, senior conservation scientist at WWF.
The potential conservation implications of the study are considerable. The observed migration takes place entirely within the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area (KAZA) – the world's largest multi-country conservation area. Spanning 109 million acres across Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Zambia and Angola, KAZA exemplifies the kind of large landscape conservation approach that will be necessary to preserve the world's remaining great terrestrial migrations.
"The findings of this study emphasize the importance of trans-frontier conservation areas in conservation of the greater landscape" said Pierre Du Preez, Chief Conservation Scientist at MET in Namibia. "This study has played a crucial role in helping determine a key wildlife corridor in KAZA."
"At a time when conservation news is inherently rather negative, the discovery of this unknown natural phenomenon should resonate with people around the world. The government's commitment to secure key migratory corridors serves to underpin the growing wildlife tourism industry. We plan to continue monitoring the migration to try and conserve such increasingly rare natural events" said Dr. Mike Chase, EWB's founder.
Continued long-term research will be needed to confirm that this is an annual and fixed migration, and whether this is genetically coded or passed behaviorally from mothers to offspring.
INFORMATION: END
Africa's longest-known terrestrial wildlife migration discovered
Researchers document zebra traveling 500 km round-trip between Namibia and Botswana
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
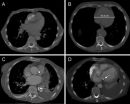
Chest CT helps predict cardiovascular disease risk
2014-05-27
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Incidental chest computed tomography (CT) findings can help identify individuals at risk for future heart attacks and other cardiovascular events, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
"In addition to diagnostic purposes, chest CT can be used for the prediction of cardiovascular disease," said Pushpa M. Jairam, M.D., Ph.D., from the University Medical Center Utrecht, in Utrecht, the Netherlands. "With this study, we have taken a new perspective by providing a different approach for cardiovascular disease risk prediction ...
An area's level of poverty or wealth may affect the distribution of cancer types
2014-05-27
A new analysis has found that certain cancers are more concentrated in areas with high poverty, while other cancers arise more often in wealthy regions. Also, areas with higher poverty had lower cancer incidence and higher mortality than areas with lower poverty. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study's findings demonstrate the importance of including measures of socioeconomic status in national cancer surveillance efforts.
Overall, socioeconomic status is not related to cancer risk—cancer strikes the rich and ...
E-cigarettes: Not a healthy alternative to smoking
2014-05-27
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (May 27, 2014) – Caveat emptor – or "buyer beware" holds true when it comes to the unknown health effects of e-cigarettes. An article in the June issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), examines risks, including the ongoing dependence on nicotine and the dual use of e-cigarettes and regular cigarettes.
The article examines the idea that one of the initial "health benefits" proposed by e-cigarettes makers was that it would help those who smoke cigarettes ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for May 27, 2014
2014-05-27
1. Task Force: Screen high-risk individuals for hepatitis B
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening for nonpregnant high-risk adolescents and adults, according to a recommendation statement being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Up to 2.2 million people in the United States have chronic HBV, and 15 to 25 percent of those infected will die from liver disease or liver cancer. Screening for HBV could identify those who may benefit from treatment. Most people born in the United States have been vaccinated for ...
Inhaling hypertonic saline decreases hospital admissions in children with bronchiolitis
2014-05-26
A team of researchers, led by physicians from Children's Hospital Los Angeles, have found that infants with bronchiolitis who were treated with inhaled hypertonic saline in the emergency department (ED) were less likely to require admission to the hospital compared to infants treated with normal saline.
The study, conducted at Children's Hospital Los Angeles and UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital Oakland, will be published in JAMA Pediatrics on May 26.
Bronchiolitis is a respiratory infection common in infants and young children that results in approximately 150,000 ...
Hot flashes/night sweats solutions: Estrogen therapy vs. Venlafaxine
2014-05-26
BOSTON, MA – A new research study from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) that compares low-dose oral estrogen and low-dose non-hormonal venlafaxine hydrochloride extended release (XR) to placebo were both found effective in reducing the number of hot flashes and night sweats reported by menopausal women. The study is the first clinical trial to simultaneously evaluate estrogen therapy (ET), known as the "gold standard" treatment for hot flashes and night sweats, and a non-hormonal treatment, venlafaxine, a first-line treatment in women who are unwilling or unable to ...
Conflicting conclusions in 2 bronchiolitis studies; editorial explains why
2014-05-26
Less Improvement in Infants with Bronchiolitis After Nebulized Hypertonic Saline Treatment
Bottom Line: Children with bronchiolitis (a common respiratory tract infection that can result in hospitalization) who were treated in the emergency department showed less clinical improvement after receiving nebulized 3 percent hypertonic saline (HS) than infants who received normal saline (NS).
Author: Todd A. Florin, M.D., M.S.C.E., of the Cincinnati Children's Hospital, and colleagues.
Background: Nebulized HS has been shown to increase mucociliary clearance (the clearing ...
Ebola vaccine success highlights dilemma of testing on captive chimps to save wild apes
2014-05-26
The first conservation-specific vaccine trial on captive chimpanzees has proved a vaccine against Ebola virus is both safe and capable of producing a robust immune response in chimpanzees.
This unprecedented study, published in the journal PNAS, shows that 'orphan' vaccines - which never complete the expensive licensing process for human use - can be co-opted for use on wildlife and might be a godsend for highly endangered species such as gorillas and chimpanzees, say researchers.
They suggest that, by ending captive research in an effort to pay back an "ethical ...
From chaos to order: How ants optimize food search
2014-05-26
Ants are capable of complex problem-solving strategies that could be widely applied as optimization techniques. An individual ant searching for food walks in random ways, biologists found. Yet the collective foraging behaviour of ants goes well beyond that, as a mathematical study to be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals: The animal movements at a certain point change from chaos to order. This happens in a surprisingly efficient self-organized way. Understanding the ants could help analyze similar phenomena - for instance how humans ...
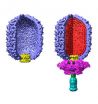
Relaxation helps pack DNA into a virus
2014-05-26
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have found that DNA packs more easily into the tight confines of a virus when given a chance to relax, they report in a pair of papers to be published in in the early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of May 26 and the May 30 issue of Physical Review Letters.
DNA is a long, unwieldy molecule that tends to repel itself because it is negatively charged, yet it can spool tightly. Within the heads of viruses, DNA can be packed to near crystalline densities, crammed in by a molecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
[Press-News.org] Africa's longest-known terrestrial wildlife migration discoveredResearchers document zebra traveling 500 km round-trip between Namibia and Botswana