(Press-News.org) Imaging scientists at Western University's Robarts Research Institute (London, Canada) have developed a better way to track the progression of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) from its earliest stages. Led by Ravi Menon, PhD, the researchers used what's called "Quantitative Susceptibility (QS) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)," to measure damage in specific areas of the brain which the study showed to be common to all patients. The findings are published in advance online, in Radiology.
"In MS research, there is something we call a clinical-radiological paradox. When you do conventional MRIs on these patients you see lesions in the brain very clearly, but the number or volume of their lesions do not correlate with the patients' disabilities. This paradox has been recognized since the MRI was introduced to clinical practice in the early 80s, and yet this is the only imaging tool we have for assessing MS," says Menon. "Our research provides a quantitative tool using a relatively conventional imaging sequence but with novel analysis. This tool shows that there is considerable damage occurring in common areas of all patients in both the white matter and in the deep brain structures –the gray matter. Those quantitative measures –what we call quantitative susceptibility, correlate with disease symptoms."
The process used a standard Siemens 3T MRI so it could be reproduced in any hospital, using the technique, called QS. The researchers mapped this MRI parameter in 25 patients with relapsing-remitting MS or clinically isolated syndrome (CIS –half of those diagnosed with CIS will go on to be diagnosed with MS) measuring both demyelination and iron deposition. Fifteen age and sex-matched control subjects were also scanned. While brain and spine lesions visualized with normal MRI tend to appear and disappear over time, QS shows common areas of damage in all patients that correlated very well with the Extended Disability Status Score (EDSS) which is a standard tool used to measure MS progression, as well as with age and time since diagnosis.
"Significantly, in white matter, even where we see no lesions whatsoever, we're able to measure damage in the same area of all patients using QS mapping. So even at the very earliest stages of the disease when the disability score is very low, or when the person hasn't yet been diagnosed with MS, there's already significant damage," adds Menon. This could have important diagnostic and prognostic implications, as there are drugs available to slow or stop the progression of MS, if started early enough.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. David Rudho, Igor Solovey, Joseph Gati and Dr. Marcelo Kremenchutsky also worked on the paper, which is titled "Multiple Sclerosis: Improved identification of disease-relevant changes in gray and white matter using susceptibility-based MR imaging."
Imaging scientists develop a better tool for tracking MS
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Steroids prescribed in the ICU linked to delirium
2014-05-27
New Johns Hopkins research suggests that critically ill patients receiving steroids in a hospital's intensive care unit (ICU) are significantly more likely to develop delirium. Results of their research, they say, suggest minimizing the use of steroids could reduce delirium in the ICU.
While it usually goes away after a few days, studies show delirium in the ICU has a long-term impact. It has been associated with worse functional recovery and cognitive impairments of a magnitude consistent with moderate traumatic brain injury or mild Alzheimer's disease.
Overall, up ...
HSP90 is a potential target for ameliorating skeletal muscle abnormalities in PD
2014-05-27
Heat shock protein (HSP90) has been suggested to be involved in neuronal protein misfolding and accumulation in Parkinson's disease (PD) brains leading to dopaminergic neuronal death and the eventual dopamine depletion. Therefore, HSP90 has been suggested as a therapeutic target in PD. Dr. Muhammed Al-Jarrah and co-workers from Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) point out exercise training significantly inhibited HSP90 overexpression in the soleus and gastrocnemius in PDe rats, which is a potential therapeutic target for ameliorating skeletal muscle abnormalities ...
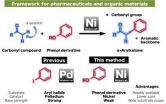
A new 'Kabuto-like' nickel catalyst forms bioactive frameworks from phenol derivatives
2014-05-27
Researchers at ITbM, Nagoya University developed a new nickel catalyst with a "Kabuto-like" structure that was found to catalyze the cross-coupling reaction between carbonyl compounds and readily available phenol derivatives, to form alpha-arylketones, which are found in many biologically active compounds (Kabuto = a helmet worn by Japanese samurai).
Nagoya, Japan – Professors Kenichiro Itami and Junichiro Yamaguchi of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) and graduate students Ryosuke Takise and Kei Muto of Nagoya University have succeeded in developing ...
New tick-borne disease threatens primarily immune suppressed persons
2014-05-27
A newly discovered tick-borne bacterium known as "Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis" has been implicated in six cases of disease in Sweden. A new international study led by the Sahlgrenska Academy has shown that this bacterium is primarily a risk for people who are already sick and who are receiving immunosuppressive drugs.
The Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis bacterium, known in the medical world by its short name Neoehrlichia, was discovered and described for the first time in a scientific article in 2010.
The bacterium, which is spread by rodents and ticks mainly ...
New jigsaw piece for the repair of DNA crosslinks
2014-05-27
Environmental influences such as ionizing radiation, intense heat or various chemical substances damage the DNA constantly. Only thanks to efficient repair systems can mutations – changes in the DNA – largely be prevented. DNA crosslinks that covalently link both strands of the DNA double helix are among the most dangerous DNA lesions. Crosslinks block DNA replication and can thus cause cell death. Moreover, their faulty repair can trigger the development of tumors. Crosslink repair is highly complex and only vaguely understood today. A team of cancer researchers headed ...
X-ray dark-field radiography provides detailed imaging of lung diseases
2014-05-27
As the team reports in the Investigative Radiology journal, this method shows promise in detecting diseases such as pulmonary emphysema at an earlier stage, than it is currently available. Conventional radiographic procedures generate images based on the absorption of X-rays as they pass through the tissue. The newly developed technique of X-ray dark-field radiography uses new technology to monitor wave changes during tissue transmission to create higher resolution images.
Detailed images
With the aid of this new technique, the team from the HMGU, KUM and TUM around Dr. ...
Two new possible drug targets for triple negative breast cancer
2014-05-27
HOUSTON -- ( May 27, 2014 ) -- The suppression of two genes reduce breast cancer tumor formation and metastasis by interfering with blood vessel formation and recruitment, report scientists from Houston Methodist and five other institutions in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (now online). The findings may help medical researchers identify effective drug targets for triple negative breast cancer, or TNBC.
The genes, MLF2 (myeloid leukemia factor 2) and RPL39 (a ribosomal protein), were found to most profoundly impact the production of nitric oxide synthase, ...
Large numbers of shadow economy entrepreneurs in developing countries, according to new report
2014-05-27
There are large numbers of entrepreneurs in developing countries who aren't registering their businesses with official authorities, hampering economic growth, according to new research.
Shadow entrepreneurs are individuals who manage a business that sells legitimate goods and services but they do not register it. This means that they do not pay tax, operating in a shadow economy where business activities are performed outside the reach of government authorities. The shadow economy results in loss of tax revenue, unfair competition to registered businesses and also poor ...
Mycotoxin protects against nematodes
2014-05-27
This news release is available in German. Most terrestrial plants enter into biocoenosis with funghi. Both sides benefit: the fungus, which surrounds the small roots of the host plant with a thick felt, supplies the plant with trace elements and water. The plant, in turn, supplies the fungus with sugars and other metabolites which it is unable to produce itself.
Toxic protein kills intestinal cells
ETH researchers from the research group of microbiology professor Markus Aebi have discovered a protein in the cells of one such ectomycorrhizal fungus which offers an ...
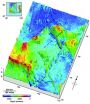
AGU: Experts publish new view of zone where Malaysia Airlines flight 370 might lie
2014-05-27
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- A new illustration of the seafloor, created by two of the world's leading ocean floor mapping experts that details underwater terrain where the missing Malaysia Airlines flight might be located, could shed additional light on what type of underwater vehicles might be used to find the missing airplane and where any debris from the crash might lie.
The seafloor topography map illustrates jagged plateaus, ridges and other underwater features of a large area underneath the Indian Ocean where search efforts have focused since contact with Malaysia Airlines ...