(Press-News.org) There are large numbers of entrepreneurs in developing countries who aren't registering their businesses with official authorities, hampering economic growth, according to new research.
Shadow entrepreneurs are individuals who manage a business that sells legitimate goods and services but they do not register it. This means that they do not pay tax, operating in a shadow economy where business activities are performed outside the reach of government authorities. The shadow economy results in loss of tax revenue, unfair competition to registered businesses and also poor productivity – factors which hinder economic development. As these businesses are not registered it takes them beyond the reach of the law and makes shadow economy entrepreneurs vulnerable to corrupt government officials.
In a study of 68 countries, Professor Erkko Autio and Dr Kun Fu from Imperial College Business School estimated that business activities conducted by informal entrepreneurs can make up more than 80 per cent of the total economic activity in developing countries. Types of businesses include unlicensed taxicab services, roadside food stalls and small landscaping operations.
This is the first time that the number of entrepreneurs operating in the shadow economy has been estimated.
The researchers found that Indonesia has the highest rate of shadow economy entrepreneurs, with a ratio of over 130 shadow economy businesses to every business that is legally registered. After Indonesia the highest rates of shadow economy entrepreneurs are found in India, the Philippines, Pakistan, Egypt and Ghana.
In contrast, the UK exhibits the lowest rate of shadow entrepreneurship among the 68 countries surveyed, with a ratio of only one shadow economy entrepreneur to some 30 legally registered businesses.
The researchers also found that the quality of economic and political institutions has a substantial effect on entrepreneurs registering their businesses around the world.
Professor Erkko Autio, co-author of the report, at Imperial College Business School, said:
"Understanding shadow economy entrepreneurship is incredibly important for developing countries because it is a key factor affecting economic development. We found that government policies could play a big role in helping shadow economy entrepreneurs transition to the formal economy. This is important because shadow economy entrepreneurs are less likely to innovate, accumulate capital and invest in the economy, which hampers economic growth."
The researchers suggest that shadow entrepreneurs are highly sensitive to the quality of political and economic institutions. Where proper economic and political frameworks are in place, individuals are more likely to become 'formal' entrepreneurs and register their business, because doing so enables them to take advantage of laws and regulations that protect their company, such as trademarking legislation.
The researchers suggest if India improved the quality of its democratic institutions to match that of Malaysia, it could boost its rate of formal economy entrepreneurs by up to 50 per cent, while cutting the rate of entrepreneurs working in the shadow economy by up to a third. This means that the government could benefit from additional revenue such as taxes.
To create their league table, the researchers combined data from the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) and the World Bank.
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Maxine Myers
Media and Communications Officer- Imperial College Business School
Tel: +44 (0)20 7594 6127
Email: maxine.myers@imperial.ac.uk
Out of hours duty press officer: +44(0)7803 886
Notes to editors:
Download a copy of the report:
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10490-014-9381-0
Download the league table showing the ratio of informal to formal entrepreneurship occurring in 68 countries
https://icseclzt.cc.ic.ac.uk/pickup.php?claimID=CaaVMWFh4Ws3eWUH&claimPasscode=C5Sv8XZQTMzN6tBq&emailAddr=maxine.myers%40imperial.ac.uk
Claim ID: CaaVMWFh4Ws3eWUH
Claim Passcode: C5Sv8XZQTMzN6tBq
2. About Imperial College London
Consistently rated amongst the world's best universities, Imperial College London is a science-based institution with a reputation for excellence in teaching and research that attracts 14,000 students and 6,000 staff of the highest international quality. Innovative research at the College explores the interface between science, medicine, engineering and business, delivering practical solutions that improve quality of life and the environment - underpinned by a dynamic enterprise culture.
Since its foundation in 1907, Imperial's contributions to society have included the discovery of penicillin, the development of holography and the foundations of fibre optics. This commitment to the application of research for the benefit of all continues today, with current focuses including interdisciplinary collaborations to improve global health, tackle climate change, develop sustainable sources of energy and address security challenges.
In 2007, Imperial College London and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust formed the UK's first Academic Health Science Centre. This unique partnership aims to improve the quality of life of patients and populations by taking new discoveries and translating them into new therapies as quickly as possible.
3. About Imperial College Business School
Established in 2003, Imperial College Business School is one of the world's fastest growing business schools with a reputation for excellence in teaching, research and translation.
The Business School is a constituent faculty of Imperial College London, and fully integrated with the College's cutting-edge work in science, engineering and medicine. It offers MBA, EMBA, MSc and PhD executive education programmes.
In 2013 Imperial College Business School announced that it will found the Brevan Howard School of Finance, a new research centre for financial market behaviour, with a £20.1 million donation from Brevan Howard.
Website: http://www.imperial.ac.uk
Imperial-PR mailing list
Sign up to Imperial Twitter at: http://twitter.com/imperialcollege and http://twitter.com/imperialspark Sign up for Imperial RSS feeds at:
http://www3.imperial.ac.uk/imperialnews/RSS_14150300.xml
More news and events online at: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/news
Large numbers of shadow economy entrepreneurs in developing countries, according to new report
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mycotoxin protects against nematodes
2014-05-27
This news release is available in German. Most terrestrial plants enter into biocoenosis with funghi. Both sides benefit: the fungus, which surrounds the small roots of the host plant with a thick felt, supplies the plant with trace elements and water. The plant, in turn, supplies the fungus with sugars and other metabolites which it is unable to produce itself.
Toxic protein kills intestinal cells
ETH researchers from the research group of microbiology professor Markus Aebi have discovered a protein in the cells of one such ectomycorrhizal fungus which offers an ...
AGU: Experts publish new view of zone where Malaysia Airlines flight 370 might lie
2014-05-27
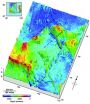
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- A new illustration of the seafloor, created by two of the world's leading ocean floor mapping experts that details underwater terrain where the missing Malaysia Airlines flight might be located, could shed additional light on what type of underwater vehicles might be used to find the missing airplane and where any debris from the crash might lie.
The seafloor topography map illustrates jagged plateaus, ridges and other underwater features of a large area underneath the Indian Ocean where search efforts have focused since contact with Malaysia Airlines ...
Rules to cut carbon emissions also reduce air pollution harmful to people, environment
2014-05-27
(Syracuse, NY – May 27, 2014) Setting strong standards for climate-changing carbon emissions from power plants would provide an added bonus – reductions in other air pollutants that can make people sick; damage forests, crops, and lakes; and harm fish and wildlife. This, according to a first-of-its-kind study released today by scientists at Syracuse University and Harvard who mapped the potential environmental and human health benefits of power plant carbon standards.
The authors of the new study, Co-benefits of Carbon Standards: Air Pollution Changes under Different ...
Skin grafts from genetically modified pigs may offer alternative for burn treatment
2014-05-27
A specially-bred strain of miniature swine lacking the molecule responsible for the rapid rejection of pig-to-primate organ transplants may provide a new source of skin grafts to treat seriously burned patients. A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) report that skin grafts from pigs lacking the Gal sugar molecule were as effective in covering burn-like injuries on the backs of baboons as skin taken from other baboons, a finding that could double the length of time burns can be protected while healing. The report in the journal Transplantation ...
EuroPCR 2014 session defines future horizons for renal denervation
2014-05-27
23 May 2014, Paris, France: During EuroPCR 2014, Felix Mahfoud, University Hospital in Homburg, Germany, and Konstantinos Tsioufis, University of Athens, Greece, reflected on the potential future role of modulation of the sympathetic nervous system in patients with difficult-to-control hypertension.
In the context of the SYMPLICITY-HTN-3 clinical trial results, questions were raised about the extent of the procedure's efficacy although the randomised, controlled trial confirmed the safety of renal denervation.
"In terms of efficacy, some studies have shown that renal ...
New biodiversity study throws out controversial scientific theory
2014-05-27
Researchers have today released ground-breaking findings that dismiss the 'Neutral Theory of Biodiversity'. The theory has dominated biodiversity research for the past decade, and been advocated as a tool for conservation and management efforts.
Professor Sean Connolly from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University (JCU) is the lead author of the international study, which he says overturns the long-used theory by employing a novel mathematical method. It is the largest study of its kind, covering a broad range of marine ...
Does apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide reduce neuronal apoptosis induced by DBI?
2014-05-27
Because the majority of patients with diffuse brain injury are not suitable candidates for surgery, neuroprotective agents are of great importance. Apolipoprotein E exerts a neuroprotective effect against brain injury, but synthetic apolipoprotein E cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, thus limiting its application.It has been reported that apolipoprotein E (138) mimetic peptide can cross the blood-brain barrier in both normal and injured brain. However, its impact on neurological function following diffuse brain injury is still unclear. Prof. Jianmin Li and team from ...
A novel disease-preventing antioxidant pathway
2014-05-27
Interested in antioxidants? They protect us against aging and cancer. It's one of the reasons we like our green tea and even our broccoli. But there is a new kid on the antioxidant block - uric acid. But wait, you're thinking, doesn't uric acid cause gout? A team in Singapore has recently showed that uric acid is a major intracellular antioxidant, possibly even more important than the antioxidants we try to eat. They also discovered how uric acid helps to prevent aging and disease and how it helps in the treatment of cancer.
Traditionally, uric acid has a bad reputation ...
Immunologists discover immune system precursor cells that fight infection
2014-05-27
The innate immune system recognizes infectious agents such as viruses and bacteria. A group of lymphocytes known as "innate lymphoid cells" or ILCs plays a central role in the defense of the human body against infective agents. Professor Andreas Diefenbach of the Research Center Immunology at the Mainz University Medical Center, working in collaboration with scientists at the University of Freiburg, has discovered previously unidentified ILCs that are able to protect epithelial surfaces, such as those of the intestinal mucosa, against infection. The results provide important ...
Using thoughts to control airplanes
2014-05-27
The pilot is wearing a white cap with myriad attached cables. His gaze is concentrated on the runway ahead of him. All of a sudden the control stick starts to move, as if by magic. The airplane banks and then approaches straight on towards the runway. The position of the plane is corrected time and again until the landing gear gently touches down. During the entire maneuver the pilot touches neither pedals nor controls.
This is not a scene from a science fiction movie, but rather the rendition of a test at the Institute for Flight System Dynamics of the Technische Universität ...