(Press-News.org) Environmental influences such as ionizing radiation, intense heat or various chemical substances damage the DNA constantly. Only thanks to efficient repair systems can mutations – changes in the DNA – largely be prevented. DNA crosslinks that covalently link both strands of the DNA double helix are among the most dangerous DNA lesions. Crosslinks block DNA replication and can thus cause cell death. Moreover, their faulty repair can trigger the development of tumors. Crosslink repair is highly complex and only vaguely understood today. A team of cancer researchers headed by Alessandro Sartori from the University of Zurich now reveals interesting details as to how cells recognize crosslink damage. In their study recently published in Cell Reports, the scientists demonstrate that the interplay between two specific proteins is crucial for the flawless repair of crosslink damage.
Repair protein recognizes crosslink damage with the aid of a signal protein
For their study, the researchers examined the Fanconi anemia signal pathway, which coordinates the complex repair of crosslinks, with the aid of genetically modified and unchanged cells. Sartori and his team wanted to find out whether and how the signal pathway and the repair protein CtIP interact with one another. "We are able to show that CtIP recognizes and repairs crosslinks efficiently with the aid of the Fanconi anemia signal pathway, or FANCD2 to be more precise," explains Sartori. The scientists also discovered the point where CtIP attaches itself to the FANCD2 protein. According to the researchers, the interplay between the two proteins is necessary for the flawless and smooth repair of crosslink damage as it prevents the relocation of entire chromosome sections to another position (see figure). Referred to as chromosomal translocation, the process is one of the main causes of the development of cancer.
These days, substances that specifically trigger crosslink damage are used in cancer chemotherapy. The new findings are therefore important for both our understanding of the development of cancer and the further development of improved drugs.
INFORMATION:
Literature:
Olga Murina, Christine von Aesch, Ufuk Karakus, Lorenza P. Ferretti, Hella A. Bolck, Kay Hänggi, and Alessandro A. Sartori. FANCD2 and CtIP Cooperate to Repair DNA Interstrand Crosslinks. Cell Reports (2014). May 1, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.069
Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare congenital disorder that was first described in 1927 by Guido Fanconi (18921979), Professor of Pediatrics at the University of Zurich. Fanconi anemia is triggered by mutations in genes that regulate the repair of DNA crosslinks. Patients who suffer from Fanconi anemia display bone marrow failure already during childhood and have a risk of developing cancer that is about 1,000 times higher compared to healthy individuals. Only around a third of Fanconi anemia patients live beyond the age of 30.
New jigsaw piece for the repair of DNA crosslinks
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
X-ray dark-field radiography provides detailed imaging of lung diseases
2014-05-27
As the team reports in the Investigative Radiology journal, this method shows promise in detecting diseases such as pulmonary emphysema at an earlier stage, than it is currently available. Conventional radiographic procedures generate images based on the absorption of X-rays as they pass through the tissue. The newly developed technique of X-ray dark-field radiography uses new technology to monitor wave changes during tissue transmission to create higher resolution images.
Detailed images
With the aid of this new technique, the team from the HMGU, KUM and TUM around Dr. ...
Two new possible drug targets for triple negative breast cancer
2014-05-27
HOUSTON -- ( May 27, 2014 ) -- The suppression of two genes reduce breast cancer tumor formation and metastasis by interfering with blood vessel formation and recruitment, report scientists from Houston Methodist and five other institutions in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (now online). The findings may help medical researchers identify effective drug targets for triple negative breast cancer, or TNBC.
The genes, MLF2 (myeloid leukemia factor 2) and RPL39 (a ribosomal protein), were found to most profoundly impact the production of nitric oxide synthase, ...
Large numbers of shadow economy entrepreneurs in developing countries, according to new report
2014-05-27
There are large numbers of entrepreneurs in developing countries who aren't registering their businesses with official authorities, hampering economic growth, according to new research.
Shadow entrepreneurs are individuals who manage a business that sells legitimate goods and services but they do not register it. This means that they do not pay tax, operating in a shadow economy where business activities are performed outside the reach of government authorities. The shadow economy results in loss of tax revenue, unfair competition to registered businesses and also poor ...
Mycotoxin protects against nematodes
2014-05-27
This news release is available in German. Most terrestrial plants enter into biocoenosis with funghi. Both sides benefit: the fungus, which surrounds the small roots of the host plant with a thick felt, supplies the plant with trace elements and water. The plant, in turn, supplies the fungus with sugars and other metabolites which it is unable to produce itself.
Toxic protein kills intestinal cells
ETH researchers from the research group of microbiology professor Markus Aebi have discovered a protein in the cells of one such ectomycorrhizal fungus which offers an ...
AGU: Experts publish new view of zone where Malaysia Airlines flight 370 might lie
2014-05-27
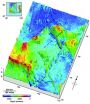
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- A new illustration of the seafloor, created by two of the world's leading ocean floor mapping experts that details underwater terrain where the missing Malaysia Airlines flight might be located, could shed additional light on what type of underwater vehicles might be used to find the missing airplane and where any debris from the crash might lie.
The seafloor topography map illustrates jagged plateaus, ridges and other underwater features of a large area underneath the Indian Ocean where search efforts have focused since contact with Malaysia Airlines ...
Rules to cut carbon emissions also reduce air pollution harmful to people, environment
2014-05-27
(Syracuse, NY – May 27, 2014) Setting strong standards for climate-changing carbon emissions from power plants would provide an added bonus – reductions in other air pollutants that can make people sick; damage forests, crops, and lakes; and harm fish and wildlife. This, according to a first-of-its-kind study released today by scientists at Syracuse University and Harvard who mapped the potential environmental and human health benefits of power plant carbon standards.
The authors of the new study, Co-benefits of Carbon Standards: Air Pollution Changes under Different ...
Skin grafts from genetically modified pigs may offer alternative for burn treatment
2014-05-27
A specially-bred strain of miniature swine lacking the molecule responsible for the rapid rejection of pig-to-primate organ transplants may provide a new source of skin grafts to treat seriously burned patients. A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) report that skin grafts from pigs lacking the Gal sugar molecule were as effective in covering burn-like injuries on the backs of baboons as skin taken from other baboons, a finding that could double the length of time burns can be protected while healing. The report in the journal Transplantation ...
EuroPCR 2014 session defines future horizons for renal denervation
2014-05-27
23 May 2014, Paris, France: During EuroPCR 2014, Felix Mahfoud, University Hospital in Homburg, Germany, and Konstantinos Tsioufis, University of Athens, Greece, reflected on the potential future role of modulation of the sympathetic nervous system in patients with difficult-to-control hypertension.
In the context of the SYMPLICITY-HTN-3 clinical trial results, questions were raised about the extent of the procedure's efficacy although the randomised, controlled trial confirmed the safety of renal denervation.
"In terms of efficacy, some studies have shown that renal ...
New biodiversity study throws out controversial scientific theory
2014-05-27
Researchers have today released ground-breaking findings that dismiss the 'Neutral Theory of Biodiversity'. The theory has dominated biodiversity research for the past decade, and been advocated as a tool for conservation and management efforts.
Professor Sean Connolly from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University (JCU) is the lead author of the international study, which he says overturns the long-used theory by employing a novel mathematical method. It is the largest study of its kind, covering a broad range of marine ...
Does apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide reduce neuronal apoptosis induced by DBI?
2014-05-27
Because the majority of patients with diffuse brain injury are not suitable candidates for surgery, neuroprotective agents are of great importance. Apolipoprotein E exerts a neuroprotective effect against brain injury, but synthetic apolipoprotein E cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, thus limiting its application.It has been reported that apolipoprotein E (138) mimetic peptide can cross the blood-brain barrier in both normal and injured brain. However, its impact on neurological function following diffuse brain injury is still unclear. Prof. Jianmin Li and team from ...