(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
This movie of NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery shows the movement of System 90L over land and dissipating between June 6 and June 7 at 2000 UTC (4 p.m. EDT)....
Click here for more information.
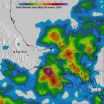
The movement of tropical storm Boris into southern Mexico and a nearly stationary low pressure system in the southern Gulf of Mexico caused heavy rainfall in that area. NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM acts like a "rain gauge in space" and calculated that one area received almost 2 feet of rainfall.
The TRMM-based, near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland monitors rainfall over the global tropics using data from the TRMM satellite. TMPA rainfall totals were calculated for the period May 29 to June 6, 2014 that covered the time that Tropical Storm Boris made landfall in southwestern Mexico and System 90L soaked eastern Mexico.
TRMM data showed the highest rainfall totals of over 535 mm where tropical storm Boris came ashore in southern Mexico. System 90L, located in the Bay Of Campeche for most of that time brought more heavy rain in southeastern Mexico before it dissipated on June 7.
On June 7, there was good and bad news about System 90L. The good news was that it moved further inland and was dissipating so it no longer had a chance to develop into a tropical cyclone. The bad news was that it moved further inland and continued to produce gusty winds and heavy rains along with life-threatening flash flooding over eastern and southeastern Mexico.
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, the NASA/NOAA GOES Project created an animation of satellite imagery from NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery. The movie shows the movement of System 90L over land and dissipating between June 6 and June 7 at 2000 UTC (4 p.m. EDT).
The Mexican Weather Service reported the city of Veracruz recorded 7.1 inches (180 mm) of rain! Huixtepec in Oaxaca reported 2.9 inches (73.4 mm) of rain.
On June 7, the National Hurricane Center noted that the low was centered near 18.0 north and 96.5 west. By June 9, System 90L had dissipated.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's TRMM satellite analyzes Mexico's soaking tropical rains
2014-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new methodology developed to monitor traffic flow
2014-06-09
"If we know not only the volume of the traffic but also the way in which the flow is taking place, we can detect when the traffic is undergoing a significant change. This information can be used, for example, when decisions are taken about signs (traffic lights, directions, etc.), road capacity, and other aspects," explained Fermín Mallor, Prof of the Department of Statistics and Operational Research.
What is new about this research is that it applies the so-called curve statistics to the specific problem of traffic control or monitoring. The use of the methodology is ...
NHAES research: New England lakes recovering rapidly from acid rain
2014-06-09
DURHAM, N.H. – For more than 40 years, policy makers have been working to reduce acid rain, a serious environmental problem that can devastate lakes, streams, and forests and the plants and animals that live in these ecosystems. Now new research funded by the NH Agricultural Experiment Station (NHAES) at the University of New Hampshire College of Life Sciences and Agriculture indicates that lakes in New England and the Adirondack Mountains are recovering rapidly from the effects of acid rain.
Researchers found that sulfate concentration in rain and snow declined by more ...
Angry faces back up verbal threats, making them seem more credible
2014-06-09
We've all been on the receiving end of an angry glare, whether from a teacher, parent, boss, or significant other. These angry expressions seem to boost the effectiveness of threats without actual aggression, according to research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
The research findings show that angry expressions lend additional weight to a negotiator's threat to walk away from the table if his or her demands aren't met, leading the other party in the negotiation to offer more money than they otherwise would have.
"Our ...
Distance from a conflict may promote wiser reasoning
2014-06-09
If you're faced with a troubling personal dilemma, such as a cheating spouse, you may think about it more wisely if you consider it as an outside observer would, according to research forthcoming in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"These results are the first to demonstrate a new type of bias within ourselves when it comes to wise reasoning about an interpersonal relationship dilemma," says psychology researcher and study author Igor Grossmann of the University of Waterloo in Canada. "We call the bias Solomon's Paradox, ...
Penn Medicine at the International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders
2014-06-09
Penn Medicine researchers will be among the featured presenters at the 18th International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders in Stockholm, Sweden, from Sunday, June 8 to Thursday, June 12, 2014.
Matthew Stern, MD, director of the Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Center in the Department of Neurology and current president of the International Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Society, will chair a plenary session entitled "New insights into the pathology, progression, and heterogeneity of Parkinson's disease."
John Q. Trojanowski, ...
What causes garlic breath? (video)
2014-06-09
WASHINGTON, June 9, 2014 — Garlic is good for your body, great for your taste buds, but terrible for your breath. In the American Chemical Society's latest Reactions video, we look at the plant beloved by chefs and feared by vampires. Once again we teamed up with the Compound Interest blog to break down the chemistry of garlic, and how to beat the bad breath it causes. The video is available at http://youtu.be/cAWLQ_4DphI.
INFORMATION:
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The ...
Health Affairs asks: Where can we find savings in health care?
2014-06-09
Reducing Maternal Mortality In Zambia and Uganda. Margaret E. Kruk of Columbia University and co-authors assessed the effectiveness of Saving Mothers, Giving Life, a new global public-private partnership that aims to reduce maternal mortality in eight districts in Uganda and Zambia. They evaluated the first six to twelve months of the program's implementation, its ownership by national ministries of health, and its effects on health systems. According to the authors, early benefits to the broader health system included greater policy attention to maternal and child health, ...
Common bean genome sequence provides powerful tools to improve critical food crop
2014-06-09
Huntsville, Ala. – String bean, snap bean, haricot bean, and pinto and navy bean. These are just a few members of the common bean family — scientifically called Phaseolus vulgaris. These beans are critically important to the global food supply. They provide up to 15 percent of calories and 36 percent of daily protein for parts of Africa and the Americas and serve as a daily staple for hundreds of millions of people.
Now, an international collaboration of researchers, led by Jeremy Schmutz of the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology and Phillip McClean, of North Dakota ...
Sequencing of citrus genomes points to need for more genetic diversity to fight disease
2014-06-09
Huntsville, Ala. – Sequencing the genomes of domesticated citrus revealed a very limited genetic diversity that could threaten the crop's survival prospects, according to an international research team. In a study published in the June issue of Nature Biotechnology, the international consortium of researchers from the United States, France, Italy, Spain and Brazil analyzed and compared the genome sequences of 10 diverse citrus varieties, including sweet and sour orange along with several important mandarin and pummelo cultivars. The findings provide the clearest insight ...
Combination therapy may help patients with follicular lymphoma
2014-06-09
A new study in The Journal of Experimental Medicine reveals that a high-risk group of patients with follicular lymphoma could benefit from a novel drug combination.
Follicular lymphoma, a B cell lymphoma, is an incurable form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is diagnosed each year in 120,000 people worldwide. Follicular lymphoma is characterized by slow and relentless tumor growth with inevitable relapses despite intense chemotherapy. Follicular lymphomas are driven by mutations that activate the BCL2 protein, which prevents cancer cells from dying, but additional genetic ...