(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 9, 2014 — Garlic is good for your body, great for your taste buds, but terrible for your breath. In the American Chemical Society's latest Reactions video, we look at the plant beloved by chefs and feared by vampires. Once again we teamed up with the Compound Interest blog to break down the chemistry of garlic, and how to beat the bad breath it causes. The video is available at http://youtu.be/cAWLQ_4DphI.
INFORMATION:
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
What causes garlic breath? (video)
2014-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Health Affairs asks: Where can we find savings in health care?
2014-06-09
Reducing Maternal Mortality In Zambia and Uganda. Margaret E. Kruk of Columbia University and co-authors assessed the effectiveness of Saving Mothers, Giving Life, a new global public-private partnership that aims to reduce maternal mortality in eight districts in Uganda and Zambia. They evaluated the first six to twelve months of the program's implementation, its ownership by national ministries of health, and its effects on health systems. According to the authors, early benefits to the broader health system included greater policy attention to maternal and child health, ...
Common bean genome sequence provides powerful tools to improve critical food crop
2014-06-09
Huntsville, Ala. – String bean, snap bean, haricot bean, and pinto and navy bean. These are just a few members of the common bean family — scientifically called Phaseolus vulgaris. These beans are critically important to the global food supply. They provide up to 15 percent of calories and 36 percent of daily protein for parts of Africa and the Americas and serve as a daily staple for hundreds of millions of people.
Now, an international collaboration of researchers, led by Jeremy Schmutz of the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology and Phillip McClean, of North Dakota ...
Sequencing of citrus genomes points to need for more genetic diversity to fight disease
2014-06-09
Huntsville, Ala. – Sequencing the genomes of domesticated citrus revealed a very limited genetic diversity that could threaten the crop's survival prospects, according to an international research team. In a study published in the June issue of Nature Biotechnology, the international consortium of researchers from the United States, France, Italy, Spain and Brazil analyzed and compared the genome sequences of 10 diverse citrus varieties, including sweet and sour orange along with several important mandarin and pummelo cultivars. The findings provide the clearest insight ...
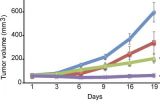
Combination therapy may help patients with follicular lymphoma
2014-06-09
A new study in The Journal of Experimental Medicine reveals that a high-risk group of patients with follicular lymphoma could benefit from a novel drug combination.
Follicular lymphoma, a B cell lymphoma, is an incurable form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is diagnosed each year in 120,000 people worldwide. Follicular lymphoma is characterized by slow and relentless tumor growth with inevitable relapses despite intense chemotherapy. Follicular lymphomas are driven by mutations that activate the BCL2 protein, which prevents cancer cells from dying, but additional genetic ...
No limits to human effects on clouds
2014-06-09
Understanding how clouds affect the climate has been a difficult proposition. What controls the makeup of the low clouds that cool the atmosphere or the high ones that trap heat underneath? How does human activity change patterns of cloud formation? The research of the Weizmann Institute's Prof. Ilan Koren suggests we may be nudging cloud formation in the direction of added area and height. He and his team have analyzed a unique type of cloud formation; their findings, which appeared recently in Science indicate that in pre-industrial times, there was less cloud cover over ...
UNC researchers pinpoint new role for enzyme in DNA repair, kidney cancer
2014-06-09
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Twelve years ago, UNC School of Medicine researcher Brian Strahl, PhD, found that a protein called Set2 plays a role in how yeast genes are expressed – specifically how DNA gets transcribed into messenger RNA. Now his lab has found that Set2 is also a major player in DNA repair, a complicated and crucial process that can lead to the development of cancer cells if the repair goes wrong.
"We found that if Set2 is mutated, DNA repair does not properly occur" said Strahl, a professor of biochemistry and biophysics. "One consequence could be that if you ...
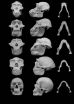
Did violence shape our faces?
2014-06-09
(Salt Lake City) —What contributed to the evolution of faces in the ape-like ancestors of humans?
The prehistoric version of a bar fight —over women, resources and other slug-worthy disagreements, new research from the University of Utah scheduled for publication in the journal Biological Reviews on June 9 suggests.
University of Utah biologist David Carrier and Michael H. Morgan, a University of Utah physician, contend that human faces —especially those of our australopith ancestors — evolved to minimize injury from punches to the face during fights between males. ...
Iron supplements improve anemia, quality of life for women with heavy periods
2014-06-09
A study by researchers from Finland found that diagnosis and treatment of anemia is important to improve quality of life among women with heavy periods. Findings published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, suggest clinicians screen for anemia and recommend iron supplementation to women with heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia).
One of the common causes of iron deficiency and anemia is heavy bleeding during menstration. Over time monthly mentrual iron loss without adequate ...
Most breast cancer patients may not be getting enough exercise
2014-06-09
Physical activity after breast cancer diagnosis has been linked with prolonged survival and improved quality of life, but most participants in a large breast cancer study did not meet national physical activity guidelines after they were diagnosed. Moreover, African-American women were less likely to meet the guidelines than white women. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings indicate that efforts to promote physical activity in breast cancer patients may need to be significantly enhanced.
The US Department ...
Longer telomeres linked to risk of brain cancer
2014-06-08
New genomic research led by UC San Francisco (UCSF) scientists reveals that two common gene variants that lead to longer telomeres, the caps on chromosome ends thought by many scientists to confer health by protecting cells from aging, also significantly increase the risk of developing the deadly brain cancers known as gliomas.
The genetic variants, in two telomere-related genes known as TERT and TERC, are respectively carried by 51 percent and 72 percent of the general population. Because it is somewhat unusual for such risk-conferring variants to be carried by a majority ...