(Press-News.org) Hot town, summer in the city — it's nothing new, but ways to handle the heat, humidity, and stormwater haven't changed much since the invention of the sewer system.
One solution offered by architectural researchers is known as a "green roof" — a roof covered in living, growing plants to soften the effects of heat, flooding, noise, and stormwater runoff.
Elizabeth J. Grant, an assistant professor of architecture and design at Virginia Tech, will present ways for architects to determine the most effective depths of green roofing for stormwater control on Thursday at the END
Virginia Tech architect reveals 'green roofs' need not go to great depths to work
Architectural researcher to tell global conferees how 'living roofs' help build better cities
2014-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientific breakthrough: International collaboration has sequence salmon genome
2014-06-10
Vancouver, BC - Today the International Cooperation to Sequence the Atlantic Salmon Genome (ICSASG) announced completion of a fully mapped and openly accessible salmon genome. This reference genome will provide crucial information to fish managers to improve the production and sustainability of aquaculture operations, and address challenges around conservation of wild stocks, preservation of at-risk fish populations and environmental sustainability. This breakthrough was announced at the International Conference on Integrative Salmonid Biology (ICISB) being held in Vancouver ...
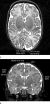
MRI shows brain abnormalities in late preterm infants
2014-06-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Babies born 32 to 36 weeks into gestation may have smaller brains and other brain abnormalities that could lead to long-term developmental problems, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
Much of the existing knowledge on preterm birth and brain development has been drawn from studies of individuals born very preterm, or less than 32 weeks into gestation at birth.
For the new study, researchers in Australia focused on moderate and late preterm (MLPT) babies —those born between 32 weeks, zero days, and 36 weeks, six days, ...
Bacteria help explain why stress, fear trigger heart attacks
2014-06-10
WASHINGTON, DC – June 10, 2014 - Scientists believe they have an explanation for the axiom that stress, emotional shock, or overexertion may trigger heart attacks in vulnerable people. Hormones released during these events appear to cause bacterial biofilms on arterial walls to disperse, allowing plaque deposits to rupture into the bloodstream, according to research published in published today in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Our hypothesis fitted with the observation that heart attack and stroke often occur following ...
Fox Chase doctors urge caution over new analysis of Medicare payments
2014-06-10
PHILADELPHIA, PA (June 9, 2014)—There's much to learn from the recent release of unprecedented amounts of data from the nation's second largest health insurer, Medicare, but only if interpreted cautiously, write two doctors at Fox Chase Cancer Center in the June 9 online edition of the Annals of Internal Medicine.
In April, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released the most detailed data in its history, related to $77 billion worth of physician billings to Medicare. In its analysis of the data, The New York Times showed that only a small percentage ...
Lifetime cancer risk from heart imaging low for most children; rises with complex tests
2014-06-09
DURHAM, N.C. -- Children with heart disease are exposed to low levels of radiation during X-rays, which do not significantly raise their lifetime cancer risk. However, children who undergo repeated complex imaging tests that deliver higher doses of radiation may have a slightly increased lifetime risk of cancer, according to researchers at Duke Medicine.
The findings, published June 9, 2014, in the American Heart Association journal Circulation, represent the largest study of cumulative radiation doses in children with heart disease and associated predictions of lifetime ...
'Jekyll and Hyde' protein linked to type 1 diabetes
2014-06-09
Researchers are a step closer to establishing the link between a protein with a split personality and type 1 diabetes.
New research, published today in the journal PNAS, shows how a protein, called GAD65, changes its shape when it turns itself on and off. Curiously, this characteristic may also link it to type 1 diabetes.
In the human brain, GAD65 performs an essential role: it makes 'neurotransmitters' - chemicals that pass messages between brain cells.
GAD65 is also found in the pancreas. Previous studies linked it to type 1 diabetes because the body makes antibodies ...
Mount Sinai researchers identify protein that keeps blood stem cells healthy as they age
2014-06-09
(New York – June 9, 2014) -- A protein may be the key to maintaining the health of aging blood stem cells, according to work by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai recently published online in Stem Cell Reports. Human adults keep stem cell pools on hand in key tissues, including the blood. These stem cells can become replacement cells for those lost to wear and tear. But as the blood stem cells age, their ability to regenerate blood declines, potentially contributing to anemia and the risk of cancers like acute myeloid leukemia and immune deficiency. ...
Viewing plant cells in 3-D (no glasses required)
2014-06-09
VIDEO:
This shows 3-D ortho-rotation of leaf mesophyll cells. Micrographs were collected by milling fixed tissue accompanied by SEM imaging using FIB-SEM. The complete videos published with the article are available...
Click here for more information.
Plant cells are beginning to look a lot different to Dr. A. Bruce Cahoon and his colleagues at Middle Tennessee State University (MTSU). They've adopted a new approach that combines the precision of an ion beam with the imaging ...
Needle biopsy underused in breast cancer diagnosis, negatively impacting diagnosis and care
2014-06-09
Needle biopsy, the standard of care radiological procedure for diagnosing breast cancer, is underused with too many patients undergoing the more invasive, excisional biopsy to detect their disease, according to research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, also finds that patients are often influenced by surgeons to undergo the unnecessary surgery -- a decision that's costly and can negatively impact their diagnosis and treatment.
A needle biopsy is a non-surgical procedure typically performed ...
Women and health-care providers differ on what matters most about contraception
2014-06-09
LEBANON, NH – When women are choosing a contraceptive, health care providers should be aware that the things they want to discuss may differ from what women want to hear, according to a survey published in the recent issue of the journal Contraception.
Most of the information women receive about contraceptives focuses heavily on the effectiveness in preventing pregnancy, but this information was ranked fifth in importance by women, according to the study conducted by researchers at Dartmouth College.
The researchers conducted an online survey of 417 women, aged 15-45, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Virginia Tech architect reveals 'green roofs' need not go to great depths to workArchitectural researcher to tell global conferees how 'living roofs' help build better cities