(Press-News.org) When it comes to electronics, silicon will now have to share the spotlight. In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, researchers from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering describe how they have overcome a major issue in carbon nanotube technology by developing a flexible, energy-efficient hybrid circuit combining carbon nanotube thin film transistors with other thin film transistors. This hybrid could take the place of silicon as the traditional transistor material used in electronic chips, since carbon nanotubes are more transparent, flexible, and can be processed at a lower cost.
Electrical engineering professor Dr. Chongwu Zhou and USC Viterbi graduate students Haitian Chen, Yu Cao, and Jialu Zhang developed this energy-efficient circuit by integrating carbon nanotube (CNT) thin film transistors (TFT) with thin film transistors comprised of indium, gallium and zinc oxide (IGZO).
"I came up with this concept in January 2013," said Dr. Chongwu Zhou, professor in USC Viterbi's Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering. "Before then, we were working hard to try to turn carbon nanotubes into n-type transistors and then one day, the idea came to me. Instead of working so hard to force nanotubes to do something that they are not good for, why don't we just find another material which would be ideal for n-type transistors—in this case, IGZO—so we can achieve complementary circuits?"
Carbon nanotubes are so small that they can only be viewed through a scanning electron microscope. This hybridization of carbon nanotube thin films and IGZO thin films was achieved by combining their types, p-type and n-type, respectively, to create circuits that can operate complimentarily, reducing power loss and increasing efficiency. The inclusion of IGZO thin film transistors was necessary to provide power efficiency to increase battery life. If only carbon nanotubes had been used, then the circuits would not be power-efficient. By combining the two materials, their strengths have been joined and their weaknesses hidden.
Zhou likened the coupling of carbon nanotube TFTs and IGZO TFTs to the Chinese philosophy of yin and yang.
"It's like a perfect marriage," said Zhou. "We are very excited about this idea of hybrid integration and we believe there is a lot of potential for it."
The potential applications for this kind of integrated circuitry are numerous, including Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs), digital circuits, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, sensors, wearable electronics, and flash memory devices. Even heads-up displays on vehicle dashboards could soon be a reality.
The new technology also has major medical implications. Currently, memory used in computers and phones is made with silicon substrates, the surface on which memory chips are built. To obtain medical information from a patient such as heart rate or brainwave data, stiff electrode objects are placed on several fixed locations on the patient's body. With this new hybridized circuit, however, electrodes could be placed all over the patient's body with just a single large but flexible object.
With this development, Zhou and his team have circumvented the difficulty of creating n-type carbon nanotube TFTs and p-type IGZO TFTs by creating a hybrid integration of p-type carbon nanotube TFTs and n-type IGZO TFTs and demonstrating a large-scale integration of circuits. As a proof of concept, they achieved a scale ring oscillator consisting of over 1,000 transistors. Up to this point, all carbon nanotube-based transistors had a maximum number of 200 transistors.
"We believe this is a technological breakthrough, as no one has done this before," said Haitian Chen, research assistant and electrical engineering PhD student at USC Viterbi. "This gives us further proof that we can make larger integrations so we can make more complicated circuits for computers and circuits."
The next step for Zhou and his team will be to build more complicated circuits using a CNT and IGZO hybrid that achieves more complicated functions and computations, as well as to build circuits on flexible substrates.
"The possibilities are endless, as digital circuits can be used in any electronics," Chen said. "One day we'll be able to print these circuits as easily as newspapers."
Zhou and Chen believe that carbon nanotube technology, including this new CNT-IGZO hybrid, will be commercialized in the next 5-10 years.
"I believe that this is just the beginning of creating hybrid integrated solutions," said Zhou. "We will see a lot of interesting work coming up."
INFORMATION:
The study is entitled, "Large scale complementary macroelectronics using hybrid integration of carbon nanotubes and IGZO thin film transistors," published in Nature Communications on June 13, 2014. The research was funded by the University of Southern California.
About the USC Viterbi School of Engineering
Engineering Studies began at the University of Southern California in 1905. Nearly a century later, the Viterbi School of Engineering received a naming gift in 2004 from alumnus Andrew J. Viterbi, inventor of the Viterbi algorithm now key to cell phone technology and numerous data applications. Consistently ranked among the top graduate programs in the world, the school enrolls more than 5,000 undergraduate and graduate students, taught by 174 tenured and tenure-track faculty, with 60 endowed chairs and professorships. http://viterbi.usc.edu
Move over, silicon, there's a new circuit in town
A new flexible and energy-efficient hybrid circuit using carbon nanotubes has big implications for the future of electronics
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Anonymous peer feedback through social networking helped residents improve their skills
2014-06-17
Surgical residents who received anonymous feedback from their peers through a social networking site on their robotic surgery skills improved more than those who did not receive any peer feedback on their procedures, UCLA researchers found.
The study is the first to examine the use of social networking to facilitate peer review of surgical procedure videos, said senior author Dr. Jim Hu, UCLA's Henry E. Singleton Professor of Urology and director of robotic and minimally invasive surgery in the urology department at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
The study ...
Death by prescription painkiller
2014-06-17
The number of deaths involving commonly prescribed painkillers is higher than the number of deaths by overdose from heroin and cocaine combined, according to researchers at McGill University. In a first-of-its-kind review of existing research, the McGill team has put the spotlight on a major public health problem: the dramatic increase in deaths due to prescribed painkillers, which were involved in more than 16,000 deaths in 2010 in the U.S. alone. Currently, the US and Canada rank #1 and #2 in per capita opioid consumption.
"Prescription painkiller overdoses have received ...
Former athletes finish first in race for top jobs
2014-06-17
ITHACA, N.Y. – Whether you were a quarterback or point guard, past participation in competitive team sports marks you as a winner in the competition for better jobs, according to a new Cornell University study.
"Participation in competitive youth sports 'spills over' to occupationally advantageous traits that persist across a person's life," says Kevin M. Kniffin, postdoctoral research associate at Cornell's Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management and lead researcher.
Research by Kniffen and his co-authors, published online this week in the Journal of Leadership ...
3-D breast imaging could revolutionize cancer screening
2014-06-17
Leesburg, VA, June 17, 2014—In community-based radiology practice, mammography screening with 3D digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) yielded lower recall rates, an increased overall cancer detection rate, and an increased detection rate for invasive cancer compared with 2D digital mammography (DM).
In the largest report to date, researchers at Washington Radiology Associates, PC, with offices in Washington, DC; Virginia; and Maryland, conducted a study of more than 59,000 patients. The results were striking: an increase in the detection rate for cancer overall of 28.6% ...
Hyperthyroidism patients more likely to take extended sick leave than healthy peers
2014-06-17
Washington, DC—People who have hyperthyroidism are more likely to take sick leave for extended periods than their healthy colleagues, particularly in the first year after diagnosis, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive. The thyroid, which is located in the front of the neck, secretes hormones that regulate how the body uses energy, consumes oxygen and produces heat.
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, ...
Pitt psychology researchers explore how engineers create
2014-06-17
PITTSBURGH—Simply put, engineers make things. But is finding that "new" invention a massive mental leap from point A to point B, or are there scores of unnoticed intermediate steps in between?
The University of Pittsburgh's Joel Chan and Christian Schunn say that not enough has been done to understand how engineers create. Understanding the process, they say, may provide a road map for speeding up innovation.
Chan, a graduate student in psychology in Pitt's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, and his mentor Schunn, a professor of psychology as well as a ...
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value
2014-06-17
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value among patients, new study says
TORONTO, June 17, 2014—Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling tests heightened their perceived importance among patients with early breast cancer who were deciding whether to have chemotherapy, a new study says.
Gene expression profiling tests, such as Oncotype Dx, analyze the patterns of 21 different genes within cancer cells to help predict how likely it is that a women's cancer will recur within 10 years after initial treatment and how beneficial ...
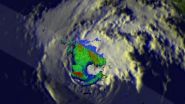
TRMM eyes rainfall in dissipating former Hurricane Cristina
2014-06-17
VIDEO:
On June 14, NASA's TRMM satellite found rain falling at a rate of almost 97 mm (about 3.8 inches) per hour in the northwestern side of Cristina's eye wall where...
Click here for more information.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over a dissipating former Hurricane Cristina and found it still contained heavy rain as it rapidly weakened.
Hurricane Cristina had sustained winds of over 130 ...
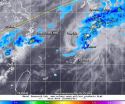
Tropical depression Hagibis gets a second chance
2014-06-17
Tropical Depression Hagibis appeared out for the count when it made landfall along southeastern China on June 16, but moved back into the South China Sea where it regenerated and sped northeast through the East China Sea. The next day, the TRMM satellite noticed power had come back to Hagibis in the form of some moderate rainfall in the depression's northeastern quadrant.
On June 17 at 10:30 UTC (6:30 a.m. EDT) the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over the regenerated Hagibis and the Precipitation Radar instrument gathered data on the storm's ...
Sleep education program spurs preschoolers to snooze 30 minutes longer at night
2014-06-17
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Taking part in an educational sleep program resulted in a 30-minute average increase in sleep duration at a one-month follow-up for preschoolers, according to a new study from the University of Michigan.
In the study, published in the journal SLEEP, families in two Head Start programs participated in the Sweet Dreamzzz Early Childhood Sleep Education Program™. The Detroit-area nonprofit organization, Sweet Dreamzzz, Inc. developed the program and offers it for free when funding allows. Head Start programs aim to give preschool opportunities to low-income ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Move over, silicon, there's a new circuit in townA new flexible and energy-efficient hybrid circuit using carbon nanotubes has big implications for the future of electronics