(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (June 19, 2014) – Rice University scientists have created a one-step process for producing highly efficient materials that let the maximum amount of sunlight reach a solar cell.
The Rice lab of chemist Andrew Barron found a simple way to etch nanoscale spikes into silicon that allows more than 99 percent of sunlight to reach the cells' active elements, where it can be turned into electricity.
The research by Barron and Rice graduate student and lead author Yen-Tien Lu appears in the Royal Society of Chemistry's Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
The more light absorbed by a solar panel's active elements, the more power it will produce. But the light has to get there. Coatings in current use that protect the active elements let most light pass but reflect some as well. Various strategies have cut reflectance down to about 6 percent, Barron said, but the anti-reflection is limited to a specific range of light, incident angle and wavelength.
Enter black silicon, so named because it reflects almost no light. Black silicon is simply silicon with a highly textured surface of nanoscale spikes or pores that are smaller than the wavelength of light. The texture allows the efficient collection of light from any angle -- from sunrise to sunset.
Barron and Lu have replaced a two-step process that involved metal deposition and electroless chemical etching with a single step that works at room temperature.
The chemical stew that makes it possible is a mix of copper nitrate, phosphorous acid, hydrogen fluoride and water. When applied to a silicon wafer, the phosphorous acid reduces the copper ions to copper nanoparticles. The nanoparticles attract electrons from the silicon wafer's surface, oxidizing it and allowing hydrogen fluoride to burn inverted pyramid-shaped nanopores into the silicon.
Fine-tuning the process resulted in a black silicon layer with pores as small as 590 nanometers (billionths of a meter) that let through more than 99 percent of light. (By comparison, a clean, un-etched silicon wafer reflects nearly 100 percent of light.)
Barron said the spikes would still require a coating to protect them from the elements, and his lab is working on ways to shorten the eight-hour process needed to perform the etching in the lab. But the ease of creating black silicon in one step makes it far more practical than previous methods, he said.
INFORMATION:
Barron is Rice's Charles W. Duncan Jr.–Welch Professor of Chemistry and a professor of materials science and nanoengineering.
Natcore Technology Inc., the Robert A. Welch Foundation and the Welsh Government Sêr Cymru Program supported the research.
Read the abstract at http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2014/ta/c4ta02006e#!divAbstract
This news release can be found online at http://news.rice.edu/2014/06/19/one-step-to-solar-cell-efficiency/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
Related Materials:
Barron Research Group: http://barron.rice.edu/Barron.html
Images for download:
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/0623_SOLAR-1-WEB.jpg
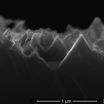
Rice University scientists have reduced to one step the process to turn silicon wafers into the black silicon used in solar cells. The advance could cut costs associated with the production of solar cells. Here, a cross section shows inverted pyramids etched into silicon by a chemical mixture over eight hours. (Credit: Barron Group/Rice University)
http://news.rice.edu/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/0623_SOLAR-2-WEB.jpg
Rice University scientists have reduced to one step the process to turn silicon wafers into the black silicon used in solar cells. The advance could cut costs associated with the production of solar cells. Here, a top-down view shows pyramid-shaped pores etched into silicon over eight hours. (Credit: Barron Group/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go here.
One step to solar-cell efficiency
Rice University researchers' chemical process may improve manufacturing
2014-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exploring how the nervous system develops
2014-06-19
The circuitry of the central nervous system is immensely complex and, as a result, sometimes confounding. When scientists conduct research to unravel the inner workings at a cellular level, they are sometimes surprised by what they find.
Patrick Keeley, a postdoctoral scholar in Benjamin Reese's laboratory at UC Santa Barbara's Neuroscience Research Institute, had such an experience. He spent years analyzing different cell types in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue lining the inner surface of the eye that mediates the first stages of visual processing. The ...
Far north at risk unless Ontario adopts new, inclusive planning process: Report
2014-06-19
THUNDER BAY – June 19, 2014 – With the Ontario government poised to spend $1 billion to promote development in the Ring of Fire, a new paper from Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) Canada and Ecojustice identifies risks inherent in the current planning legislation and provides a solution.
Ontario's Far North is the world's largest ecologically intact area of boreal forest. It contains North America's largest wetlands, is home to a number of at-risk species, including caribou and lake sturgeon, and is a one of the world's critical storehouses of carbon. First Nations ...
BICEP2 researchers publish nuanced account of stunning patterns in the microwave sky
2014-06-19
Following a thorough peer-review process, the researchers who previously announced the detection of B-mode polarization in a patch of the microwave sky have published their findings today in the journal Physical Review Letters (PDF available at http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.241101). The researchers provide some evidence that the signals they have found may be the result of gravitational waves from the earliest moments of the universe's existence and thus might constitute the first observation of phenomena from the rapid expansion of the universe ...
New target: Researchers identify pancreatic cancer resistance mechanism
2014-06-19
Pancreatic cancer tumors addicted to mutant Kras signaling for their growth and progression have a ready-made substitute to tap if they're ever forced to go cold-turkey on the mutant oncogene, scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report in the journal Cell.
When researchers dialed up mutant Kras to spur pancreatic cancer growth in mice, and then shut it down, a group of recurrent tumors grew back independently of mutant Kras, reliant on a different oncogene.
"There's a great deal of effort under way trying to find ways to target Kras or some ...
Neurons get their neighbors to take out their trash
2014-06-19
Biologists have long considered cells to function like self-cleaning ovens, chewing up and recycling their own worn out parts as needed. But a new study challenges that basic principle, showing that some nerve cells found in the eye pass off their old energy-producing factories to neighboring support cells to be "eaten." The find, which may bear on the roots of glaucoma, also has implications for Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other diseases that involve a buildup of "garbage" in brain cells.
The study was led by Nicholas Marsh-Armstrong, ...
Emerging HIV epidemics among people who inject drugs in the Middle East and North Africa
2014-06-19
DOHA, QATAR (June 17, 2014) -- HIV epidemics are emerging among people who inject drugs in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa. Though HIV infection levels were historically very low in the Middle East and North Africa, substantial levels of HIV transmission and emerging HIV epidemics have been documented among people who inject drugs in at least one-third of the countries of this region, according to findings published today in PLOS Medicine.
The HIV epidemics among people who inject drugs (PWID) are recent overall, starting largely around 2003 and ...
Possible new combination treatment for cancer
2014-06-19
A few years ago, a molecule known as "JQ1" was developed, which can block so called BET bromodomain proteins. This switch off the known cancer gene MYC thereby preventing cancer cells from dividing.
The discovery was regarded as a major breakthrough. A problem was that JQ1 did not function optimally in animal experiments, and this means that it has not been possible to test the treatment on cancer patients.
New molecule
Jonas Nilsson and his research group have developed, in collaboration with the Canadian company Zenith epigenetics, a new molecule known as "RVX2135", ...
Long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery shows greater rate of diabetes remission
2014-06-19
In a study that included long-term follow-up of obese patients with type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery was associated with more frequent diabetes remission and fewer complications than patients who received usual care, according to a study in the June 11 issue of JAMA, a diabetes theme issue.
Obesity and diabetes have reached epidemic proportions and constitute major health and economic burdens. Worldwide, 347 million adults are estimated to live with diabetes and half of them are undiagnosed.
Studies show that type 2 diabetes is preventable. The incidence of diabetes ...
New cocaine tracking system could lead to better drug enforcement
2014-06-19
Law enforcement authorities need to better understand trafficking patterns of cocaine in the United States to address one of the world's largest illegal drug markets, according to a Michigan State University researcher whose new methodology might help.
Siddharth Chandra, an economist, studied wholesale powdered cocaine prices in 112 cities to identify city-to-city links for the transit of the drug. He used data published by the National Drug Intelligence Center of the U.S. Department of Justice from 2002 to 2011, which field intelligence officers and local, regional and ...
In hairless man, arthritis drug spurs hair growth -- lots
2014-06-19
A man with almost no hair on his body has grown a full head of it after a novel treatment by doctors at Yale University.
There is currently no cure or long-term treatment for alopecia universalis, the disease that left the 25-year-old patient bare of hair. This is the first reported case of a successful targeted treatment for the rare, highly visible disease.
The patient has also grown eyebrows and eyelashes, as well as facial, armpit, and other hair, which he lacked at the time he sought help.
"The results are exactly what we hoped for," said Brett A. King, M.D., ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
[Press-News.org] One step to solar-cell efficiencyRice University researchers' chemical process may improve manufacturing