(Press-News.org) Case Western Reserve University scientists have discovered how a family of proteins — cation diffusion facilitators (CDFs) — regulates an important cellular cycle where a cell's energy generated is converted to necessary cellular functions. The finding has the potential to inform future research aimed at identifying ways to ensure the process works as designed and, if successful, could lead to significant breakthroughs in the treatment of Parkinson's, chronic liver disease and heart disease.
The results of this research were posted online June 22 by the journal Nature and will be published in the print edition at a later date.
"CDF is a major protein family type found in all forms of life," said senior author Mark R. Chance, PhD, the Charles W. and Iona A. Mathias Professor of Cancer Research, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. "Mutations or altered regulation of human CDFs modify the concentrations of metal ions critical to cell function and are associated with key human diseases, including those affecting endocrine, neurologic, hepatic and cardiovascular systems."
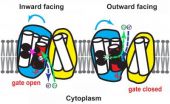
To understand how the cell cycle works, envision a gate to human cells that controls the flow of substances necessary to maintain cell survival. When and how that gate opens and closes is critical to fundamental cellular functions, and in turn, to human health. CDFs ensure the gate's seamless operation by controlling the flow of metal ions as energy is cycled. In this investigation, Case Western Reserve scientists sought to understand the intricate details of CDF molecular function and mechanisms of transport.
Chance and his colleagues studied a form of CDF found in bacteria where the protein YiiP functions like a motor, using energy in the form of a gradient of protons (hydrogen atoms) to pump zinc ions out of cells.
While zinc is pushed successfully out of the cell, a flow of protons is pulled into it. A perfectly functioning zinc-proton flow cycle, then, brings in protons, which the YiiP protein converts into conformational changes in the protein structure. Those changes, in turn, send zinc out of the cell. If the CDF-regulated gate controlling the zinc-proton cycle malfunctions, a range of diseases can result.
To visualize the zinc-proton cycle, Case Western Reserve scientists used sophisticated dynamic imaging technology — the cellular cycle operates on time scales comparable to the blink of the eye. Dynamic imaging involved a labeling system — x-ray-mediated hydroxyl radical footprinting — that recognizes water molecules in transmembrane proteins. The scientists also used mass spectrometry, a powerful atom-and-molecule recognition technology, to study the labeled proteins. These technologies allowed investigators to watch the YiiP protein in real time as it took up zinc atoms and rearranged its structure cycle through a pumping sequence.
"Membrane proteins (including CDF) are some of the most important cellular drug targets, including G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR), which represent 50 percent of the non-antibiotic drug market." Chance said.
GPCRs are protein molecules that sense chemical signals outside the cell and then activate cellular responses to these signals. Chance and his colleagues have studied GPCR structure and dynamics using innovative mass spectrometry-based technology. In this more recent work on CDFs, a dynamic picture of the membrane protein has emerged. It is a complex, but explainable, machine that uses a widely available form of energy, the proton gradient, to carry out cellular functions.
"We have now produced high-resolution pictures of signal transmission and ion transport mechanisms for a range of ion channels and GPCRs," Chance said. "Our work in CDFs is a visible example of the power of these new technologies to solve important problems in the membrane protein field. We must continue to examine CDFs to understand their mechanisms of action, especially in the context of drug effects on the biochemical mechanisms of action."
INFORMATION:
Collaborating with Chance on this investigation was senior author Dax Fu, PhD, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore. Additional researchers included Sayan Gupta, PhD, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine (lead author); Jin Chai, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, N.Y.; Jie Cheng, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; and Rhijuta D'Mello, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
This research is supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under grant R01 GM065137; Office of Basic Energy Sciences, U.S. Department of Energy grant DOE KC0304000; and NIH's National Institute for Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering under grants P30-EB-09998 and R01-EB-09688. The National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02-98CH10886.
About Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
Founded in 1843, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine is the largest medical research institution in Ohio and is among the nation's top medical schools for research funding from the National Institutes of Health. The School of Medicine is recognized throughout the international medical community for outstanding achievements in teaching. The School's innovative and pioneering Western Reserve2 curriculum interweaves four themes--research and scholarship, clinical mastery, leadership, and civic professionalism--to prepare students for the practice of evidence-based medicine in the rapidly changing health care environment of the 21st century. Nine Nobel Laureates have been affiliated with the School of Medicine.
Annually, the School of Medicine trains more than 800 MD and MD/PhD students and ranks in the top 25 among U.S. research-oriented medical schools as designated by U.S. News & World Report's "Guide to Graduate Education."
The School of Medicine's primary affiliate is University Hospitals Case Medical Center and is additionally affiliated with MetroHealth Medical Center, the Louis Stokes Cleveland Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, and the Cleveland Clinic, with which it established the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University in 2002. http://casemed.case.edu
Family of proteins plays key role in cellular pump dynamics
Case Western Reserve scientists pinpoint channeling of cell's energy flow in moving metal ions
2014-06-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evidence found for the Higgs boson direct decay into fermions
2014-06-22
For the first time, scientists from the CMS experiment on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN have succeeded in finding evidence for the direct decay of the Higgs boson into fermions. Previously, the Higgs particle could only be detected through its decay into bosons. "This is a major step forwards," explains Professor Vincenzo Chiochia from the University of Zurich's Physics Institute, whose group was involved in analyzing the data. "We now know that the Higgs particle can decay into both bosons and fermions, which means we can exclude certain theories predicting that ...
Protons power protein portal to push zinc out of cells
2014-06-22
Researchers at The Johns Hopkins University report they have deciphered the inner workings of a protein called YiiP that prevents the lethal buildup of zinc inside bacteria. They say understanding YiiP's movements will help in the design of drugs aimed at modifying the behavior of ZnT proteins, eight human proteins that are similar to YiiP, which play important roles in hormone secretion and in signaling between neurons.
Certain mutations in one of them, ZnT8, have been associated with an increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes, but mutations that destroy its function ...
Molecular footballs could revolutionize your next World Cup experience!
2014-06-22
This work focuses on the interactions between molecules and in particular on "amphiphilic" molecules, which contain two distinct parts to them. Household detergent is a good example of a product that relies on interacting amphiphilic molecules. Detergent molecules comprise two distinct parts: one that prefers to form bonds with water (hydrophilic) and the other that likes oily substances (hydrophobic). Detergents are used for cleaning because when they are added to dirty water, they orient and assemble around oily dirt, forming small clusters that allow grease and dirt ...
Antidepressant use during pregnancy may lead to childhood obesity and diabetes
2014-06-21
Hamilton, ON (June 21, 2014) - Women who take antidepressants during pregnancy may be unknowingly predisposing their infants to type 2 diabetes and obesity later in life, according to new research from McMaster University.
The study finds a correlation between the use of the medication fluoxetine
during pregnancy and an increased risk of obesity and diabetes in children.
Currently, up to 20 per cent of woman in the United States and approximately seven per cent of Canadian women are prescribed an antidepressant during pregnancy.
"Obesity and Type 2 diabetes in ...
Church-going is not enough to affect job satisfaction and commitment, Baylor study finds
2014-06-20
A congregation's beliefs about work attitudes and practices affect a churchgoer on the job — but how much depends in part on how involved that person is in the congregation, according to a Baylor University study funded by the National Science Foundation.
"We already knew that about 60 percent of American adults are affiliated with congregations, but we wanted to delve into whether that carries over from weekend worship services to the work day," said Jerry Z. Park, Ph.D., associate professor of sociology in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences. "It turns out it does make ...
Beaumont research finds advanced CT scanners reduce patient radiation exposure
2014-06-20
Computed tomography scans are an accepted standard of care for diagnosing heart and lung conditions. But clinicians worry that the growing use of CT scans could be placing patients at a higher lifetime risk of cancer from radiation exposure.
Beaumont Health System research, published in the June 20 online issue of the Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, found that the use of advanced CT scanning equipment is helping to address this important concern.
The study, of 2,085 patients at nine centers in the U.S. and Middle East, found that using newer generation, ...
Inner ear stem cells hold promise for restoring hearing
2014-06-20
New Rochelle, NY, June 20, 2014—Spiral ganglion cells are essential for hearing and their irreversible degeneration in the inner ear is common in most types of hearing loss. Adult spiral ganglion cells are not able to regenerate. However, new evidence in a mouse model shows that spiral ganglion stem cells present in the inner ear are capable of self-renewal and can be grown and induced to differentiate into mature spiral ganglion cells as well as neurons and glial cells, as described in an article in BioResearch Open Access, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
Miriam Hospital researchers analyze AUDs, sexual behavior among South African men
2014-06-20
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In a study of South African men who drink alcohol in informal drinking environments or "shebeens," researchers from The Miriam Hospital have found a high prevalence of Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) that directly correlates to unprotected sex. Findings support the need for interventions targeting both alcohol and HIV-risk behaviors among South African men who drink alcohol in alcohol-serving venues. The study and its findings are published in the July issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
Lori A. Scott-Sheldon, Ph.D., lead author and researcher at The ...
Researchers find gene critical for development of brain motor center
2014-06-20
Ottawa – June 20, 2014 – In a report published today in Nature Communications, an Ottawa-led team of researchers describe the role of a specific gene, called Snf2h, in the development of the cerebellum. Snf2h is required for the proper development of a healthy cerebellum, a master control centre in the brain for balance, fine motor control and complex physical movements.
Athletes and artists perform their extraordinary feats relying on the cerebellum. As well, the cerebellum is critical for the everyday tasks and activities that we perform, such as walking, eating and ...
New study explains how organs coordinate their development with the whole body
2014-06-20
This news release is available in Portuguese. This news release is available in Portuguese. A research group led by Christen Mirth at Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (Portugal) uncovered that the development of wings in fruit flies does not progress synchronously with the organism's development. Instead, it is coordinated with the whole body only at distinct 'milestones'. This study, published in the latest issue of the scientific journal PLOS Genetics*, helps explain how an organism facing environmental and physiological perturbations retains the ability to build ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
CU Anschutz School of Medicine receives best ranking in NIH funding in 20 years
Mayo Clinic opens patient information office in Cayman Islands
Phonon lasers unlock ultrabroadband acoustic frequency combs
Babies with an increased likelihood of autism may struggle to settle into deep, restorative sleep, according to a new study from the University of East Anglia.
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
[Press-News.org] Family of proteins plays key role in cellular pump dynamicsCase Western Reserve scientists pinpoint channeling of cell's energy flow in moving metal ions