(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (June 23, 2014) – New structures discovered within cilia show a relationship between certain proteins and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. The discovery, made at the University of Minnesota, was named paper of the week in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, and sheds new light on the microstructure of cilia.
Cilia are microscopic, hair-like structures occurring in large numbers on the surface of some of the body's cells and are involved in movement and perception. Cilia are composed of double microtubules, which are in turn composed of protofilaments.
Richard Linck, Ph.D., professor in the College of Biological Sciences and the Medical School at the University of Minnesota, worked closely with a team to identify specialized ribbons of four protofilaments within the microtubules of cilia. The function of these ribbons had been elusive to researchers, but unlocking the function of these elements improves understanding of how they fit into the bigger picture.
Utilizing cryo-electron tomography and sea urchin sperm tails, researchers identified a single ribbon of four protofilaments in each microtubule, with each microtubule containing a single filament of the protein tektin. Despite the extremely high resolution and protofilament ribbon identifications, there is still a small zone of confusion where the filament meets the ribbon. Thus, it is remains unclear how the filament fits into the structure of the ribbon.
"This discovery may not seem like a giant leap, but it does help us answer some pretty major questions," said Linck. "This structural mapping, similar to taking apart an engine to understand the subcomponents, allows us to see inside cilia. We're getting the highest resolution on this structure to date and finding where the parts belong and how they contribute to the overall structure and function."
As part of the push for structural mapping, Linck and his research team applied biochemical analysis to the ribbon. In this assessment, several proteins have been localized to the ribbon, including tektin and two others casually associated with human disease, including juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
It is still unclear if the cilia are directly involved in the cause of the epilepsy and other diseases, or if the relevant proteins function in other, non-ciliary ways to cause disease. However, the mapping itself begins to unlock those clues.
Future research is needed to understand the relationship of these ribbon-associated proteins to human disease, as well as to better understand how the filament is structured in the larger ribbon.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this project was provided by the National Science Foundation award 1024963, the National Institutes of Health grant GM083122, the Characterization Facility, and entities within the University of Minnesota.
The University of Minnesota Medical School, with its two campuses in the Twin Cities and Duluth, is a leading educator of the next generation of physicians. Our graduates and the school's 3,800 faculty physicians and scientists advance patient care, discover biomedical research breakthroughs with more than $180 million in sponsored research annually, and enhance health through world-class patient care for the state of Minnesota and beyond. Visit http://www.med.umn.edu to learn more.
UMN research uncovers structure, protein elements critical to human function and disease
2014-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chronic brain damage not as prevalent in NFL players, say researchers
2014-06-25
ROSEMONT, IL – A study published online today in Sports Health: A Multidisciplinary Approach provides a different take on previous information regarding the prevalence of chronic brain damage in retired NFL players.
Researchers performed in-depth neurological examinations of 45 retired NFL players, ranging in age from 30-to 60-years old. The analysis included state-of-the-art magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) along with comprehensive neuropsychological and neurological examinations, interviews, blood ...
Stanley Miller's forgotten experiments, analyzed
2014-06-25
VIDEO:
Graduate student and study first author Eric Parker talks about the famous spark discharge experiment and the latest findings from a first-ever analysis of Miller's samples from 1958.
Click here for more information.
Stanley Miller, the chemist whose landmark experiment published in 1953 showed how some of the molecules of life could have formed on a young Earth, left behind boxes of experimental samples that he never analyzed. The first-ever analysis of some of Miller's ...
Restoring thyroid hormones in heart may prevent heart disease from diabetes
2014-06-25
Old Westbury, N.Y. (June 25, 2014) –Administering low doses of a thyroid hormone to rats with diabetes helps restore hormone levels in their hearts and prevented deterioration of heart function and pathology, according to a new study by NYIT College of Osteopathic Medicine professor A. Martin Gerdes.
The study, published in the online edition of Molecular Medicine provides the first clear indication that low thyroid hormone levels in cardiac tissue of diabetic individuals may be the major cause of their associated heart disease, says Gerdes.
The study finds that diabetes ...
Neural sweet talk: Taste metaphors emotionally engage the brain
2014-06-25
So accustomed are we to metaphors related to taste that when we hear a kind smile described as "sweet," or a resentful comment as "bitter," we most likely don't even think of those words as metaphors. But while it may seem to our ears that "sweet" by any other name means the same thing, new research shows that taste-related words actually engage the emotional centers of the brain more than literal words with the same meaning.
Researchers from Princeton University and the Free University of Berlin report in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience the first study to experimentally ...
Special edition of the Red Journal highlights the need for radiation oncology services in LMICs
2014-06-25
Fairfax, Va., June 25, 2014—The July 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology ● Biology ● Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), features a special section of 10 articles focusing on global health and radiation oncology in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs.)
Three papers examine the overall need for more and the current opportunities to provide radiation oncology in LMICs, C. Norman Coleman, MD, FASTRO, highlights the work and the four main principles of ...
Study highlights carbon monoxide hazards on houseboats
2014-06-25
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (June 25, 2014) — Boaters and marina workers should exercise caution this summer before taking to the seas. A study published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene (JOEH) outlines hazards posed by carbon monoxide levels on houseboats that use gasoline-powered generators without emission controls, along with controls that are available to reduce exposure to carbon monoxide from the generators.
The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), found that uncontrolled generators ...
New treatment option in development for individuals with food allergy
2014-06-25
New Rochelle, NY, June 25, 2014—For some children an allergic reaction to common foods such as milk, eggs, or peanuts can cause an anaphylactic reaction. At present no effective treatment for food allergy exists, and strict dietary avoidance of known food triggers is the only preventive option available. Ongoing trials are exploring options for oral immunotherapy (OIT) for desensitization in the treatment of Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergy, as described in a Review article in Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary ...
Deploying midwives in poorest nations could avert millions of maternal and newborn deaths
2014-06-25
A modest increase in the number of skilled midwives in the world's poorest nations could save the lives of a substantial number of women and their babies, according to new analyses by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Maternal mortality is a leading cause of death for women in many developing countries and public health efforts to avert it have only made headway in a few countries. Elsewhere, progress has either never started or has stalled in recent years. Poor nations also have troubling rates of infant and fetal deaths. Midwives ...
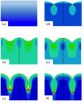
Mathematical models explain how a wrinkle becomes a crease
2014-06-25
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Wrinkles, creases and folds are everywhere in nature, from the surface of human skin to the buckled crust of the Earth. They can also be useful structures for engineers. Wrinkles in thin films, for example, can help make durable circuit boards for flexible electronics.
A new mathematical model developed by researchers from Brown University could help engineers control the formation of wrinkle, crease, and fold structures in a wide variety of materials. It may also help scientists understand how these structures form in nature. The ...
Nanoscale ruler reveals organization of the cell membrane
2014-06-25
This news release is available in German.
After a ten-year effort, Prof. Dr. Michael Reth from the Institute of Biology III of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics has developed a method to investigate the cell surface's organization on a nanometer scale. This allows him to monitor how the antigen receptor, which B cells of the immune system use to recognize foreign substances, changes after activation. This study shows that the receptor components dissociate from each other– rather than assemble, as previously ...