Silver in the washing machine
Nano-coatings release almost no nano-particles
2014-06-30
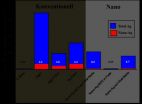
(Press-News.org) If it contains 'nano', it doesn't primarily leak 'nano': at least that's true for silver-coated textiles, explains Bernd Nowack of the Technology and Society division at Empa. During each wash cycle a certain amount of the silver coating is washed out of the textiles and ends up in the waste water. Empa analysed this water; it turned out that nano-coated textiles release hardly any nano-particles. That's quite the opposite to ordinary coatings, where a lot of different silver particles were found. Moreover, nano-coated silver textiles generally lose less silver during washing. This is because considerably less silver is incorporated into textile fabrics with nano-coating, and so it is released in smaller quantities for the antibacterial effect than is the case with ordinary coatings. A surprising result that has a transformative effect on future analyses and on the treatment of silver textiles. "All silver textiles behave in a similar manner - regardless of whether they are nano-coated or conventionally-coated," says Nowack. This is why nano-textiles should not be subjected to stricter regulation than textiles with conventional silver-coatings, and this is relevant for current discussions concerning possible special regulations for nano-silver.
But what is the significance of silver particles in waste water? Exposed silver reacts with the (small quantities of) sulphur in the air to form silver sulphite, and the same process takes place in the waste water treatment plant. The silver sulphite, which is insoluble, settles at the bottom of the sedimentation tank and is subsequently incinerated with the sewage sludge. So hardly any of the silver from the waste water remains in the environment. Silver is harmless because it is relatively non-toxic for humans. Even if silver particles are released from the textile fabric as a result of strong sweating, they are not absorbed by healthy skin.
Which detergent for which coating?
Next, Nowack's team wants to investigate how silver textiles respond to various ordinary laundry detergents. Studies have shown that some active ingredients of laundry detergents can alter the form in which silver is present. For example, before washing researchers have detected silver ions, i.e. dissolved silver (a conventional form of silver) in textile fabrics, whereas after washing they detected elemental, i.e. metallic, nano-silver or other silver compounds, such as (insoluble) silver chloride.
So silver textiles ultimately contain a number of silver compounds that constantly change and undergo chemical transformations. And they don't just do that during washing, as Nowack stresses. Even during the manufacturing and coating processes, external influences can have an effect on the composition of the silver particles in textiles, even before the customer has got the product hanging in their wardrobe at home.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene variants found that increase pain sensation after common childhood surgery
2014-06-30
In the first genome-wide analysis of postsurgical pain in children, pediatric researchers identified variations in genes that affect a child's need for pain-control drugs. The findings suggest that at some point physicians may calibrate pain-medication dosages according to a child's individual genetic makeup.
"Although this research is only a first step for our team, it provides tremendous new insight into the biological mechanisms and brings us a little closer to personalizing medicine for pain control," said Scott D. Cook-Sather, M.D., a pediatric anesthesiologist at ...
It may take guts to cure diabetes
2014-06-30
New York, NY (June 30, 2014) — By switching off a single gene, scientists at Columbia University's Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center have converted human gastrointestinal cells into insulin-producing cells, demonstrating in principle that a drug could retrain cells inside a person's GI tract to produce insulin.
The new research was reported today in the online issue of the journal Nature Communications.
"People have been talking about turning one cell into another for a long time, but until now we hadn't gotten to the point of creating a fully functional insulin-producing ...
Newly identified gene provides reliable visual cue for oil palm fruit ripeness
2014-06-30
A genetic discovery by a team of scientists from the Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB), aided by scientists from Orion Genomics, paves the way for increased production of palm oil, which accounts for 45 percent of the world's edible oil, while also helping to conserve sensitive wild habitats at risk of being turned into agricultural land.
In the study published in the journal Nature Communications, the scientists identified the VIR gene as responsible for fruit color. Currently, the majority of the oil palm fruit harvested in Malaysia and Indonesia is the nigrescens variety ...
No link between fertility drugs and breast, ovarian and uterine cancers
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: There is "little evidence" that the use of conventional fertility hormones used for ovarian stimulation in the treatment of infertility increases the long-term risk of breast and gynecological cancers, according to the results of a substantial 30-year follow-up study. However, the extended use of clomiphene citrate was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer among women who had used the fertility drug for 12 cycles or more. Gonadotrophins, more commonly used for ovarian stimulation today, were not generally associated with any increased risk, ...
Children born to women after fertility treatment at greater risk of psychiatric disorders
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: Children born to women with fertility problems have a higher risk of psychiatric disorders than naturally conceived children. The increase in risk was described as "modest" by researchers from Denmark, but was found to persist throughout childhood and into young adulthood.
The results, which are presented today at the 30th Annual Meeting of ESHRE in Munich by Dr Allan Jensen of the Danish Cancer Society Research Center at the University of Copenhagen, were derived from a register study of all children born in Denmark between 1969 and 2006.
From ...
Efficacy doubts over pre-IVF hysteroscopy
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: A large multicentre trial seems finally to have resolved one of IVF's long-running controversies - whether the outlook for women with a poor IVF record can be improved by routine hysteroscopy performed before further IVF treatment.(1) For the TROPHY study, whose results are reported today at the 30th Annual Meeting of ESHRE in Munich by Dr Tarek El-Toukhy from Guy's and St Thomas's Hospital, London, has now found no significant difference in IVF success rates between those who had outpatient hysteroscopy performed before their IVF and those who didn't. ...
Study finds videoconferencing with family, friends lowers stress for pediatric patients
2014-06-30
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —To ease isolation during extended hospitalizations, UC Davis Children's Hospital offers secure videoconferencing for patients and families. While anecdotal accounts have suggested the Family-Link program enhances quality of life during long hospital stays, clinicians wondered if the technology also offered clinical benefits.
To answer that, a team led by UC Davis professor James Marcin studied 367 children who were hospitalized for at least four days. They found that access to Family-Link significantly reduced patient stress. The study was published ...
One-third of knee replacements classified as inappropriate
2014-06-30
New research reports that more than one third of total knee replacements in the U.S. were classified as "inappropriate" using a patient classification system developed and validated in Spain. The study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), highlights the need for consensus on patient selection criteria among U.S. medical professionals treating those with the potential need of knee replacement surgery.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reports more than 600,000 knee replacements are performed in the ...
Young teens who receive sexts are 6 times more likely to report having had sex
2014-06-30
A study from USC researchers provides new understanding of the relationship between "sexting" and sexual behavior in early adolescence, contributing to an ongoing national conversation about whether sexually explicit text messaging is a risk behavior or just a technologically-enabled extension of normal teenage flirtation. The latest research, published in the July 2014 issue of the journal Pediatrics, found that among middle school students, those who reported receiving a sext were 6 times more likely to also report being sexually active.
While past research has examined ...
The outcome of fertility treatments using donor sperm is dependent on the quality of sperm
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: Despite emerging evidence of a decline in sperm quality with increasing age, an analysis of every first fertility treatment cycle performed in the UK using sperm donation shows that outcome in terms of live birth is not affected by the age of the sperm donor. Results from the study, said its principal investigator Dr Meenakshi Choudhary, from the Newcastle Fertility Centre at Life, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom, reaffirm the observation that a couple's fertility appears significantly more dependent on the age of the female partner than on that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] Silver in the washing machineNano-coatings release almost no nano-particles