(Press-News.org) The ability of microorganisms to overcome antibiotic treatments is one of the top concerns of modern medicine. The effectiveness of many antibiotics has been reduced by bacteria's ability to rapidly evolve and develop strategies to resist antibiotics. Bacteria achieve this by specific mechanisms that are tailored to the molecular structure or function of a particular antibiotic. For example, bacteria would typically develop drug resistance by evolving a mutation that breaks down the drug.
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem set out to determine if they could predict a different evolutionary process and follow it in real time. Using the quantitative approach of physicists, the team developed experimental tools to measure precisely the bacterial response to antibiotics, and developed a mathematical model of the process. The model led them to hypothesize that a daily three-hour dose would enable the bacteria to predict delivery of the drug, and go dormant for that period in order to survive.
The research was led by Prof. Nathalie Q. Balaban at the Racah Institute of Physics in the Hebrew University's Faculty of Science, working with colleagues at the Racah Institute, the Hebrew University's Sudarsky Center for Computational Biology, and the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT. The research paper, "Optimization of lag time underlies tolerance in bacterial populations evolved under intermittent antibiotic exposure," appears in the June 25 edition of the journal Nature (available at http://bit.ly/lagtime).
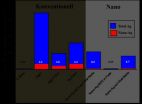
To test their hypothesis, the researchers delivered antibiotics to bacterial populations in the lab for precisely three hours each day. After only ten days they were able to observe the bacteria using a new survival tactic. When exposed to these repeated cycles of antibiotic treatments, the bacteria evolved an adaptation to the duration of the antibiotic stress by remaining dormant for the treatment period.
The results demonstrated that bacteria can evolve within days. Most significantly, it showed for the first time that bacteria can develop a biological timer to survive under antibiotic exposure.
To further test their hypothesis, the researchers delivered antibiotics for different periods, exposing three different bacteria populations to repeated daily antibiotic exposures lasting 3, 5, or 8 hours. Remarkably, each of the populations adapted by prolonging their dormant stage to match the exposure duration.
With this new understanding of how bacterial populations evolve survival strategies against antibiotics, scientists could develop new approaches for slowing the evolution of antibiotic resistance.
Now that they have identified the mutation responsible for the biological timer, the researchers want to gather clinical data to see if a similar timed response to antibiotics is active in people, allowing bacteria to render less effective the antibiotics people take on a fixed schedule. If this is discovered to be the case, it may explain the failure of antibiotic treatments observed in several diseases. In the future, it may help doctors to recommend different treatment schedules. It could also lead to the development and greater use of drugs that can maintain constant levels in the body.
According to the researchers, the study demonstrates that quantitative approaches from Physics can be used to address fundamental as well as clinically relevant issues in Biology.
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by European Research Council (Starting Grant #260871) and the Israel Science Foundation (#592/10), with Levtzion Fellowship support for researcher Ofer Fridman.
A first: Scientists show bacteria can evolve a biological timer to survive antibiotics
Hebrew University research demonstrates that quantitative approaches from physics can be used to address fundamental as well as clinically relevant issues in biology
2014-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More carbohydrates make trees more resistant to drought
2014-06-30
Water is the limiting factor for many plants and trees. Consequently, there are grave concerns that the rainfall patterns altered by climate change could trigger a forest decline on a global scale. According to climate researchers, Switzerland is also affected: The climate models even project hotter and drier summers for this country. An international research team headed by Michael O'Brien, an ecologist at the University of Zurich, is now studying which factors govern the resistance of tropical trees to periods of drought. As the scientists reveal in their study published ...
Women's groups recommended by WHO as an intervention to cut newborn deaths
2014-06-30
The World Health Organisation has recommended an intervention developed and tested by partners in four countries and UCL researchers to improve maternal and newborn health. The intervention involves groups of women working together in a four-stage facilitated process: 1) Identifying problems during pregnancy, delivery, and post-partum; 2) Developing strategies to address these problems; 3) Implementing these strategies; and 4) Evaluating the strategies.
A meta-analysis of research into Participatory Women's Groups was conducted by Dr Audrey Prost and others, largely ...
Cocaine addiction: Phase-specific biology and treatment?
2014-06-30
Philadelphia, PA, June 30, 2014 – Current pharmacotherapies for addiction follow the dictum "one size fits all". Medications are prescribed in the same way for all patients, regardless of whether they have just started experimenting with a drug or have an established drug habit. Even more troubling, there are no FDA-approved pharmacotherapies for some addictions, such as compulsive cocaine use.
Perhaps testing drugs in ways that focus on particular phases of addiction or particular clinical features of addiction, such as a patient's level of impulsivity, might advance ...
Silver in the washing machine
2014-06-30
If it contains 'nano', it doesn't primarily leak 'nano': at least that's true for silver-coated textiles, explains Bernd Nowack of the Technology and Society division at Empa. During each wash cycle a certain amount of the silver coating is washed out of the textiles and ends up in the waste water. Empa analysed this water; it turned out that nano-coated textiles release hardly any nano-particles. That's quite the opposite to ordinary coatings, where a lot of different silver particles were found. Moreover, nano-coated silver textiles generally lose less silver during washing. ...
Gene variants found that increase pain sensation after common childhood surgery
2014-06-30
In the first genome-wide analysis of postsurgical pain in children, pediatric researchers identified variations in genes that affect a child's need for pain-control drugs. The findings suggest that at some point physicians may calibrate pain-medication dosages according to a child's individual genetic makeup.
"Although this research is only a first step for our team, it provides tremendous new insight into the biological mechanisms and brings us a little closer to personalizing medicine for pain control," said Scott D. Cook-Sather, M.D., a pediatric anesthesiologist at ...
It may take guts to cure diabetes
2014-06-30
New York, NY (June 30, 2014) — By switching off a single gene, scientists at Columbia University's Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center have converted human gastrointestinal cells into insulin-producing cells, demonstrating in principle that a drug could retrain cells inside a person's GI tract to produce insulin.
The new research was reported today in the online issue of the journal Nature Communications.
"People have been talking about turning one cell into another for a long time, but until now we hadn't gotten to the point of creating a fully functional insulin-producing ...
Newly identified gene provides reliable visual cue for oil palm fruit ripeness
2014-06-30
A genetic discovery by a team of scientists from the Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB), aided by scientists from Orion Genomics, paves the way for increased production of palm oil, which accounts for 45 percent of the world's edible oil, while also helping to conserve sensitive wild habitats at risk of being turned into agricultural land.
In the study published in the journal Nature Communications, the scientists identified the VIR gene as responsible for fruit color. Currently, the majority of the oil palm fruit harvested in Malaysia and Indonesia is the nigrescens variety ...
No link between fertility drugs and breast, ovarian and uterine cancers
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: There is "little evidence" that the use of conventional fertility hormones used for ovarian stimulation in the treatment of infertility increases the long-term risk of breast and gynecological cancers, according to the results of a substantial 30-year follow-up study. However, the extended use of clomiphene citrate was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer among women who had used the fertility drug for 12 cycles or more. Gonadotrophins, more commonly used for ovarian stimulation today, were not generally associated with any increased risk, ...
Children born to women after fertility treatment at greater risk of psychiatric disorders
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: Children born to women with fertility problems have a higher risk of psychiatric disorders than naturally conceived children. The increase in risk was described as "modest" by researchers from Denmark, but was found to persist throughout childhood and into young adulthood.
The results, which are presented today at the 30th Annual Meeting of ESHRE in Munich by Dr Allan Jensen of the Danish Cancer Society Research Center at the University of Copenhagen, were derived from a register study of all children born in Denmark between 1969 and 2006.
From ...
Efficacy doubts over pre-IVF hysteroscopy
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: A large multicentre trial seems finally to have resolved one of IVF's long-running controversies - whether the outlook for women with a poor IVF record can be improved by routine hysteroscopy performed before further IVF treatment.(1) For the TROPHY study, whose results are reported today at the 30th Annual Meeting of ESHRE in Munich by Dr Tarek El-Toukhy from Guy's and St Thomas's Hospital, London, has now found no significant difference in IVF success rates between those who had outpatient hysteroscopy performed before their IVF and those who didn't. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
[Press-News.org] A first: Scientists show bacteria can evolve a biological timer to survive antibioticsHebrew University research demonstrates that quantitative approaches from physics can be used to address fundamental as well as clinically relevant issues in biology