(Press-News.org) Researchers have made a giant leap towards the goal of 'bio-printing' transplantable tissues and organs for people affected by major diseases and trauma injuries, a new study reports.
Scientists from the Universities of Sydney, Harvard, Stanford and MIT have bio-printed artificial vascular networks mimicking the body's circulatory system that are necessary for growing large complex tissues.
"Thousands of people die each year due to a lack of organs for transplantation," says study lead author and University of Sydney researcher, Dr Luiz Bertassoni.
"Many more are subjected to the surgical removal of tissues and organs due to cancer, or they're involved in accidents with large fractures and injuries.
"Imagine being able to walk into a hospital and have a full organ printed – or bio-printed, as we call it – with all the cells, proteins and blood vessels in the right place, simply by pushing the 'print' button in your computer screen.
"We are still far away from that, but our research is addressing exactly that. Our finding is an important new step towards achieving these goals.
"At the moment, we are pretty much printing 'prototypes' that, as we improve, will eventually be used to change the way we treat patients worldwide."
The research challenge – networking cells with a blood supply.
Cells need ready access to nutrients, oxygen and an effective 'waste disposal' system to sustain life. This is why 'vascularisation' – a functional transportation system – is central to the engineering of biological tissues and organs.
"One of the greatest challenges to the engineering of large tissues and organs is growing a network of blood vessels and capillaries," says Dr Bertassoni.
"Cells die without an adequate blood supply because blood supplies oxygen that's necessary for cells to grow and perform a range of functions in the body."
"To illustrate the scale and complexity of the bio-engineering challenge we face, consider that every cell in the body is just a hair's width from a supply of oxygenated blood.
"Replicating the complexity of these networks has been a stumbling block preventing tissue engineering from becoming a real world clinical application."
But this is what researchers have now achieved.
What the researchers achieved
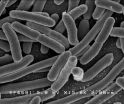
Using a high-tech 'bio-printer', the researchers fabricated a multitude of interconnected tiny fibres to serve as the mold for the artificial blood vessels.
They then covered the 3D printed structure with a cell-rich protein-based material, which was solidified by applying light to it.
Lastly they removed the bio-printed fibres to leave behind a network of tiny channels coated with human endothelial cells, which self organised to form stable blood capillaries in less than a week (see diagram below).
The study reveals that the bioprinted vascular networks promoted significantly better cell survival, differentiation and proliferation compared to cells that received no nutrient supply.
Significance of the breakthrough
According to Dr Bertassoni, a major benefit of the new bio-printing technique is the ability to fabricate large three-dimensional micro-vascular channels capable of supporting life on the fly, with enough precision to match individual patients' needs.
"While recreating little parts of tissues in the lab is something that we have already been able to do, the possibility of printing three-dimensional tissues with functional blood capillaries in the blink of an eye is a game changer," he says.
"Of course, simplified regenerative materials have long been available, but true regeneration of complex and functional organs is what doctors really want and patients really need, and this is the objective of our work.
INFORMATION:
A step closer to bio-printing transplantable tissues and organs: Study
2014-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists develop force sensor from carbon nanotubes
2014-06-30
A group of researchers from Russia, Belarus and Spain, including Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology professor Yury Lozovik, have developed a microscopic force sensor based on carbon nanotubes. The device is described in an article published in the journal Computational Materials Science and is also available as a preprint.
The scientists proposed using two nanotubes, one of which is a long cylinder with double walls one atom thick. These tubes are placed so that their open ends are opposite to each other. Voltage is then applied to them, and a current of about ...
A first: Scientists show bacteria can evolve a biological timer to survive antibiotics
2014-06-30
The ability of microorganisms to overcome antibiotic treatments is one of the top concerns of modern medicine. The effectiveness of many antibiotics has been reduced by bacteria's ability to rapidly evolve and develop strategies to resist antibiotics. Bacteria achieve this by specific mechanisms that are tailored to the molecular structure or function of a particular antibiotic. For example, bacteria would typically develop drug resistance by evolving a mutation that breaks down the drug.
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem set out to determine if they could ...
More carbohydrates make trees more resistant to drought
2014-06-30
Water is the limiting factor for many plants and trees. Consequently, there are grave concerns that the rainfall patterns altered by climate change could trigger a forest decline on a global scale. According to climate researchers, Switzerland is also affected: The climate models even project hotter and drier summers for this country. An international research team headed by Michael O'Brien, an ecologist at the University of Zurich, is now studying which factors govern the resistance of tropical trees to periods of drought. As the scientists reveal in their study published ...
Women's groups recommended by WHO as an intervention to cut newborn deaths
2014-06-30
The World Health Organisation has recommended an intervention developed and tested by partners in four countries and UCL researchers to improve maternal and newborn health. The intervention involves groups of women working together in a four-stage facilitated process: 1) Identifying problems during pregnancy, delivery, and post-partum; 2) Developing strategies to address these problems; 3) Implementing these strategies; and 4) Evaluating the strategies.
A meta-analysis of research into Participatory Women's Groups was conducted by Dr Audrey Prost and others, largely ...
Cocaine addiction: Phase-specific biology and treatment?
2014-06-30
Philadelphia, PA, June 30, 2014 – Current pharmacotherapies for addiction follow the dictum "one size fits all". Medications are prescribed in the same way for all patients, regardless of whether they have just started experimenting with a drug or have an established drug habit. Even more troubling, there are no FDA-approved pharmacotherapies for some addictions, such as compulsive cocaine use.
Perhaps testing drugs in ways that focus on particular phases of addiction or particular clinical features of addiction, such as a patient's level of impulsivity, might advance ...
Silver in the washing machine
2014-06-30
If it contains 'nano', it doesn't primarily leak 'nano': at least that's true for silver-coated textiles, explains Bernd Nowack of the Technology and Society division at Empa. During each wash cycle a certain amount of the silver coating is washed out of the textiles and ends up in the waste water. Empa analysed this water; it turned out that nano-coated textiles release hardly any nano-particles. That's quite the opposite to ordinary coatings, where a lot of different silver particles were found. Moreover, nano-coated silver textiles generally lose less silver during washing. ...
Gene variants found that increase pain sensation after common childhood surgery
2014-06-30
In the first genome-wide analysis of postsurgical pain in children, pediatric researchers identified variations in genes that affect a child's need for pain-control drugs. The findings suggest that at some point physicians may calibrate pain-medication dosages according to a child's individual genetic makeup.
"Although this research is only a first step for our team, it provides tremendous new insight into the biological mechanisms and brings us a little closer to personalizing medicine for pain control," said Scott D. Cook-Sather, M.D., a pediatric anesthesiologist at ...
It may take guts to cure diabetes
2014-06-30
New York, NY (June 30, 2014) — By switching off a single gene, scientists at Columbia University's Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center have converted human gastrointestinal cells into insulin-producing cells, demonstrating in principle that a drug could retrain cells inside a person's GI tract to produce insulin.
The new research was reported today in the online issue of the journal Nature Communications.
"People have been talking about turning one cell into another for a long time, but until now we hadn't gotten to the point of creating a fully functional insulin-producing ...
Newly identified gene provides reliable visual cue for oil palm fruit ripeness
2014-06-30
A genetic discovery by a team of scientists from the Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB), aided by scientists from Orion Genomics, paves the way for increased production of palm oil, which accounts for 45 percent of the world's edible oil, while also helping to conserve sensitive wild habitats at risk of being turned into agricultural land.
In the study published in the journal Nature Communications, the scientists identified the VIR gene as responsible for fruit color. Currently, the majority of the oil palm fruit harvested in Malaysia and Indonesia is the nigrescens variety ...
No link between fertility drugs and breast, ovarian and uterine cancers
2014-06-30
Munich, 30 June 2014: There is "little evidence" that the use of conventional fertility hormones used for ovarian stimulation in the treatment of infertility increases the long-term risk of breast and gynecological cancers, according to the results of a substantial 30-year follow-up study. However, the extended use of clomiphene citrate was associated with a higher risk of breast cancer among women who had used the fertility drug for 12 cycles or more. Gonadotrophins, more commonly used for ovarian stimulation today, were not generally associated with any increased risk, ...