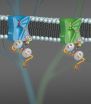
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Johns Hopkins have spotted a strong family trait in two distant relatives: The channels that permit entry of sodium and calcium ions into cells turn out to share similar means for regulating ion intake, they say. Both types of channels are critical to life. Having the right concentrations of sodium and calcium ions in cells enables healthy brain communication, heart contraction and many other processes. The new evidence is likely to aid development of drugs for channel-linked diseases ranging from epilepsy to heart ailments to muscle weakness.
"This discovery was long in coming," says David Yue, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's Department of Biomedical Engineering. His team's report, which appears in the June 19 issue of the journal Cell, had its genesis in the 1990s with another group's observation that sodium and calcium channels bear a striking resemblance in a small portion of an otherwise very different structure. "It looked like this 'resemblance element' might be a molecular time capsule derived from a primeval ion channel thought to have birthed distinct sodium and calcium channels a billion years ago," Yue says.
For calcium channels, Yue's and other research groups found that the resemblance element supports an important function, preventing the channel from opening when the cellular calcium level gets high. This prevents too much calcium from building up within cells, much like a thermostat controls household temperatures. This calcium control requires a calcium-sensing molecule called calmodulin, which binds to channels within the resemblance element.
The picture for sodium channels, however, was muddier, with different researchers reporting conflicting findings about whether calmodulin and the resemblance element prevent the opening of sodium channels; perhaps the time capsule was damaged over the millenia or was never there.
Manu Ben-Johny, a graduate student in Yue's laboratory, took up the question. "We thought that the conflicting results for sodium channels might be related to difficulties in existing methods to control the calcium concentrations that might affect these channels," Ben-Johny says.
Looking for a new way to approach the problem, Yue's team bound calcium ions in molecular "cages" that could be opened with a flash of light. This enabled them to "smuggle" calcium ions into cells and see what happened to sodium channels when the calcium concentration changed abruptly. They found that, as with calcium channels, increasing calcium concentrations caused calmodulin to bind within the resemblance element of sodium channels and prevent their opening, just as in calcium channels.
The implications of a common control element in sodium and calcium channels are vast, Yue says, including unified understanding of conditions that spring from defects in the calcium control of these channels. In addition, he says, "Researchers have long sought drugs that modulate sodium and calcium channels in new ways. Targeting the common control element offers a new frontier for developing next-generation pharmaceuticals."
INFORMATION:
Link to the paper: http://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674%2814%2900614-X
David Yue: http://www.bme.jhu.edu/people/primary.php?id=405
Other authors on the paper are Philemon S. Yang, Jacqueline Niu, Wanjun Yang and Rosy Joshi-Mukherjee, all of The Johns Hopkins University.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (grant number R01 NS073874) and the National Institute of Mental Health (grant number F31MH088109).
Related stories:
Johns Hopkins Scientists Identify a Key to Body's Use of Free Calcium
Understanding Night Blindness and Calcium
Tiny Proteins Have Outsized Influence on Nerve Health
Cellular gates for sodium and calcium controlled by common element of ancient origin
Find likely to affect drug development
2014-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mayo Clinic: Proton therapy has advantages over IMRT for advanced head and neck cancers
2014-07-01
Rochester, Minn. -- A new study by radiation oncologists at Mayo Clinic comparing the world's literature on outcomes of proton beam therapy in the treatment of a variety of advanced head and neck cancers of the skull base compared to intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) has found that proton beam therapy significantly improved disease free survival and tumor control when compared to IMRT. The results appear in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the clinical outcomes of patients treated with proton therapy ...
Video games could provide venue for exploring sustainability concepts
2014-07-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Could playing video games help people understand and address global sustainability issues such as pollution, drought or climate change? At least two researchers believe so, outlining their argument in a concept paper published in the journal First Monday.
Video games have the potential to educate the public and encourage development of creative solutions to social, economic and environmental problems, said Oregon State University's Shawna Kelly, one of the two authors of the article.
"Video games encourage creative and strategic thinking, which could ...
Studies: Addiction starts with an overcorrection in the brain
2014-07-01
The National Institutes of Health has turned to neuroscientists at the nation's most "Stone Cold Sober" university for help finding ways to treat drug and alcohol addiction.
Brigham Young University professor Scott Steffensen and his collaborators have published three new scientific papers that detail the brain mechanisms involved with addictive substances. And the NIH thinks Steffensen's on the right track, as evidenced by a $2-million grant that will help fund projects in his BYU lab for the next five years.
"Addiction is a brain disease that could be treated like ...
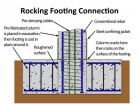
New bridge design improves earthquake resistance, reduces damage and speeds construction
2014-07-01
SEATTLE, Wash. - Researchers have developed a new design for the framework of columns and beams that support bridges, called "bents," to improve performance for better resistance to earthquakes, less damage and faster on-site construction.
The faster construction is achieved by pre-fabricating the columns and beams off-site and shipping them to the site, where they are erected and connected quickly.
"The design of reinforced concrete bridges in seismic regions has changed little since the mid-1970s," said John Stanton, a professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental ...
Chinese herbal extract may help kill off pancreatic cancer cells
2014-07-01
Bethesda, Md. (July 1, 2014) — A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer—the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the U.S.—can be devastating. Due in part to aggressive cell replication and tumor growth, pancreatic cancer progresses quickly and has a low five-year survival rate (less than 5 percent).
GRP78, a protein that protects cells from dying, is more abundant in cancer cells and tissue than in normal organs and is thought to play a role in helping pancreatic cancer cells survive and thrive. Researchers at the University of Minnesota have found triptolide, an extract ...
Tags reveal Chilean devil rays are among ocean's deepest divers
2014-07-01
Thought to dwell mostly near the ocean's surface, Chilean devil rays (Mobula tarapacana) are most often seen gliding through shallow, warm waters. But a new study by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and international colleagues reveals that these large and majestic creatures are actually among the deepest-diving ocean animals.
"So little is known about these rays," said Simon Thorrold, a biologist at WHOI and one of the authors of the paper, published July 1, 2014, in the journal Nature Communications. "We thought they probably travelled long ...
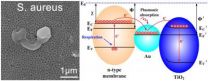
Bringing the bling to antibacterials
2014-07-01
WASHINGTON D.C., July 1, 2014 – Bacteria love to colonize surfaces inside your body, but they have a hard time getting past your rugged, salty skin. Surgeries to implant medical devices often give such bacteria the opportunity needed to gain entry into the body cavity, allowing the implants themselves to act then as an ideal growing surface for biofilms.
A group of researchers at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics in the Chinese Academy of Sciences are looking to combat these dangerous sub-dermal infections by upgrading your new hip or kneecap in a fashion appreciated ...
Efforts to cut unnecessary blood testing bring major decreases in health care spending
2014-07-01
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center used two relatively simple tactics to significantly reduce the number of unnecessary blood tests to assess symptoms of heart attack and chest pain and to achieve a large decrease in patient charges.
The team provided information and education to physicians about proven testing guidelines and made changes to the computerized provider order entry system at the medical center, part of the Johns Hopkins Health System. The guidelines call for more limited use of blood tests for so-called cardiac biomarkers. A year after implementation, ...
Separating finely mixed oil and water
2014-07-01
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Whenever there is a major spill of oil into water, the two tend to mix into a suspension of tiny droplets, called an emulsion, that is extremely hard to separate — and that can cause severe damage to ecosystems. But MIT researchers have discovered a new, inexpensive way of getting the two fluids apart again.
Their newly developed membrane could be manufactured at industrial scale, and could process large quantities of the finely mixed materials back into pure oil and water. The process is described in the journal Scientific Reports by MIT professor Kripa ...
Mayo Clinic researchers reveal treasure trove of genes key to kidney cancer
2014-07-01
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — A genomic analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common form of kidney cancer, from 72 patients has uncovered 31 genes that are key to development, growth and spread of the cancer, say researchers from Mayo Clinic in Florida. Eight of these genes had not been previously linked to kidney cancer, and six other genes were never known to be involved in any form of cancer.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
Their study, in the journal Oncotarget, is the most extensive analysis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Cellular gates for sodium and calcium controlled by common element of ancient originFind likely to affect drug development