(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. – Could playing video games help people understand and address global sustainability issues such as pollution, drought or climate change? At least two researchers believe so, outlining their argument in a concept paper published in the journal First Monday.
Video games have the potential to educate the public and encourage development of creative solutions to social, economic and environmental problems, said Oregon State University's Shawna Kelly, one of the two authors of the article.
"Video games encourage creative and strategic thinking, which could help people make sense of complex problems," said Kelly, who teaches new media communications in the School of Arts and Communication at Oregon State's College of Liberal Arts.
"Entertainment has always been a space for exposing people to new ideas. Using video games, it's possible to introduce sustainability concepts to the mass public in a way that's not pedantic, that's not educational," Kelly said. "Instead, it could be fun and it could be challenging."
Kelly wrote the paper with Bonnie Nardi, an anthropologist with University of California, Irvine's Department of Informatics, who studies sustainability, collapse-preparedness and information technology.
Kelly and Nardi identified four key areas in which video games could support sustainable practices. The areas are:
Shift away from growth as the end goal of a game. Uncontrollable growth is unsustainable and asks little of players' imaginations.
Emphasize scavenging instead of combat to collect resources. Encourage players to interact with their environment in creative ways instead of simply looking for targets.
Offer complex avenues for social interaction. Move beyond "us versus them" and focus on other types of social collaborations.
Encourage strategizing with resources such as scenarios that incorporate long-term consequences and interdependencies of resource use.
Some video games already are using some of the elements Kelly and Nardi recommend. Economics-based games such as "EVE Online" challenge players to strategize between their short-term personal resource demands and the long-term needs of a larger group of players, their corporation. "DayZ" is a combat simulation game that requires players to scavenge for resources and work with other players, deciding on their own which players are friends and which are enemies.
Those are the kinds of game mechanics that make video games fun and challenging, but those mechanics also could be used to encourage players to think about real problems related to sustainability, Kelly said.
The culture of video gaming rewards people for solving problems and coming up with unique solutions. There is a common interest and connection among players, and knowledge is easily shared via game-specific wikis, message boards, instant messaging and more, Kelly pointed out.
"There's a huge set of people out there who love to problem-solve," she said. "Why not harness that power that is already there?"
INFORMATION:
Video games could provide venue for exploring sustainability concepts
2014-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Studies: Addiction starts with an overcorrection in the brain
2014-07-01
The National Institutes of Health has turned to neuroscientists at the nation's most "Stone Cold Sober" university for help finding ways to treat drug and alcohol addiction.
Brigham Young University professor Scott Steffensen and his collaborators have published three new scientific papers that detail the brain mechanisms involved with addictive substances. And the NIH thinks Steffensen's on the right track, as evidenced by a $2-million grant that will help fund projects in his BYU lab for the next five years.
"Addiction is a brain disease that could be treated like ...
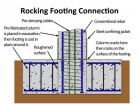
New bridge design improves earthquake resistance, reduces damage and speeds construction
2014-07-01
SEATTLE, Wash. - Researchers have developed a new design for the framework of columns and beams that support bridges, called "bents," to improve performance for better resistance to earthquakes, less damage and faster on-site construction.
The faster construction is achieved by pre-fabricating the columns and beams off-site and shipping them to the site, where they are erected and connected quickly.
"The design of reinforced concrete bridges in seismic regions has changed little since the mid-1970s," said John Stanton, a professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental ...
Chinese herbal extract may help kill off pancreatic cancer cells
2014-07-01
Bethesda, Md. (July 1, 2014) — A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer—the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the U.S.—can be devastating. Due in part to aggressive cell replication and tumor growth, pancreatic cancer progresses quickly and has a low five-year survival rate (less than 5 percent).
GRP78, a protein that protects cells from dying, is more abundant in cancer cells and tissue than in normal organs and is thought to play a role in helping pancreatic cancer cells survive and thrive. Researchers at the University of Minnesota have found triptolide, an extract ...
Tags reveal Chilean devil rays are among ocean's deepest divers
2014-07-01
Thought to dwell mostly near the ocean's surface, Chilean devil rays (Mobula tarapacana) are most often seen gliding through shallow, warm waters. But a new study by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and international colleagues reveals that these large and majestic creatures are actually among the deepest-diving ocean animals.
"So little is known about these rays," said Simon Thorrold, a biologist at WHOI and one of the authors of the paper, published July 1, 2014, in the journal Nature Communications. "We thought they probably travelled long ...
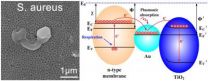
Bringing the bling to antibacterials
2014-07-01
WASHINGTON D.C., July 1, 2014 – Bacteria love to colonize surfaces inside your body, but they have a hard time getting past your rugged, salty skin. Surgeries to implant medical devices often give such bacteria the opportunity needed to gain entry into the body cavity, allowing the implants themselves to act then as an ideal growing surface for biofilms.
A group of researchers at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics in the Chinese Academy of Sciences are looking to combat these dangerous sub-dermal infections by upgrading your new hip or kneecap in a fashion appreciated ...
Efforts to cut unnecessary blood testing bring major decreases in health care spending
2014-07-01
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center used two relatively simple tactics to significantly reduce the number of unnecessary blood tests to assess symptoms of heart attack and chest pain and to achieve a large decrease in patient charges.
The team provided information and education to physicians about proven testing guidelines and made changes to the computerized provider order entry system at the medical center, part of the Johns Hopkins Health System. The guidelines call for more limited use of blood tests for so-called cardiac biomarkers. A year after implementation, ...
Separating finely mixed oil and water
2014-07-01
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Whenever there is a major spill of oil into water, the two tend to mix into a suspension of tiny droplets, called an emulsion, that is extremely hard to separate — and that can cause severe damage to ecosystems. But MIT researchers have discovered a new, inexpensive way of getting the two fluids apart again.
Their newly developed membrane could be manufactured at industrial scale, and could process large quantities of the finely mixed materials back into pure oil and water. The process is described in the journal Scientific Reports by MIT professor Kripa ...
Mayo Clinic researchers reveal treasure trove of genes key to kidney cancer
2014-07-01
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — A genomic analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common form of kidney cancer, from 72 patients has uncovered 31 genes that are key to development, growth and spread of the cancer, say researchers from Mayo Clinic in Florida. Eight of these genes had not been previously linked to kidney cancer, and six other genes were never known to be involved in any form of cancer.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
Their study, in the journal Oncotarget, is the most extensive analysis ...
Alcohol use disorders linked to decreased 'work trajectory'
2014-07-01
July 1, 2014 - John D. Meyer, MD, MPH, of Icahn-Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, and Miriam Mutambudzi, PhD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, studied the relationship between occupation and AUDs in workers followed up from early adulthood to middle age. The study focused on the "substantive complexity" of work as an indicator of work trajectory—whether individuals were progressing in their careers in terms of factors such as decision latitude and expanded work abilities.
Based on factors such as drinking more than intended or unsuccessful ...
NIH study reveals gene critical to the early development of cilia
2014-07-01
Researchers at the National Eye Institute (NEI) have described the functions of a gene responsible for anchoring cilia – sensory hair-like extensions present on almost every cell of the body. They show in a mouse model that without the gene Cc2d2a, cilia throughout the body failed to grow, and the mice died during the embryonic stage. The finding adds to an expanding body of knowledge about ciliopathies, a class of genetic disorders that result from defects in the structure or function of cilia. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
The findings are published ...