(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – After a concussion, teens who are sensitive to light or noise may be more likely to also have emotional symptoms such as anxiety, according to a study released today that will be presented at The Sports Concussion Conference in Chicago, July 11 to 13, 2014, hosted by the American Academy of Neurology, the world's leading authority on diagnosing and managing sports concussion. The conference will feature the latest scientific advances in diagnosing and treating sports concussion from leading experts in the field.
The symptoms after a concussion can vary widely from person to person. Symptoms can include physical, emotional and cognitive difficulties.
"While most people recover from a concussion within a week, a number of factors affect people's recovery, and studies have shown that teenage athletes may take up to seven to 10 days longer to recover than older athletes," said study author Lisa M. Koehl, MS, and Dong (Dan) Y. Han, PsyD, of the University of Kentucky in Lexington.
The study involved 37 athletes age 12 to 17 who had persisting symptoms for an average of 37 days following a concussion. Participants were excluded if they had a previous history of psychological issues. One group of 22 teens had emotional symptoms such as irritability, aggression, anxiety, depression, apathy, frequent mood changes or excessive emotional reactions after the concussion. The second group of 15 teens did not have emotional symptoms. There were no differences between the two groups in factors such as what percentage experienced loss of consciousness or amnesia, indicating that the groups were likely comparable in the level of severity of concussion.
The study found that of the 22 teens who had emotional symptoms, five teens (23 percent) were sensitive to light while three teens (14 percent) were sensitive to noise. In comparison, of the 15 teens without emotional symptoms only two teens (13 percent) were sensitive to light and no teens were sensitive to noise.
The number of concussions experienced and whether teens also had headaches or nausea were not related to whether they also had emotional symptoms. Researchers also found that having a family history of psychiatric problems did not make teens any more or less likely to have emotional symptoms after a concussion.
Teens who had anxiety were 55 percent more likely to self-report attention difficulties than those without anxiety, while teens with irritability/aggression were 35 percent more likely to self-report problems with attention than teens without irritability. The authors noted that the findings are preliminary with small samples and stressed the importance of replicating this study with a larger sample size.
"Identifying factors such as these that may exacerbate issues teens experience after concussion may help in planning for the appropriate treatment and in making decisions about when to return to play and what accommodations are needed at school for these athletes," Koehl and Han said.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the American College of Sports Medicine Research Foundation.
Learn more about concussion at http://www.aan.com/concussion.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of 28,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Rachel Seroka, rseroka@aan.com, (612) 928-6129
Michelle Uher, muher@aan.com, (612) 928-6120
After a concussion, which teens will have emotional symptoms?
2014-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
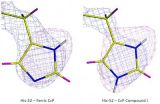
Neutron crystallography solves long-standing biological mystery
2014-07-10
The controversy centres around a family of enzymes known as heme enzymes, due to the presence of a heme group in their active site. At the centre of the heme cofactor is an iron (Fe) atom, which becomes oxidised (ferryl) when a reacting heme is in an intermediate state called Compound I. The question that has remained unanswered for decades is whether this oxidation involves just an oxygen atom (O), or a hydroxyl group (OH). Resolving this fundamental question has implications for understanding oxidative processes within living cells, which is critically important for drug ...
Astronomers find 7 dwarf galaxies with new telescope
2014-07-10
Meet the seven new dwarf galaxies.
Yale University astronomers, using a new type of telescope made by stitching together telephoto lenses, recently discovered seven celestial surprises while probing a nearby spiral galaxy. The previously unseen galaxies may yield important insights into dark matter and galaxy evolution, while possibly signaling the discovery of a new class of objects in space.
For now, scientists know they have found a septuplet of new galaxies that were previously overlooked because of their diffuse nature: The ghostly galaxies emerged from the night ...
Study provides new approach to forecast hurricane intensity
2014-07-10
VIDEO:
This is the one-of-a-kind, Alfred C. Glassell, Jr., SUSTAIN research facility at the UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, where Haus and colleagues will conduct further studies on...
Click here for more information.
MIAMI – New research from University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science suggests that physical conditions at the air-sea interface, where the ocean and atmosphere meet, is a key component to improve forecast ...
Extinct sea scorpion gets a Yale eye exam, with surprising results
2014-07-10
Poor peepers are a problem, even if you are a big, bad sea scorpion.
One minute, you're an imperious predator, scouring the shallow waters for any prey in sight. The next, thanks to a post-extinction eye exam by Yale University scientists, you're reduced to trolling for weaker, soft-bodied animals you stumble upon at night.
Such is the lot of the giant pterygotid eurypterid, the largest arthropod that ever lived. A new paper by Yale paleontologists, published in the journal Biology Letters, dramatically re-interprets the creature's habits, capabilities, and ecological ...
Despite setback, 'Mississippi Baby' represents significant breakthrough in effort to end AIDS
2014-07-10
Washington, D.C.—July 10, 2014—In response to today's announcement that the "Mississippi Baby," believed to have been functionally cured of HIV, has now been found to have detectable levels of the virus, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF) expresses disappointment in this setback but remains hopeful that the scientific breakthrough that allowed the child's HIV levels to remain undetectable for more than two years will continue to help researchers understand how to control HIV and ultimately develop a cure.
"Although we had high hopes that the child ...
Hubble spots spiral bridge of young stars linking two ancient galaxies
2014-07-10
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed an unusual structure 100,000 light years long, which resembles a corkscrew-shaped string of pearls and winds around the cores of two colliding galaxies.
The unique structure of the star spiral may yield new insights into the formation of stellar superclusters that result from merging galaxies and gas dynamics in this rarely seen process.
"We were surprised to find this stunning morphology. We've long known that the 'beads on a string' phenomenon is seen in the arms of spiral galaxies and in tidal bridges between interacting ...
Active shooter training increases comfort level of emergency responders
2014-07-10
(Boston) – Emergency Medical Service (EMS) responders felt better prepared to respond to an active shooter incident after receiving focused tactical training according to a new study in the journal Prehospital and Disaster Medicine. This is the first study to specifically examine the EMS provider comfort level with respect to entering a scene where a shooter has not yet been neutralized or working with law enforcement personnel during that response.
Incidents such as the Columbine High School shooting, the Virginia Tech campus shooting, the 2009 Fort Hood shooting, the ...
Scorpions are master architects, according to new research from Ben-Gurion University
2014-07-10
BEER-SHEVA, Israel – Ben-Gurion University of the Negev scientists have discovered that scorpions create a platform in their burrows where they warm up before the evening hunt.
As ectothermic animals, scorpions rely on energy from the environment to regulate
their internal temperature. The researchers believe that this platform provides a safe, warm spot for the scorpions to increase their body temperature before they leave their hiding places to forage at night.
After trapping the wild large-clawed scorpions (Scorpio maurus palmatus) in Israel's Negev desert the ...
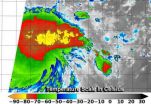
NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite sees power within newborn Tropical Depression 09W
2014-07-10
As the Northwestern Pacific is bidding goodbye to Tropical Cyclone Neoguri, another tropical depression has formed. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Depression 09W (TD09W) and captured infrared data on the storm indicating some powerful thunderstorms within.
Because TD09W is close to land areas, watches are already in effect. On July 10, a tropical storm watch is in force for Guam, Rota, Tinian and Saipan.
Tropical depression 09W was formerly known as low pressure System 92W. VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken July 10 at ...
Scripps Florida scientists shed new light on nerve cell growth
2014-07-10
JUPITER, FL, July 10, 2014 – Amidst the astounding complexity of the billions of nerve cells and trillions of synaptic connections in the brain, how do nerve cells decide how far to grow or how many connections to build? How do they coordinate these events within the developing brain?
In a new study, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shed new light on these complex processes, showing that a particular protein plays a far more sophisticated role in neuron development than previously thought.
The study, published in the journal ...