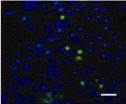
(Press-News.org) The main pathological changes of Alzheimer's disease (AD) include amyloid-beta protein-induced hippocampal neuronal injury and neurite outgrowth impairment. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway are the important signaling pathways respectively responsible for regulating synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. In view of the fact that ginsenoside Rb1 exhibits anti-aging and anti-dementia effects, Prof. Qionglan Yuan and her team, Department of Anatomy & Neurobiology, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China performed a study, in which ginsenoside Rb1 was used, and found that ginsenoside Rb1 promoted hippocampal neuronal neurite outgrowth and protected against neurotoxicity induced by amlyloid-beta (23-25) via a mechanism involving Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling. Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 9, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on hippocampal neuronal injury and neurite outgrowth," by Juan Liu, Jing He, Liang Huang, Ling Dou, Shuang Wu, Qionglan Yuan (Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China)
Liu J, He J, Huang L, Dou L, Wu S, Yuan QL. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on hippocampal neuronal injury and neurite outgrowth. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(9):943-950.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Signaling pathway for ginsenoside Rb1 promoting hippocampal neuronal neurite outgrowth
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The ADC does not reflect cytotoxic edema on the uninjured side after TBI
2014-07-15
It is currently difficult to treat traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the clinic. There are abundant neural network connections and humoral regulation mechanisms between the cerebral hemispheres. Brain tissue on the uninjured side after TBI may also undergo abnormal changes, but these changes remain poorly understood. Hong Lu and her team, Affiliated Haikou Hospital, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, in China performed a study to investigate whether apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements can reflect cytotoxic edema on the uninjured side using ...
Protective effect of α-synuclein knockdown on dopaminergic neurons
2014-07-15
The over-expression of α-synuclein is a major factor in the death of dopaminergic neurons in a methamphetamine-induced model of Parkinson's disease (PD). Dr. Huijun Wang, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, China and his team injected α-synuclein-shRNA lentivirus stereotaxically into the right striatum of experimental rats to inhibit α-synuclein mRNA and protein expression. Results showed that after α-synuclein knockdown, the depression manifestations of PD rats were reduced, striatal dopamine and tyrosine hydroxylase levels ...
Shanghai scientists challenge classical phenomenon that water always completely wets water
2014-07-15
The molecular scale behavior of water at a solid/liquid interface holds fundamental significance in a diverse set of technical and scientific contexts, ranging from the efficiency of oil mining to the activity of biological molecules. Recently, it has become recognized that both the physical interactions and the surface morphology have significant impact on the behavior of interfacial water, including the water structures and wetting properties of the surface.
In a new review, Chunlei Wang, Yizhou Yang and Haiping Fang of the Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics report ...
SWI assesses signal strength in different brain regions after acute hemorrhagic anemia
2014-07-15
Acute hemorrhagic anemia can decrease blood flow and oxygen supply to brain, and affect its physiological function. Detecting changes in brain function in patients with acute hemorrhagic anemia is helpful for preventing neurological complications and evaluating therapeutic effects. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) imaging is a novel, non-invasive method for detecting changes in cerebral oxygen levels that may provide more detailed information regarding cerebral blood flow in patients with hemorrhage. Dr. Jun Xia, Second People's Hospital of Shenzhen City, First Affiliated ...
Taking B vitamins won't prevent Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-15
Taking B vitamins doesn't slow mental decline as we age, nor is it likely to prevent Alzheimer's disease, conclude Oxford University researchers who have assembled all the best clinical trial data involving 22,000 people to offer a final answer on this debate.
High levels in the blood of a compound called homocysteine have been found in people with Alzheimer's disease, and people with higher levels of homocysteine have been shown to be at increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. Taking folic acid and vitamin B-12 are known to lower levels of homocysteine in the body, so ...
How strongly does tissue decelerate the therapeutic heavy ion beam?
2014-07-15
Irradiation with heavy ions is suitable in particular for patients suffering from cancer with tumours which are difficult to access, for example in the brain. These particles hardly damage the penetrated tissue, but can be used in such a way that they deliver their maximum energy only directly at the target: the tumour. Research in this relatively new therapy method is focussed again and again on the exact dosing: how must the radiation parameters be set in order to destroy the cancerous cells "on the spot" with as low a damage as possible to the surrounding tissue? The ...
New hope for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-15
Montreal, July 15 2014 - Judes Poirier, PhD, C.Q., from the Douglas Mental Health Institute and McGill University in Montréal (Canada) and his team have discovered that a relatively frequent genetic variant actually conveys significant protection against the common form of Alzheimer's disease and can delay the onset of the disease by as much as 4 years. This discovery opens new avenues for treatment against this devastating disease.
Dr. Poirier announced his findings as the annual Alzheimer's Association International Conference was taking place in Copenhagen. This large-scale ...
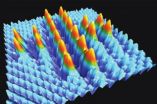
Smallest Swiss cross -- Made of 20 single atoms
2014-07-15
The manipulation of atoms has reached a new level: Together with teams from Finland and Japan, physicists from the University of Basel were able to place 20 single atoms on a fully insulated surface at room temperature to form the smallest "Swiss cross", thus taking a big step towards next generation atomic-scale storage devices. The academic journal Nature Communications has published their results.
Ever since the 1990s, physicists have been able to directly control surface structures by moving and positioning single atoms to certain atomic sites. A number of atomic ...
Cholesterol activates signaling pathway that promotes cancer
2014-07-15
Everyone knows that cholesterol, at least the bad kind, can cause heart disease and hardening of the arteries. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago describe a new role for cholesterol in the activation of a cellular signaling pathway that has been linked to cancer.
The finding is reported in Nature Communications.
Cells employ thousands of signaling pathways to conduct their functions. Canonical Wnt signaling is a pathway that promotes cell growth and division and is most active in embryonic cells during development. Overactivity of this signaling ...
Researchers assess emergency radiology response after Boston Marathon bombings
2014-07-15
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An after-action review of the Brigham and Women's Hospital emergency radiology response to the Boston Marathon bombings highlights the crucial role medical imaging plays in emergency situations and ways in which radiology departments can improve their preparedness for mass casualty events. The new study is published online in the journal Radiology.
"It's important to analyze our response to events like the Boston Marathon bombing to identify opportunities for improvement in our institutional emergency operations plan," said senior author Aaron Sodickson ...