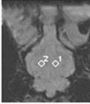
(Press-News.org) Acute hemorrhagic anemia can decrease blood flow and oxygen supply to brain, and affect its physiological function. Detecting changes in brain function in patients with acute hemorrhagic anemia is helpful for preventing neurological complications and evaluating therapeutic effects. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) imaging is a novel, non-invasive method for detecting changes in cerebral oxygen levels that may provide more detailed information regarding cerebral blood flow in patients with hemorrhage. Dr. Jun Xia, Second People's Hospital of Shenzhen City, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, China and his team found that the SWI signals from the frontal cortex, temporal lobe, and thalamus after the second, third, fourth and fifth bloodletting procedures were significantly lower compared with the corresponding control (pre-bleed) values and that the contrast between cerebral gray and white matter was higher after bloodletting (particularly after the fourth and fifth procedures) than beforehand. These results provide the information regarding pathophysiological changes of the brain after acute hemorrphagic anemia. These findings were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 9, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " Susceptibility-weighted imaging is suitable for evaluating signal strength in different brain regions of a rabbit model of acute hemorrhagic anemia," by Jun Xia1, Ni Xie2, Anyu Yin1, Guozhao Teng3, Fan Lin1, Yi Lei1 (1 Department of Radiology, Second People's Hospital of Shenzhen City, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China; 2 Biobank, Second People's Hospital of Shenzhen City, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China; 3 Medical Record and Statistics Room, Second People's Hospital of Shenzhen City, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China)
Xia J, Xie N, Yin AY, Teng GZ, Lin F, Lei Y. Susceptibility-weighted imaging is suitable for evaluating signal strength in different brain regions of a rabbit model of acute hemorrhagic anemia. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(9):990-992.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
SWI assesses signal strength in different brain regions after acute hemorrhagic anemia
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Taking B vitamins won't prevent Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-15
Taking B vitamins doesn't slow mental decline as we age, nor is it likely to prevent Alzheimer's disease, conclude Oxford University researchers who have assembled all the best clinical trial data involving 22,000 people to offer a final answer on this debate.
High levels in the blood of a compound called homocysteine have been found in people with Alzheimer's disease, and people with higher levels of homocysteine have been shown to be at increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. Taking folic acid and vitamin B-12 are known to lower levels of homocysteine in the body, so ...
How strongly does tissue decelerate the therapeutic heavy ion beam?
2014-07-15
Irradiation with heavy ions is suitable in particular for patients suffering from cancer with tumours which are difficult to access, for example in the brain. These particles hardly damage the penetrated tissue, but can be used in such a way that they deliver their maximum energy only directly at the target: the tumour. Research in this relatively new therapy method is focussed again and again on the exact dosing: how must the radiation parameters be set in order to destroy the cancerous cells "on the spot" with as low a damage as possible to the surrounding tissue? The ...
New hope for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-15
Montreal, July 15 2014 - Judes Poirier, PhD, C.Q., from the Douglas Mental Health Institute and McGill University in Montréal (Canada) and his team have discovered that a relatively frequent genetic variant actually conveys significant protection against the common form of Alzheimer's disease and can delay the onset of the disease by as much as 4 years. This discovery opens new avenues for treatment against this devastating disease.
Dr. Poirier announced his findings as the annual Alzheimer's Association International Conference was taking place in Copenhagen. This large-scale ...
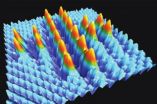
Smallest Swiss cross -- Made of 20 single atoms
2014-07-15
The manipulation of atoms has reached a new level: Together with teams from Finland and Japan, physicists from the University of Basel were able to place 20 single atoms on a fully insulated surface at room temperature to form the smallest "Swiss cross", thus taking a big step towards next generation atomic-scale storage devices. The academic journal Nature Communications has published their results.
Ever since the 1990s, physicists have been able to directly control surface structures by moving and positioning single atoms to certain atomic sites. A number of atomic ...
Cholesterol activates signaling pathway that promotes cancer
2014-07-15
Everyone knows that cholesterol, at least the bad kind, can cause heart disease and hardening of the arteries. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago describe a new role for cholesterol in the activation of a cellular signaling pathway that has been linked to cancer.
The finding is reported in Nature Communications.
Cells employ thousands of signaling pathways to conduct their functions. Canonical Wnt signaling is a pathway that promotes cell growth and division and is most active in embryonic cells during development. Overactivity of this signaling ...
Researchers assess emergency radiology response after Boston Marathon bombings
2014-07-15
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An after-action review of the Brigham and Women's Hospital emergency radiology response to the Boston Marathon bombings highlights the crucial role medical imaging plays in emergency situations and ways in which radiology departments can improve their preparedness for mass casualty events. The new study is published online in the journal Radiology.
"It's important to analyze our response to events like the Boston Marathon bombing to identify opportunities for improvement in our institutional emergency operations plan," said senior author Aaron Sodickson ...
No anti-clotting treatment needed for most kids undergoing spine surgeries
2014-07-15
Blood clots occur so rarely in children undergoing spine operations that most patients require nothing more than vigilant monitoring after surgery and should be spared risky and costly anti-clotting medications, according to a new Johns Hopkins Children's Center study.
Because clotting risk in children is poorly understood, treatment guidelines are largely absent, leaving doctors caring for pediatric patients at a loss on whom to treat and when.
The Johns Hopkins' team findings, published online July 15 in the journal Spine, narrow down the pool of high-risk patients ...
Little too late: Researchers identify disease that may have plagued 700-year-old skeleton
2014-07-15
European researchers have recovered a genome of the bacterium Brucella melitensis from a 700-year-old skeleton found in the ruins of a Medieval Italian village.
Reporting this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, the authors describe using a technique called shotgun metagenomics to sequence DNA from a calcified nodule in the pelvic region of a middle-aged male skeleton excavated from the settlement of Geridu in Sardinia, an island off the coast of Italy. Geridu is thought to have been abandoned in the late 14th century. ...
Study reveals how gardens could help dementia care
2014-07-15
A new study has revealed that gardens in care homes could provide promising therapeutic benefits for patients suffering from dementia.
The research is published in the Journal of the American Medical Directors Association and by critically reviewing the findings from 17 different pieces of research, has found that outdoor spaces can offer environments that promote relaxation, encourage activity and reduce residents' agitation.
Conducted by a team at the University of Exeter Medical School and supported by the National Institute for Health Research Collaboration for ...
Fungicides for crops: Worrying link to fungal drug resistance in UK warns scientists
2014-07-15
Crop spraying on British farms could be aiding a life-threatening fungus suffered by tens of thousand of people in the UK each year.
New research by British and Dutch scientists has found that Aspergillus – a common fungus that attacks the lungs and is found in soil and other organic matter – has become resistant to life - saving drugs in parts of rural Yorkshire.
It's the first time a link has been made in the UK between drug resistance in Aspergillus and fungicide used on crops. Experts warn their findings, now published, are significant and raise serious implications ...