(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study of the anti-sweatshop campaigns of the 1990s reveals which companies are most likely to become targets of anti-corporate activists.
Researchers found that companies tended to attract the attention of labor activists if they were large, had prominent brand images, or had good corporate reputations. When combined, these factors were especially important.
"Companies that had all of these characteristics were nearly guaranteed to be a target of activism," said Tim Bartley, lead author of the study and associate professor of sociology at The Ohio State University.
"Social movements are increasingly pressuring companies to act in socially or environmentally responsible ways, so we wanted to see which companies are most likely to be pushed into this role. Nearly all of the large firms in the apparel industry of the 1990s could be credibly charged with benefiting from sweatshops, but only a small subset were named and shamed by activists."
Bartley said the results suggest that activists chose companies whose visibility in the public and overall good reputation might make them more "shameable" than other firms. "Activists have enthusiastically adopted the strategy of trying to turn corporate strengths into vulnerabilities."
The researchers focused on 151 large U.S. lead firms in the apparel, textile and footwear industries. They looked for evidence of anti-sweatshop activism from 1993 to 2000 that was reported in major trade journals.
Bartley conducted the study with Curtis Child of Brigham Young University. Their results appear online in the journal American Sociological Review and will be published in the August print edition.
One surprise was that globalization didn't seem to play a role in which firms were targeted, Bartley said. Companies that relied heavily on foreign factories were not necessarily more likely to attract activism than firms with less of a global reach.
"Anti-sweatshop activism wasn't as much a backlash against globalization as it has been portrayed," he said.
Bartley said the tactics used by activists against apparel firms in the 1990s are now being used against the electronics industry today. He believes many of the results found here would apply to today's activism.
But will it have an effect on the companies?
In a previous study, Bartley found that anti-sweatshop activism did lead to lower sales for specialized apparel and footwear brands, and that major anti-sweatshop events hurt corporate stock prices, at least for a while.
"Companies are realizing that not every campaign against them will make a dent, but some of them will," Bartley said.
INFORMATION:
Contact: Tim Bartley, 614-688-1364; Bartley.83@osu.edu
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, 614-292-8457; Grabmeier.1@osu.edu
Study finds why some firms are 'named and shamed' by activists
Research looks at anti-sweatshop campaigns of the 1990s
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fundamental chemistry findings could help extend Moore's Law
2014-07-15
Over the years, computer chips have gotten smaller thanks to advances in materials science and manufacturing technologies. This march of progress, the doubling of transistors on a microprocessor roughly every two years, is called Moore's Law. But there's one component of the chip-making process in need of an overhaul if Moore's law is to continue: the chemical mixture called photoresist. Similar to film used in photography, photoresist, also just called resist, is used to lay down the patterns of ever-shrinking lines and features on a chip.
Now, in a bid to continue decreasing ...
Study: Body Dysmorphic Disorder patients have higher risk of personal and appearance-based rejection sensitivity
2014-07-15
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In a recent study, researchers at Rhode Island Hospital found that fear of being rejected because of one's appearance, as well as rejection sensitivity to general interpersonal situations, were significantly elevated in individuals with Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD). These fears, referred to as personal rejection sensitivity and appearance-based rejection sensitivity, can lead to diminished quality of life and poorer mental and overall health. BDD is a common, often severe, and under-recognized body image disorder that affects an estimated 1.7 to 2.4 ...
Prostate cancer in young men -- More frequent and more aggressive?
2014-07-15
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- The number of younger men diagnosed with prostate cancer has increased nearly 6-fold in the last 20 years, and the disease is more likely to be aggressive in these younger men, according to a new analysis from researchers at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Typically, prostate cancer occurs more frequently as men age into their 70s or 80s. Many prostate cancers are slow-growing and many older men diagnosed with early stage prostate cancer will end up dying from causes other than prostate cancer.
But, the researchers found, ...
Rollout strategy for diagnostic test in India may impact TB
2014-07-15
Xpert MTB/RIF, a recently implemented tuberculosis (TB) test, has the potential to control the TB epidemic in India, but only if the current, narrow, implementation strategy is replaced by a more ambitious one that is better funded, also includes the private sector, and better referral networks are developed between public and private sectors, according to new research published in this week's PLOS Medicine. The study by David Dowdy, from Johns Hopkins University, United States, and colleagues is a mathematical model that suggests alternative strategies that include engagement ...
Molecular 'eat now' signal makes cells devour dying neighbors
2014-07-15
A team of researchers has devised a Pac-Man-style power pellet that gets normally mild-mannered cells to gobble up their undesirable neighbors. The development may point the way to therapies that enlist patients' own cells to better fend off infection and even cancer, the researchers say.
A description of the work will be published July 15 in the journal Science Signaling.
"Our goal is to build artificial cells programmed to eat up dangerous junk in the body, which could be anything from bacteria to the amyloid-beta plaques that cause Alzheimer's to the body's own ...
Neurons, brain cancer cells require the same little-known protein for long-term survival
2014-07-15
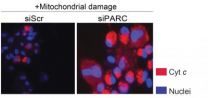
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the UNC School of Medicine have discovered that the protein PARC/CUL9 helps neurons and brain cancer cells override the biochemical mechanisms that lead to cell death in most other cells. In neurons, long-term survival allows for proper brain function as we age. In brain cancer cells, though, long-term survival contributes to tumor growth and the spread of the disease.
These results, published in the journal Science Signaling, not only identify a previously unknown mechanism used by neurons for their much-needed survival, but show that ...
Rollout strategy is key to battling India's TB epidemic, researchers find
2014-07-15
A new study led by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers suggests that getting patients in India quickly evaluated by the right doctors can be just as effective at curbing tuberculosis (TB) as a new, highly accurate screening test.
While ideally all suspected TB cases would be evaluated with the new test, it is primarily being used only on the highest-risk populations and only in public health clinics, partly because of its cost and the complexity of the nation's health care system. This slows diagnosis of a disease that must be caught early, the ...
New assay to spot fake malaria drugs could save thousands of lives
2014-07-15
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Chemists and students in science and engineering at Oregon State University have created a new type of chemical test, or assay, that's inexpensive, simple, and can tell whether or not one of the primary drugs being used to treat malaria is genuine – an enormous and deadly problem in the developing world.
The World Health Organization has estimated that about 200,000 lives a year may be lost due to the use of counterfeit anti-malarial drugs. When commercialized, the new OSU technology may be able to help address that problem by testing drugs for efficacy ...
3-D nanostructure could benefit nanoelectronics, gas storage
2014-07-15
A three-dimensional porous nanostructure would have a balance of strength, toughness and ability to transfer heat that could benefit nanoelectronics, gas storage and composite materials that perform multiple functions, according to engineers at Rice University.
The researchers made this prediction by using computer simulations to create a series of 3-D prototypes with boron nitride, a chemical compound made of boron and nitrogen atoms. Their findings were published online July 14 in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
The 3-D prototypes fuse one-dimensional boron nitride ...
TGen-led study finds likely origin of lung fungus invading Pacific Northwest
2014-07-15
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. - Cryptococcus gattii, a virulent fungus that has invaded the Pacific Northwest is highly adaptive and warrants global "public health vigilance," according to a study by an international team led by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen).
C. gattii, which likely originated in Brazil, is responsible for dozens of deaths in recent years since it was first found in 1999 on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, well outside its usual tropical habitats.
"We identified several genes that may make the outbreak strains more capable of surviving ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
[Press-News.org] Study finds why some firms are 'named and shamed' by activistsResearch looks at anti-sweatshop campaigns of the 1990s