(Press-News.org) Obese women were better able to identify cues that predict monetary rewards than those that predict food rewards, according to a study by Yale School of Medicine researchers and their colleagues in the journal Current Biology. The findings could result in specific behavioral interventions to treat obesity.
"Instead of focusing on reactions to the food itself, such interventions could focus on modifying the way in which obese individuals learn about the environment and about cues predicting food rewards," said lead author Ifat Levy, assistant professor of comparative medicine and neurobiology at Yale School of Medicine.
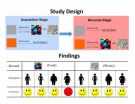
Levy and her colleagues examined how 133 normal-weight and obese men and women learn associations between cues and rewards. Participants saw two colored squares. One color was sometimes followed by an image of a reward; the other color was never followed by a reward. At some point, these contingencies switched—the second color was followed by a reward, while the first was not.
When presented with each color, participants indicated on a 1-9 scale how likely they thought it was that a reward image would appear. These ratings indicated how well they learned the cue-reward associations. Half of the participants did the experiment with food rewards (chocolate or pretzels) and half with money. Participants were informed that at the end of the experiment they would receive all the rewards they saw during the experiment.
The research team found that 18 obese women who performed the task with food rewards were impaired at learning and modifying cue-reward associations. These women rated both color squares as highly predictive of a food reward. Conversely, 16 obese women who performed the task with money rewards were able to both learn the initial associations and to modify them, as were normal-weight women in both the money and food groups. In an unexpected finding, there were no other differences between obese and normal-weight male participants in the study.
"What we observed is not a learning impairment, but rather a food-specific impairment present only in obese female participants," said Levy.
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the study include Zhihao Zhang, Kirk F. Manson, and Daniela Schiller of Mount Sinai.
Citation: Current Biology http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.075
When it comes to food, obese women's learning is impaired
2014-07-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oregon study details brain pathways linking visual function, running
2014-07-16
EUGENE, Ore. – (July 16, 2014) – A new study by researchers at the University of Oregon published today in the journal Neuron describes a brainstem circuit in mice that may help explain how active movement impacts the way the brain processes sensory information.
"Previous studies have examined changes in the visual cortex of mice during running. What was unknown was how do running and vision get linked together in the first place?" said Cristopher Niell, a biology professor in the Institute of Neuroscience and the senior author on the paper "Identification of a Brainstem ...
Efficient structures help build a sustainable future
2014-07-16
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (July 14, 2014) -- When envisioning a new structure, engineers often have to balance design choices against the environmental impact of materials used. It is estimated that 40 to 50 percent of greenhouse gases are produced by the construction industry, according to the California Integrated Waste Management Board. Lessening the impact of construction on the environment is a work in progress.
Researchers at the University of Miami (UM) and the University of Milwaukee School of Engineering are searching for designs and materials that are less harmful ...
A natural way to monitor, and possibly control populations of, stink bugs
2014-07-16
Anyone who has squashed a stink bug knows why they got their name. Although just a nuisance to homeowners, the insects feed on and damage fruits and vegetables, causing significant economic losses for farmers. Now scientists report in ACS' Journal of Natural Products that they've discovered certain stink bug pheromone components and made them artificially in the lab for the first time, and these substances can be used to monitor and manage their populations.
Ashot Khrimian and colleagues explain that the brown marmorated stink bug, also known as Halyomorpha halys, is ...
Abdominal aortic aneurysms: Mayo Clinic surgeon explains who needs screening, treatment
2014-07-16
Rochester, Minn. — An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a potentially life-threatening condition: If the body's major blood vessel ruptures, it can prove deadly. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recently updated its recommendations on screening. Mayo Clinic vascular surgeon Peter Gloviczki, M.D., explains who should be watched for abdominal aortic aneurysms, how they are diagnosed and how surgery, which now includes a less invasive endovascular option, is improving survival rates:
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
What ...
ORNL, UTGSM study compares structures of Huntington's disease protein
2014-07-16
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., July 16, 2014 -- Neutron scattering research at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has revealed clear structural differences in the normal and pathological forms of a protein involved in Huntington's disease.
Huntington's disease, an incurable neurodegenerative disorder, starts as a genetic mutation that leads to an overabundance of "huntingtin" protein fragments, which form clumps in the brain.
Valerie Berthelier of the University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine, who co-led the study published in Biophysical Journal ...
Expert guidance on hand hygiene in healthcare settings
2014-07-16
CHICAGO (July 16, 2014) – Expert guidance released today offers updated evidence reviews and recommendations for hand hygiene in healthcare facilities. The guidance is featured in the August issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology and emphasizes best practices for implementing and optimizing hand hygiene programs to prevent the spread of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The guidance is part of the Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections in Acute Care Hospitals: 2014 Updates produced in a collaborative effort led by the Society ...
Drug's effect on Alzheimer's may depend on severity of disease
2014-07-16
A cancer drug that has shown promise against Alzheimer's disease in mice and has begun early clinical trials has yielded perplexing results in a novel mouse model of AD that mimics the genetics and pathology of the human disease more closely than any other animal model.
The drug, bexarotene, was found to reduce levels of the neurotoxic protein amyloid-beta in experimental mice with late-stage Alzheimer's but to increase levels during early stages of disease.
The finding, by researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, was reported July 16 ...
Research connects pregnancy loss and cardiovascular disease
2014-07-16
The Annals of Family Medicine today published an article detailing research showing that women with a history of pregnancy loss are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease later in adulthood than other women, work completed by physicians in the Center for Primary Care and Prevention (CPCP) at Memorial Hospital of Rhode Island.
The article "Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Postmenopausal Women with Prior Pregnancy Loss: The Women's Health Initiative" stems from the analysis of data from the maternity experiences of a sample of 77,701 women, according to Donna Parker, ...
Dispersant from Deepwater Horizon spill found to persist in the environment
2014-07-16
The 2010 Deepwater Horizon (DWH) spill in the Gulf of Mexico was the largest accidental release of oil into the ocean, with approximately 210 million gallons gushing from the blown out well. In an attempt to prevent vast quantities of oil from fouling beaches and marshes, BP applied 1.84 million gallons of chemical dispersant to oil to oil released in the subsurface and to oil slicks at the sea surface. The dispersant was thought to rapidly degrade in the environment.
A new study by scientists at Haverford College and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has found ...
Researchers develop EHR algorithms to identify undiagnosed hypertension
2014-07-16
CHICAGO – A new study authored by Northwestern Medicine® researchers found that reviewing electronic health records (EHRs) using algorithms can successfully identify patients with previously undiagnosed hypertension, or high blood pressure, with a high rate of accuracy. Of the 1,033 patients that were identified with the EHR algorithms and evaluated, 361 were formally diagnosed with the hypertension and 290 others were diagnosed with related blood pressure conditions such as prehypertension, white-coat hypertension or elevated blood pressure. The study, "A Technology-Based ...