(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. – During the 2011 and 2012 migration seasons, University of Missouri researchers monitored mallard ducks with new remote satellite tracking technology, marking the first time ducks have been tracked closely during the entirety of their migration from Canada to the American Midwest and back. The research revealed that mallards use public and private wetland conservation areas extensively as they travel hundreds of miles across the continent. Dylan Kesler, an assistant professor of fisheries and wildlife in the College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources at MU, says these findings illustrate the importance of maintaining protected wetland areas.
"We have lost nearly 90 percent of wetland areas in Missouri in the last century and 50 percent of wetlands across the country since the early 1800s," Kesler said. "This loss has affected migratory bird populations and migration timing and routes. Our research shows the importance of these wetland areas to maintain healthy populations of migratory birds and other species, especially in an age of budget cuts for government programs protecting these few remaining wetland areas. If we don't maintain these wildlife preserves it will put dozens, if not hundreds, of wildlife species in danger."
For the project, the MU researchers attached small solar-powered tracking devices to the ducks, which transmitted their locations every four hours. Using the new technology, researchers monitored the ducks' progress in real time.
"The tracking devices allowed us to evaluate the ducks' behavior and biology on an exceptionally detailed scale throughout their annual migration cycle," Kesler said. "Previously, we only knew when the birds left and when they arrived and some other small things. Now, we have an extensive data set from which to understand the role of different habitats and other factors in migratory populations. We can begin to understand migration in a way that it has never been understood before."
Lisa Webb, an assistant professor of wildlife in CAFNR and a research ecologist with the U.S. Geological Survey Cooperative Research Unit, says the information gathered will be useful to conservationists looking for ways to ensure healthy duck populations.
"Our research shows private lands enrolled in the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Wetland Reserve Program (WRP) have become a critical component of ducks' migration," Webb said. "The WRP provides landowners with technical and financial support for restoring and maintaining wetland areas that have conservation benefits. Also, this information is important because it shows how decisions and habitat preferences exist throughout the birds' annual life cycles and can help waterfowl biologists better manage for the habitat needs of birds."
Sanctuaries on public areas such as the National Wildlife Refuge System, the largest protected area network in North America with more than 150 million acres of land stretching from Alaska to the Caribbean, also are used frequently by migratory ducks.
This research has now created baseline information for future research into what influences duck migration flight paths, landing site selection and foraging behavior. Kesler also says that scientists now know more about the pre-migratory feeding habits of the ducks. A duck's ability to gain weight before its long flight is an important factor that determines if the duck will make it to the northern breeding grounds and southern wintering stations.
"In addition to their pre-migration habits, our data also revealed that during the non-breeding season, ducks forage food for up to 20 miles away from their roosting areas," Kesler said. "This discovery shows how conservation areas being used by migrating ducks can be improved."
INFORMATION:
The research was a collaboration among the MU College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, the U.S. Geological Survey, Missouri Department of Conservation, the Arkansas Fish and Game Commission, Ducks Unlimited and Ducks Unlimited Canada. The team plans on conducting future research to further determine behavior of migratory ducks. The results were published in Biological Conservation.
Duck migration study reveals importance of conserving wetlands, MU researchers find
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
National Xenopus resource at the MBL innovates new way to study proteins
2014-07-17
WOODS HOLE, Mass.— Proteomics, the study of large groups of proteins, can enhance our understanding of a wide range of organisms, with applications in medicine and developmental biology. Such analyses traditionally require a complete genome for the organism being studied in order to obtain a reference set of proteins. However, many organisms that hold potential for proteomic analysis do not yet have completely sequenced and well-interpreted genomes because the costs, in terms of both time and money, can be prohibitive. Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog, is one such ...
Birdsongs automatically decoded by computer scientists
2014-07-17
Birdsongs automatically decoded by computer scientists
Scientists from Queen Mary University of London have found a successful way of identifying bird sounds from large audio collections, which could be useful for expert and amateur bird-watchers alike.
The analysis used recordings of individual birds and of dawn choruses to identify characteristics of bird sounds. It took advantage of large datasets of sound recordings provided by the British Library Sound Archive, and online sources such as the Dutch archive called Xeno Canto.
Publishing in the journal PeerJ, ...
Study shows how effects of starvation can be passed to future generations
2014-07-17
NEW YORK, NY — Evidence from human famines and animal studies suggests that starvation can affect the health of descendants of famished individuals. But how such an acquired trait might be transmitted from one generation to the next has not been clear. A new study, involving roundworms, shows that starvation induces specific changes in so-called small RNAs and that these changes are inherited through at least three consecutive generations, apparently without any DNA involvement. The study, conducted by Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers, offers ...
How does working part-time versus working full-time affect breastfeeding goals?
2014-07-17
Los Angeles, CA -- Breastfeeding is known to provide significant health benefits for both infants and their mothers. However, while many women intend to breastfeed despite returning to work, a new study finds that mothers who plan to breastfeed for at least three months but return to work full-time are less likely to meet their breastfeeding goals. Conversely, there is no association between women who return to work part-time and failure to reach the breastfeeding goal of at least three months. This new study was published today in the Journal of Human Lactation.
Studying ...
Improving the cost and efficiency of renewable energy storage
2014-07-17
A major challenge in renewable energy is storage. A common approach is a reaction that splits water into oxygen and hydrogen, and uses the hydrogen as a fuel to store energy. The efficiency of 'water splitting' depends heavily on a solid substance called a catalyst. However, only the surface of the catalyst acts on the reaction, while its bulk is inactive. This restricts how much catalyst can be used, and limits the efficiency of water splitting in energy systems. Publishing in Nature Communications, EPFL scientists have developed a new method for maximizing the catalyst's ...
For the sickest emergency patients, death risk is lowest at busiest emergency centers
2014-07-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — When a medical emergency strikes, our gut tells us to get to the nearest hospital quickly. But a new study suggests that busier emergency centers may actually give the best chance of surviving – especially for people suffering life-threatening medical crises.
In fact, the analysis finds that patients admitted to a hospital after an emergency had a 10 percent lower chance of dying in the hospital if they initially went to one of the nation's busiest emergency departments, compared with the least busy.
The risk of dying differed even more for patients ...
Best anticoagulants after orthopedic procedures depends on type of surgery
2014-07-17
Current guidelines do not distinguish between aspirin and more potent blood thinners for protecting against blood clots in patients who undergo major orthopedic operations, leaving the decision up to individual clinicians. A new analysis published today in the Journal of Hospital Medicine provides much-needed information that summarizes existing studies about which medications are best after different types of surgery.
Every year, hundreds of thousands of Americans undergo major orthopedic surgery such as hip and knee replacements and hip fracture repairs. Patients undergoing ...
Findings suggest antivirals underprescribed for patients at risk for flu complications
2014-07-17
Patients likely to benefit the most from antiviral therapy for influenza were prescribed these drugs infrequently during the 2012-2013 influenza season, while antibiotics may have been overprescribed. Published in Clinical Infectious Diseases and now available online, the findings suggest more efforts are needed to educate clinicians about the appropriate use of antivirals and antibiotics in the outpatient setting.
Influenza is a significant cause of mortality and morbidity, resulting in more than 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. each year, on average. While annual ...
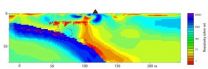
New view of Rainier's volcanic plumbing
2014-07-17
SALT LAKE CITY, July 17, 2014 – By measuring how fast Earth conducts electricity and seismic waves, a University of Utah researcher and colleagues made a detailed picture of Mount Rainier's deep volcanic plumbing and partly molten rock that will erupt again someday.
"This is the most direct image yet capturing the melting process that feeds magma into a crustal reservoir that eventually is tapped for eruptions," says geophysicist Phil Wannamaker, of the university's Energy & Geoscience Institute and Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. "But it does not provide ...
Asthma drugs suppress growth
2014-07-17
Corticosteroid drugs that are given by inhalers to children with asthma may suppress their growth, evidence suggests. Two new systematic reviews published in The Cochrane Library focus on the effects of inhaled corticosteroid drugs (ICS) on growth rates. The authors found children's growth slowed in the first year of treatment, although the effects were minimised by using lower doses.
Inhaled corticosteroids are prescribed as first-line treatments for adults and children with persistent asthma. They are the most effective drugs for controlling asthma and clearly reduce ...