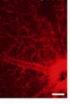
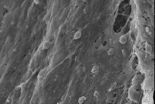
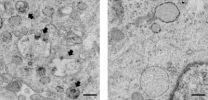
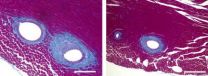
(Press-News.org) There is evidence that astrocytes are closely related to the development and formation of retinal vessels. Dysfunction of astrocytes is an important cause of many retinal vascular disorders and blood-retinal barrier. Huanling Yao, Institute of Neurobiology, College of Life Science, Henan University, China, investigated development of the retinal vascular system and formation of the blood-retinal barrier in mice using immunofluorescence staining, gelatin-ink perfusion, and transmission electron microscopy. The development of the vasculature in the retina followed the rules of "center to periphery" and "superficial layer to deep layers". Its development and maturation were spatially and temporally consistent with the functional performance of retinal neurons and photosensitivity. The blood-retinal barrier gradually became mature via the process of interactions between astrocytes and blood vessel cells. These results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " The development of blood-retinal barrier during the interaction of astrocytes with vascular wall cells," by Huanling Yao, Tianshi Wang, Jiexin Deng, Ding Liu, Xiaofei Li, Jinbo Deng (Institute of Neurobiology, College of Life Science, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan Province, China)
Yao HL, Wang TS, Deng JX, Liu D, Li XF, Deng JB. The development of blood-retinal barrier during the interaction of astrocytes with vascular wall cells. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10):1047-1054.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
The development of blood-retinal barrier during astrocyte/vascular wall cell interaction
2014-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using a novel scaffold to repair spinal cord injury
2014-07-21
Dr. Ning Yuan, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, China and his colleagues, developed a novel neural stem cell scaffold that has two layers: the inner loose layer and the outer compact layer. The loose layer was infiltrated with a large amount of neural stem cells before it was transplanted in vivo. Thus a plenty of neural stem cells can be provided at the target spinal cord site. The loose layer was adhered to the injured side and the compact layer was placed against the lateral side. The compact layer has very small holes, so it can prevent ingrowth of adjacent scar tissue. ...
Using a deacetyl chitin conduit and short-term electrical stimulation for PNI
2014-07-21
Previous studies have demonstrated that deacetyl chitin conduit nerve bridging or electrical stimulation shows therapeutic effect on peripheral nerve injury (PNI). Dr. Peixun Zhang, Peking University People's Hospital, China and his team bridged the injured right rat sciatic nerve using a deacetyl chitin conduit combined with electrical stimulation (0.1 ms, 3 V, 20 Hz, for 1 hour). At 6 and 12 weeks after treatment, nerve conduction velocity, myelinated axon number, fiber diameter, axon diameter and the thickness of the myelin sheath in the stimulation group were better ...
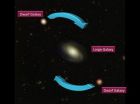
Mysterious dance of dwarfs may force a cosmic rethink
2014-07-21
The discovery that many small galaxies throughout the universe do not 'swarm' around larger ones like bees do but 'dance' in orderly disc-shaped orbits is a challenge to our understanding of how the universe formed and evolved.
The finding, by an international team of astronomers, including Professor Geraint Lewis from the University of Sydney's School of Physics, has just been announced in Nature.
"Early in 2013 we announced our startling discovery that half of the dwarf galaxies surrounding the Andromeda Galaxy are orbiting it in an immense plane" said Professor ...
Study links enzyme to Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-21
Unclogging the body's protein disposal system may improve memory in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), according to a study from scientists at Kyungpook National University in Korea published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
In AD, various biochemical functions of brain cells go awry, leading to progressive neuronal damage and eventual memory loss. One example is the cellular disposal system, called autophagy, which is disrupted in patients with AD, causing the accumulation of toxic protein plaques characteristic of the disease. Jae-sung Bae and colleagues ...
Healing the heart with fat
2014-07-21
Too much dietary fat is bad for the heart, but the right kind of fat keeps the heart healthy, according to a paper published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Unsaturated dietary fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are known to protect against cardiovascular diseases. However, the mechanism and the specific fat metabolites responsible for this protection were unknown.
A group of Japanese scientists now show that mice engineered to produce their own EPA are protected against heart disease and have improved cardiac function. One particular EPA metabolite, ...
When temperatures get cold, newly-discovered process helps fruit flies cope
2014-07-21
Cold-blooded animals cannot regulate their body temperature, so their cells are stressed when facing temperature extremes. Worse still, even at slightly colder temperatures, some biological processes in the cell are slowed down more than others, which should throw the cells' delicate chemical balance out of whack. Yet, those cells manage to keep their biological processes coordinated. Now researchers from the University of Rochester and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory have found out how they do that.
"The production of proteins is a key process in all cells, ...
Scientists successfully generate human platelets using next-generation bioreactor
2014-07-21
Boston, MA – Scientists at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have developed a scalable, next-generation platelet bioreactor to generate fully functional human platelets in vitro. The work is a major biomedical advancement that will help address blood transfusion needs worldwide.
The study is published July 21, 2014 in Blood.
"The ability to generate an alternative source of functional human platelets with virtually no disease transmission represents a paradigm shift in how we collect platelets that may allow us meet the growing need for blood transfusions," said Jonathan ...
Refined biological evolution model
2014-07-21
Models for the evolution of life are now being developed to try and clarify the long term dynamics of an evolving system of species. Specifically, a recent model proposed by Petri Kärenlampi from the University of Eastern Finland in Joensuu accounts for species interactions with various degrees of symmetry, connectivity, and species abundance. This is an improvement on previous, simpler models, which apply random fitness levels to species. The findings published in EPJ E demonstrate that the resulting replicator ecosystems do not appear to be a self-organised critical model, ...
Iodine may alleviate swelling in retinitis pigmentosa patients' retinas
2014-07-21
Boston – Cystoid macular edema (CME) is a common complication of retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a family of retinal diseases in which patients typically lose night and side vision first and then develop impaired central vision. CME can also decrease central vision. Current treatments for CME in RP are not always effective and can lead to adverse results.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Harvard Medical School, and Boston University School of Medicine tested whether the extent of retinal swelling due to CME was inversely related to dietary iodine intake in patients ...
Missing sleep may hurt your memory
2014-07-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Lack of sleep, already considered a public health epidemic, can also lead to errors in memory, finds a new study by researchers at Michigan State University and the University of California, Irvine.
The study, published in the journal Psychological Science, found participants deprived of a night's sleep were more likely to flub the details of a simulated burglary they were shown in a series of images.
Distorted memory can have serious consequences in areas such as criminal justice, where eyewitness misidentifications are thought to be the leading ...