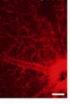
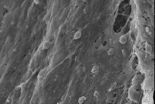
Described novel regulator of a protein inactive in over 50 percent of human tumors
2014-07-21
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) and the University of Barcelona have discovered the interaction between HERC2 proteins with another protein called p53 that is inactivated in more than half of human tumors. The study results were published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Regulation of the activity of p53 by HERC2
The team of José Luis Rosa, at the growth factors and cell differentiation research group at IDIBELL studies the molecular mechanisms of HERC family proteins. These proteins are ubiquitin ligases that regulate the function of other proteins. "In recent years," explained Rosa "it has been shown that alterations in HERC family proteins are associated with various pathologies including ataxia, mental retardation and cancer."
"Under physiological conditions, the role of the p53 protein is to protect from uncontrolled cell growth. Thus, mutations or other mechanisms to inhibit the function of p53, are associated with increased cell proliferation" as the researcher says "as a tumor is formed by uncontrolled cell growth, it is not surprising that an important step in tumor progression would be the inactivation of p53."
P53 protein regulates the expression of genes involved in important cellular processes such as cell proliferation. Its activity is dependent on acquiring a structure of four associated molecules called tetramer. Researchers have found that HERC2 is necessary for the formation of the tetramer of p53 (termed oligomerization process) and thus HERC2 regulates p53 activity under physiological conditions.
HERC2 and cancer
The study suggests that mutations in HERC2 also may be associated with cancer in humans. "In the laboratory we have observed that without HERC2 cells increases proliferation. It's the same effect as if they inactivated p53" says Rosa.
INFORMATION:
Article reference
Cubillos-Rojas M., F. Amair-Pinedo, R. Peiro-Joran, Bartron R., JL Rosa and F. Ventura The E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase Modulates the Activity of HERC2 Tumor Protein p53 by Regulating Its oligomerization. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. April 9, 2014, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M113.527978
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Potential new flu drugs target immune response, not virus
2014-07-21
The seriousness of disease often results from the strength of immune response, rather than with the virus, itself. Turning down that response, rather than attacking the virus, might be a better way to reduce that severity, says Juliet Morrison of the University of Washington, Seattle. She and her collaborators have now taken the first step in doing just that for the H7N9 influenza, and their work has already led to identification of six potential therapeutics for this highly virulent strain. The research is published ahead of print in the Journal of Virology.
"We set ...
More than glitter
2014-07-21
A special class of tiny gold particles can easily slip through cell membranes, making them good candidates to deliver drugs directly to target cells.
A new study from MIT materials scientists reveals that these nanoparticles enter cells by taking advantage of a route normally used in vesicle-vesicle fusion, a crucial process that allows signal transmission between neurons. In the July 21 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe in detail the mechanism by which these nanoparticles are able to fuse with a membrane.
The findings suggest possible strategies ...
Mammals metabolize some pesticides to limit their biomagnification
2014-07-21
The concentrations of many historically used, and now widely banned, pesticides and other toxic chemicals—called legacy contaminants—can become magnified in an animal that eats contaminated food; however, a new Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry study has found that Arctic mammals metabolize some currently used pesticides, preventing such 'biomagnification.'
Researchers who studied the vegetation-caribou-wolf food chain in the Bathurst region of Canada say that currently use pesticides enter the food chain and become concentrated in vegetation, but the evidence shows ...
Examining the causes of a devastating debris flow
2014-07-21
Storm-triggered landslides cause loss of life, property damage, and landscape alterations. For instance, the remnants of Hurricane Camille in 1969 caused 109 deaths in central Virginia, after 600 mm of rain fell in mountainous terrain in 6 hours. More recently, on 8 August 2010, a rainstorm-induced landslide devastated the Chinese county of Zhouqu, causing more than 1000 deaths. A new modeling study by Ren (Geophysical Research Letters) examines the multiple factors, both natural and human caused, that came together to produce this event. The triad of storm-triggered landslides ...
New research links bad diet to loss of smell
2014-07-21
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Could stuffing yourself full of high-fat foods cause you to lose your sense of smell?
A new study from Florida State University neuroscientists says so, and it has researchers taking a closer look at how our diets could impact a whole range of human functions that were not traditionally considered when examining the impact of obesity.
"This opens up a lot of possibilities for obesity research," said Florida State University post-doctoral researcher Nicolas Thiebaud, who led the study examining how high-fat foods impacted smell.
Thiebaud led the ...
Study provides insights into birds' migration routes
2014-07-21
By tracking hybrids between songbird species, investigators have found that migration routes are under genetic control and could be preventing interbreeding. The research, which is published in Ecology Letters, was conducted using geolocators that, like GPS, record the position of a bird and allow its long distance movement to be tracked.
Compared with their parents, hybrids exhibited increased variability in their migratory routes: some used intermediate routes across less suitable areas, while others used the same routes as one parental group on fall migration and the ...
Motoneuron-like cell transplantation and GDNF delivery for repair of SCI
2014-07-21
Adipose-derived stem cells-transdifferentiated motoneurons after transplantation can integrate in the host cord. However, cell survival has been restricted by a lack of ideal environment for nerve cell growth. Taki Tiraihi, Shefa Neuroscience Research Center at Khatam Al-Anbia Hospital, Iran developed rat models of spinal cord injury (SCI) and injected adipose-derived stem cells-transdifferentiated motoneurons into the epicenter, rostral and caudal regions of the impact site and simultaneously transplanted glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)-gelfoam complex ...
The development of blood-retinal barrier during astrocyte/vascular wall cell interaction
2014-07-21
There is evidence that astrocytes are closely related to the development and formation of retinal vessels. Dysfunction of astrocytes is an important cause of many retinal vascular disorders and blood-retinal barrier. Huanling Yao, Institute of Neurobiology, College of Life Science, Henan University, China, investigated development of the retinal vascular system and formation of the blood-retinal barrier in mice using immunofluorescence staining, gelatin-ink perfusion, and transmission electron microscopy. The development of the vasculature in the retina followed the rules ...
Using a novel scaffold to repair spinal cord injury
2014-07-21
Dr. Ning Yuan, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, China and his colleagues, developed a novel neural stem cell scaffold that has two layers: the inner loose layer and the outer compact layer. The loose layer was infiltrated with a large amount of neural stem cells before it was transplanted in vivo. Thus a plenty of neural stem cells can be provided at the target spinal cord site. The loose layer was adhered to the injured side and the compact layer was placed against the lateral side. The compact layer has very small holes, so it can prevent ingrowth of adjacent scar tissue. ...
Using a deacetyl chitin conduit and short-term electrical stimulation for PNI
2014-07-21
Previous studies have demonstrated that deacetyl chitin conduit nerve bridging or electrical stimulation shows therapeutic effect on peripheral nerve injury (PNI). Dr. Peixun Zhang, Peking University People's Hospital, China and his team bridged the injured right rat sciatic nerve using a deacetyl chitin conduit combined with electrical stimulation (0.1 ms, 3 V, 20 Hz, for 1 hour). At 6 and 12 weeks after treatment, nerve conduction velocity, myelinated axon number, fiber diameter, axon diameter and the thickness of the myelin sheath in the stimulation group were better ...