(Press-News.org) Stanford, CA—Eating meat contributes to climate change, due to greenhouse gasses emitted by livestock. New research finds that livestock emissions are on the rise and that beef cattle are responsible for far more greenhouse gas emissions than other types of animals. It is published by Climactic Change.
Carbon dioxide is the most-prevalent gas when it comes to climate change. It is released by vehicles, industry, and forest removal and comprises the greatest portion of greenhouse gas totals. But methane and nitrous oxide are also greenhouse gasses and account for approximately 28 percent of global warming activity.
Methane and nitrous oxide are released, in part, by livestock. Animals release methane as a result of microorganisms that are involved in their digestive processes and nitrous oxide from decomposing manure. These two gasses are responsible for a quarter of these non-carbon dioxide gas emissions and 9 percent of total greenhouse gas emissions overall.
The research team, including Dario Caro, formerly of Carnegie and now at the University of Siena in Italy, and Carnegie's Ken Caldeira, estimated the greenhouse gas emissions related to livestock in 237 countries over a nearly half a century and found that livestock emissions increased by 51 percent over this period.
They found a stark difference between livestock-related emissions in the developing world, which accounts for most of this increase, and that released by developed countries. This is expected to increase further going forward, as demand for meat, dairy products, and eggs is predicted by some scientists to double by 2050. By contrast, developed countries reached maximum livestock emissions in the 1970s and have been in decline since that time.
"The developing world is getting better at reducing greenhouse emissions caused by each animal, but this improvement is not keeping up with the increasing demand for meat," said Caro. "As a result, greenhouse gas emissions from livestock keep going up and up in much of the developing world."
Breaking it down by animal, beef and dairy cattle comprised 74 percent of livestock-related greenhouse gas emissions, 54 percent coming from beef cattle and 17 percent from dairy cattle. Part of this is due to the abundance of cows, but it is also because cattle emit greater quantities of methane and nitrous oxide than other animals. Sheep comprised 9 percent, buffalo 7 percent, pigs 5 percent, and goats 4 percent.
"That tasty hamburger is the real culprit," Caldeira said. "It might be better for the environment if we all became vegetarians, but a lot of improvement could come from eating pork or chicken instead of beef."
INFORMATION:
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
Climate: Meat turns up the heat
2014-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can amyloid plaque in Alzheimer's disease affect remote regions of the brain?
2014-07-21
New Rochelle, NY, July 21, 2014—In Alzheimer's disease, accumulation of amyloid plaque in the brain is believed to play an important role in many characteristic disease symptoms, including memory loss and other mental state changes. But how these plaque deposits affect brain function is not well understood. Important new study results showing that plaque buildup in one area of the brain can negatively affect metabolism in a more distant brain region have been published in Brain Connectivity, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is ...
Increased overall survival for advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer patients is associated with availability of less toxic chemotherapy
2014-07-21
DENVER – A 10-year population-based study shows that increased availability of better systemic chemo- and targeted-therapies for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) coincides with increased usage of these therapies. This in turn leads to a significant increase in overall survival.
Researchers from the British Columbia Cancer Agency, Vancouver, Canada, performed a retrospective chart review of all patients referred to the agency with advanced stage (IIIB or IV) lung cancer and grouped the patients into 4 one-year time frame cohorts; one termed "baseline" ...
ROS1 gene fusions are found in 2.4 percent of Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma
2014-07-21
DENVER -- ROS1 fusion genes were successfully detected independent of gender or smoking history in young East Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma, a histological subgroup in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) diagnostic tests.
In NSCLC treatment algorithms, a personalized therapy approach is now being taken based on the genetic characteristics of the cancer. Patients with specific oncogenic molecular aberrations, for example EGFR mutations and ALK gene fusions, ...
New accurate epigenetic test could eliminate unnecessary repeat biopsies for prostate cancer
2014-07-21
New York, NY -- More than one million prostate biopsies are performed each year in the U.S. alone, including many repeat biopsies for fear of cancer missed. Therefore there is a need to develop diagnostic tests that will help avoid unnecessary repeat biopsies. Two independent trials have now validated the performance of an epigenetic test that could provide physicians with a better tool to help eliminate unnecessary repeat prostate biopsies, report investigators in The Journal of Urology®.
In the previously reported independent MATLOC (Methylation Analysis To Locate Occult ...
Oregon chemists eye improved thin films with metal substitution
2014-07-21
EUGENE, Ore. – (July 21, 2014) – The yield so far is small, but chemists at the University of Oregon have developed a low-energy, solution-based mineral substitution process to make a precursor to transparent thin films that could find use in electronics and alternative energy devices.
A paper describing the approach is highlighted on the cover of the July 21 issue of the journal Inorganic Chemistry, which draws the most citations of research in the inorganic and nuclear chemistry fields. The paper was chosen by the American Chemical Society journal as an ACS Editor's ...
Overcoming barriers to physical activity for African-American women
2014-07-21
AURORA, Colo. (July 21, 2014) - According to the Centers for Disease Control, approximately four out of five black women are overweight or obese and 36 percent meet physical activity objectives as determined by the CDC. That's compared to 50 percent of white women meeting the same objectives.
A study conducted by the Center for African American Health and the University of Colorado School of Medicine's Center for Women's Health Research finds that African American women whose hairstyle is affected by perspiration may avoid physical activity altogether. Prior studies ...
Study offers new clues about the source of racial health disparities
2014-07-21
A first-of-its-kind study by researchers at USC and Loyola Marymount University (LMU) has found evidence that the persistent health disparities across race may, in part, be related to anxiety about being confronted by negative racial stereotypes while receiving healthcare.
Stereotype threat, which is the threat of being judged by or confirming a negative stereotype about a group you belong to, has already been shown to influence the outcome of standardized testing, such as performance on the SAT (the most widely used college admissions exam). For example, when confronted ...
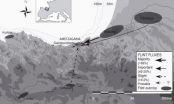
The economic territory of Upper Palaeolithic groups is specified by flint
2014-07-21
This news release is available in Spanish.
Never before had the mobility patterns and management of lithic resources in the Upper Palaeolithic been determined so precisely. The study of flint remains found in the open-air Ametzagaina site in Donostia-San Sebastian has determined the economic territory of the human groups that lived there for about 2,000 years. The paper, Where to and What for? Mobility Patterns and the Management of Lithic Resources by Gravettian Hunter-Gatherers in the Western Pyrenees, has been published in the Journal of Anthropological Research.
The ...
Cost of World Cup may be too high for Brazil
2014-07-21
Brazil's World Cup has been estimated to be the priciest of any yet, with a projected cost of $11.5 billion. Some predictions even claim that the Brazilian government will have spent up to $14 billion on building and renovating 12 stadiums; upgrading federal, state and city infrastructure; and ensuring security.
In a country with many economic and social issues that need to be addressed, such amounts of spending—more than three times the amount spent on the last World Cup—seem irresponsible to Brazilian citizens who are eager to understand the benefits of such spending, ...
Filter bed substrates, plant types recommended for rain gardens
2014-07-21
RALEIGH, NC – Urban stormwater runoff is causing problems for the world's water sources. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency found stormwater runoff to be one of the top 10 causes of compromised environments in rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, bays, and estuaries. The pollutants from urban stormwater runoff can harm fish and wildlife populations, foul drinking water, and make recreational areas unsafe.
Researchers from North Carolina State University are looking to rain gardens as one way to remediate the water quality concerns caused by ...