(Press-News.org) For the first time, Spanish researchers have detected an unknown interaction between microorganisms and salt. When Escherichia coli cells are introduced into a droplet of salt water and is left to dry, bacteria manipulate the sodium chloride crystallisation to create biomineralogical biosaline 3D morphologically complex formations, where they hibernate. Afterwards, simply by rehydrating the material, bacteria are revived. The discovery was made by chance with a home microscope, but it made the cover of the Astrobiology journal and may help to find signs of life on other planets.
The bacterium Escherichia coli is one of the most studied living forms by biologists, but none had to date noticed what this microorganism can do within a simple drop of salt water: create impressive biomineralogical patterns in which it shelters itself when it dries.
"It was a complete surprise, a fully unexpected result, when I introduced E. coli cells into salt water and I realised that the bacteria had the ability to join the salt crystallisation and modulate the development and growth of the sodium chloride crystals," biologist José María Gómez told SINC.
"Thus, in around four hours, in the drop of water that had dried, an impressive tapestry of biosaline patterns was created with complex 3D architecture," added the researcher, who made the discovery with the microscope in his house, although he later confirmed it with the help of his colleagues from the Laboratory of BioMineralogy and Astrobiological Research (LBMARS, University of Valladolid-CSIC), Spain.
Until present, we knew of similar patterns created from saline solutions and isolated proteins, but this is the first report that demonstrates how whole bacterial cells can manage the crystallisation of sodium chloride (NaCl) and generate self-organised biosaline structures of a fractal or dendritic appearance. The study and the striking three-dimensional patterns are on the front cover of this month's 'Astrobiology' edition.
"The most interesting result is that the bacteria enter a state of hibernation inside these desiccated patterns, but they can later be 'revived' simply by rehydration," said Gómez, who highlighted a very important result from an astrobiological point of view: "Given the richness and complexity of these formations, they may be used as biosignatures in the search for life in extremely dry environments outside our own planet, such as the surface of Mars or that of Jupiter's satellite, Europa".
In fact, the LBMARS laboratory participates in the development of the Raman RLS instrument of the ExoMars rover, the mission that the European Space Agency (ESA) will send to the red planet in 2018, and this new finding may help them search for possible biological signs. According to the researcher, "the patterns observed will help calibrate the instrument and test its detection of signs of hibernation or traces of Martian life".
"The challenge we now face is to understand how the bacteria control the crystallisation of NaCl to create these incredible 3D structures and vice-versa, how salt influences this action, as well as studying the structure of these microorganisms that withstand desiccation," said Gómez, who reminds us that a simple curiosity and excitement about science, although it may be with simple means, still allows us to make some interesting discoveries: "This is a tribute to scientists such as the Spaniard Santiago Ramón y Cajal and the Dutch scientist Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who also worked from home with their own microscopes".
INFORMATION:
References
José María Gómez Gómez, Jesús Medina, David Hochberg, Eva Mateo-Martí, Jesús Martínez-Frías, Fernando Rull "Drying Bacterial Biosaline Patterns Capable of Vital Reanimation upon Rehydration: Novel Hibernating Biomineralogical Life Formations". Astrobiology 14 (7): 589-602, 2014. Doi: 10.1089/ast.2014.1162
Bacteria manipulate salt to build shelters to hibernate
2014-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breakthrough laser experiment reveals liquid-like motion of atoms in an ultra-cold cluster
2014-07-25
A new study by researchers from the University of Leicester has furthered our understanding of how tiny nanosystems function, unlocking the potential to create new materials using nanosized 'building blocks'.
The study, which has been published in the prestigious academic journal Physical Review Letters, used a novel laser technique to examine in rich detail the structure and internal atomic motion of a small cluster containing an acetylene molecule and a single helium atom.
The technique excited single clusters and generated rotational wavepackets, which are composed ...
Magnets for fusion energy: A revolutionary manufacturing method developed
2014-07-25
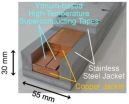
The National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), of the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) in Japan, has achieved an electrical current of 100,000 amperes, which is by far the highest in the world, by using the new idea of assembling the state-of-the-art yttrium-based high-temperature superconducting tapes to fabricate a large-scale magnet conductor.
NIFS is undertaking the development of a high-temperature superconducting coil that is appropriate for the fusion reactor magnet. Using the state-of-the-art yttrium-based high-temperature superconducting tapes ...
Physicists create tool to foresee language destruction impact and thus prevent it
2014-07-25
There have been numerous cases of cultural changes throughout history. Either by imposition or assimilation, cultural traits are transmitted between neighbouring regions and often one replaces the original cultural traits of the other. Physicists Joaquim Fort, from the University of Girona (UdG), and Neus Isern, from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), are experts in modelling these phenomena by adequately representing a reality, as they have demonstrated with their previous projects.
In this occasion, the researchers applied their expertise to the area of language ...
Collecting just the right data
2014-07-25
Much artificial-intelligence research addresses the problem of making predictions based on large data sets. An obvious example is the recommendation engines at retail sites like Amazon and Netflix.
But some types of data are harder to collect than online click histories —information about geological formations thousands of feet underground, for instance. And in other applications — such as trying to predict the path of a storm — there may just not be enough time to crunch all the available data.
Dan Levine, an MIT graduate student in aeronautics and astronautics, and ...
Could age of first period influence development of diseases in older women?
2014-07-25
BOSTON—A novel study shows that the age girls reach puberty is influenced by 'imprinted genes'—a subset of genes whose activity differs depending on which parent contributes the gene. This is the first evidence that imprinted genes can control the rate of development after birth and details of this study were published today in the journal Nature.
Age of the first period, known as menarche, is a marker for the timing of puberty in females. Medical evidence shows that the onset of menses varies between girls, is an inherited trait, and is linked to breast cancer, diabetes ...
It takes two to court
2014-07-25
KANSAS CITY, MO—Researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research have identified the functions of two classes of pheromone receptors, and found pheromones crucial to triggering the mating process in mice.
They found one class of receptors helps a male mouse detect pheromones that indicate when a female is present. The other class of receptors lets him know if the female mouse is ovulating and ready to mate. Both sets of pheromones are critical to trigger mating. Stowers' researchers believe mice developed this system through evolution to maximize the chance of ...
Experiences at every stage of life contribute to cognitive abilities in old age
2014-07-25
Early life experiences, such as childhood socioeconomic status and literacy, may have greater influence on the risk of cognitive impairment late in life than such demographic characteristics as race and ethnicity, a large study by researchers with the UC Davis Alzheimer's Disease Center and the University of Victoria, Canada, has found.
"Declining cognitive function in older adults is a major personal and public health concern," said Bruce Reed, professor of neurology and associate director of the UC Davis Alzheimer's Disease Center.
"But not all people lose cognitive ...
Why do men prefer nice women?
2014-07-25
People's emotional reactions and desires in initial romantic encounters determine the fate of a potential relationship. Responsiveness may be one of those initial "sparks" necessary to fuel sexual desire and land a second date. However, it may not be a desirable trait for both men and women on a first date. Does responsiveness increase sexual desire in the other person? Do men perceive responsive women as more attractive, and does the same hold true for women's perceptions of men? A study published in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin seeks to answer those questions. ...
Heart attack patients could be treated more quickly after Manchester research
2014-07-25
Heart attack patients could be treated more quickly after Manchester research
Clinical judgement, combined with an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood test on arrival, is effective in reducing unnecessary hospital admissions for chest pain, a new study shows.
The findings of a research group in Manchester, published in the Emergency Medicine Journal, could potentially make a huge difference to a large number of patients.
Chest pain is the most common reason for emergency hospital admission. In Manchester, the incidence of premature death due to heart disease and stroke ...
Test increases odds of correct surgery for thyroid cancer patients
2014-07-25
PITTSBURGH -- The routine use of a molecular testing panel developed at UPMC greatly increases the likelihood of performing the correct initial surgery for patients with thyroid nodules and cancer, report researchers from the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI), partner with UPMC CancerCenter.
The test, available at the UPMC/UPCI Multidisciplinary Thyroid Center and other diagnostic testing agencies, improved the chances of patients getting the correct initial surgery by 30 percent, according to the study published this month in the Annals of Surgery.
"Before ...