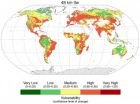
(Press-News.org) New research has identified areas of the Earth that are high priorities for conservation in the face of climate change.
Europe is particularly vulnerable, as it has the lowest fraction of its land area, only four per cent, of any continent in 'refugia' – areas of biological diversity that support many species where natural environmental conditions remain relatively constant during times of great environmental change. The refugia that do exist in Europe are mostly in Scandinavia and Scotland.
The biggest refugia are in the Amazon, the Congo basin, the boreal forests of Russia, the Artic and the Australian outback.
The study identifies such climate change refugia based on the amount of natural habitat present and the risk that regions shift to a different type of natural vegetation due to climate change – a phenomenon known as 'biome shift'.
The research was led by University of Southampton biologist Dr Felix Eigenbrod working in collaboration with Dr Patrick Gonzalez, Climate Change Scientist at the U.S. National Park Service, and two other Southampton scientists – Dr Jadu Dash and Dr Ilse Steyl. They found that 10 to 28 per cent of the world is located in potential refugia or areas less vulnerable to future climate change and biome shift.
In addition, only one to two per cent of the world's vegetated area, however, is classified as refugia and protected by a national park or other protected area.
The results suggest that, in regions where relatively large, intact wilderness areas remain (for example, Africa, Australia and South America), conservation of the remaining large-scale refugia is the priority. In human-dominated landscapes, (most of Europe, much of North America and Southeast Asia), focusing on finer scale refugia is a priority because large-scale wilderness refugia simply no longer exist.
Dr Felix Eigenbrod: says: "Our research will help governments to better understand where to invest resources to safeguard wild plants and animals in the face of the combined threats of habitat destruction and climate change."
The findings, published in the journal Global Change Biology, are based on spatial and statistical analyses of historical climate data, satellite data on current vegetation, and projections of potential vegetation under climate change.
Past field research has shown that human climate change has already shifted vegetation at the biome level upslope and towards the Poles or the Equator. A biome is the highest level of ecological system – rainforests, woodlands, grasslands, temperate forest, alpine and tundra – so a change in climate that can shift the location of a biome is a very substantial force. When a biome shifts, plants and wildlife that cannot cope may shift or disappear locally. When a road, town, or clear-cutting then destroys parts of the natural habitat, the ecosystem becomes even more vulnerable.
INFORMATION: END
Study finds Europe's habitat and wildlife is vulnerable to climate change
2014-07-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why do dogs smell each other's behinds? Chemical communication explained (video)
2014-07-28
WASHINGTON, July 28, 2014 — Here at Reactions, we ask the tough questions to get to the bottom of the biggest scientific quandaries. In that spirit, this week's video explains why dogs sniff each other's butts. It's a somewhat silly question with a surprisingly complex answer. This behavior is just one of many interesting forms of chemical communication in the animal kingdom. Find out more at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PZlJ8XfwiNg.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The ...
Refrigerator magnets
2014-07-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The magnets cluttering the face of your refrigerator may one day be used as cooling agents, according to a new theory formulated by MIT researchers.
The theory describes the motion of magnons — quasi-particles in magnets that are collective rotations of magnetic moments, or "spins." In addition to the magnetic moments, magnons also conduct heat; from their equations, the MIT researchers found that when exposed to a magnetic field gradient, magnons may be driven to move from one end of a magnet to another, carrying heat with them and producing a cooling ...
Children with disabilities benefit from classroom inclusion
2014-07-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The secret to boosting the language skills of preschoolers with disabilities may be to put them in classrooms with typically developing peers, a new study finds.
Researchers found that the average language skills of a child's classmates in the fall significantly predicted the child's language skills in the spring – especially for children with disabilities.
The results support inclusion policies in schools that aim to have students with disabilities in the same classrooms alongside their typically developing peers, said Laura Justice, co-author of the ...
Study shows new link between obesity in the young and the lowering of age of puberty
2014-07-28
A new link has been identified between obesity in childhood and the lowering of the age of puberty.
The research which discovered the link, carried out at Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, is published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The study focuses on a protein called sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), the regulation and role of which in children are poorly defined. SHBG binds to the sex hormones androgen and oestrogen. SHGB levels are initially high in childhood but decline significantly before puberty, in ...
Henry Ford study: Burnout impacts transplant surgeons
2014-07-28
VIDEO:
Despite saving thousands of lives yearly, nearly half of organ transplant surgeons report a low sense of personal accomplishment and 40 percent feel emotionally exhausted, according to a new national...
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – Despite saving thousands of lives yearly, nearly half of organ transplant surgeons report a low sense of personal accomplishment and 40% feel emotionally exhausted, according to a new national study on transplant surgeon burnout.
The ...
Many people never grow out of their growing pains
2014-07-28
Over the years, many adolescents have been forced to accept the diagnosis "growing pains" when they complained about pain in their knees. A new PhD study involving 3,000 adolescents has now shown that the knee pain often carries on:
"We can see from the study that one in three young people between the ages of 12 and 19 experience problems with pain in their knees. Seven percent of the adolescents experience daily knee pain in the front of the knee," says physiotherapist and PhD Michael Skovdal Rathleff from Aarhus University, and continues:
"More than half still have ...
Glow in space is evidence of a hot bubble in our galaxy
2014-07-28
VIDEO:
Dr. Massimilano Galeazzi discusses his work on a sounding rocket, sent into the atmosphere to search for answers about the universe.
Click here for more information.
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (July 27, 2014) — When we look up to the heavens on a clear night, we see an immense dark sky with uncountable stars. With a small telescope we can also see galaxies, nebulae, and the disks of planets. If you look at the sky with an X-ray detector, you would see many of these same familiar ...
Interfering with interferon
2014-07-28
Using the body's natural virus killers to prevent and treat HIV infection has been problematic until now because of the strong inflammatory response these molecules can arouse as they get rid of the invaders. Now, collaborative research conducted by scientists at the Weizmann Institute and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have demonstrated how suppressing the activity of these molecules – interferons – around the time of infection could have long-term implications for the course of the disease. Their research appeared in Nature.
Interferons, named for their ability ...
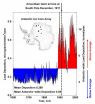
Industrial lead pollution beat explorers to the South Pole by 22 years and persists today
2014-07-28
RENO – Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen became the first man to reach the South Pole in December of 1911. More than 100 years later, an international team of scientists led by Joe McConnell of Nevada's Desert Research Institute (DRI) have proven that air pollution from industrial activities arrived long before.
Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, McConnell's team created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over the Earth's southernmost continent. ...
Building 'invisible' materials with light
2014-07-28
A new method of building materials using light, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, could one day enable technologies that are often considered the realm of science fiction, such as invisibility cloaks and cloaking devices.
Although cloaked starships won't be a reality for quite some time, the technique which researchers have developed for constructing materials with building blocks a few billionths of a metre across can be used to control the way that light flies through them, and works on large chunks all at once. Details are published today (28 ...