(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
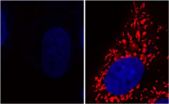
Parkinson's disease affects neurons in the Substantia nigra brain region – their mitochondrial activity ceases and the cells die. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics show that supplying D-lactate or glycolate, two products of the gene DJ-1, can stop and even counteract this process: Adding the substances to cultured HeLa cells and to cells of the nematode C. elegans restored the activity of mitochondria and prevented the degeneration of neurons. They also showed that the two substances rescued the toxic effects of the weed killer Paraquat. Cells that had been treated with this herbicide, which is known to cause a Parkinson's like harm of mitochondria, recovered after the addition of the two substances. Both glycolic and D-lactic acids occur naturally in unripe fruits and certain kinds of yoghurt. Products with an enriched concentration of these substances could thus be a therapeutic route for a treatment of Parkinson's or for even preventing the onset of the disease.
Teymuras Kurzchalia and Tony Hyman both have labs at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics with rather different research programs – but both happened to stumble upon the gene DJ-1 and joined forces. This gene, originally thought of as an oncogene, has been linked to Parkinson's disease since 2003. Recent studies showed that DJ-1 belongs to a novel glyxolase family. The major function of these genes is assumed to detoxify aggressive aldehyde by-products from mitochondrial metabolism. The Dresden research team now showed that the products of DJ-1, D-lactate and glycolate, are actually required to maintain the high mitochondrial potential and thus can prevent the degeneration of neurons implicated in Parkinson's disease.
Their experiments proved that both substances are lifesavers for neurons: Adding them to affected cells, in other words cells treated with the environmental poison Paraquat or with a down-regulated DJ-1, decreased the toxic effect of the herbicide, restored the activity of the mitochondria and thus ensured the survival of the neurons.
„We do not yet understand how exactly D-lactate and glycolate achieve this curative and preventive effect, but the next step will be to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying this process", say Hyman and Kurzchalia. In addition to further molecular investigation, they also have more concrete plans for the future: As Kurzchalia says "we can develop a yoghurt enriched with D-lactate: It could serve as a protection against Parkinson's and is actually very tasty at the same time!" This is why the researchers have filed a patent for their finding.
Many diseases are associated with a decline in mitochondrial activity, not only Parkinson's. Thus, the researchers believe that the DJ1-products could have a general role in protecting cells from decline.
INFORMATION:
Original publication:
Yusuke Toyoda, Cihan Erkut, Francisco Pan-Montojo, Sebastian Boland, Martin P. Stewart, Daniel J. Müller, Wolfgang Wurst, Anthony Hyman und Teymuras V. Kurzchalia
Products of the Parkinson's-disease-related glyxolase DJ-1, D-lactate and glycolate, support mitochondrial membrane potential and neuronal survival
The Company of Biologists, 25 July 2014 (doi: 10.1242/bio.20149399)
Potential treatment and prevention of Parkinson's disease
Max Planck researchers show that 2 products of the gene DJ-1 can increase the survival of neurons
2014-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA eyes powerful bands of thunderstorms in newborn Tropical Storm Iselle
2014-08-01
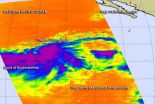
Tropical Storm Iselle was born in the Eastern Pacific Ocean soon after NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared imagery on the storm that showed powerful thunderstorms wrapping into developing storm's center. Iselle is not close enough to land to cause any watches or warnings.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 95E on July 31 at 5:23 p.m. EDT from gathered infrared data before it became Tropical Storm Iselle. The data was made into a false-colored image at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. ...
Heavy metals and hydroelectricity
2014-08-01
Boulder, Colorado, USA – Hydraulic engineering is increasingly relied on for hydroelectricity generation. However, redirecting stream flow can yield unintended consequences. In the August 2014 issue of GSA Today, Donald Rodbell of Union College-Schenectady and coauthors from the U.S. and Peru document the wholesale contamination of the Lake Junín National Reserve by acid mine drainage from the Cerro de Pasco mining district.
According to the World Bank, about 60% of Peru's electricity is generated by hydropower, which during the dry season relies heavily on glacial meltwater ...
Scripps Research Institute scientists find new calorie-burning switch in brown fat
2014-08-01
LA JOLLA, CA—August 1, 2014—Biologists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have identified a signaling pathway that switches on a powerful calorie-burning process in brown fat cells.
The study, which is reported in this week's online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, sheds light on a process known as "brown fat thermogenesis," which is of great interest to medical researchers because it naturally stimulates weight loss and may also protect against diabetes.
"This finding offers new possibilities for the therapeutic activation ...
New mothers still excessively sleepy after 4 months: QUT study
2014-08-01
New mums are being urged to be cautious about returning to work too quickly, after a QUT study found one in two were still excessively sleepy four months after giving birth.
Dr Ashleigh Filtness, from QUT's Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS-Q), studied the sleep patterns and tiredness of postpartum mums and found despite new mums recording stable night sleep times at 18 weeks, they continued to report being excessively tired.
The CARRS-Q study, published in PLOS ONE, followed 33 healthy new mums who recorded their postpartum sleep patterns ...
Effect of microenvironment modulation on stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury pain
2014-08-01
Spinal cord injury (SCI) currently ranks second after mental retardation among neurological disorders in terms of cost to society. Pain is a debilitating consequence of SCI related to the nature of the lesion, neurological structures damaged, and secondary pathophysiological changes of surviving tissues1. Approximately two-thirds of persons who have sustained SCI experience clinically significant pain after injury, of whom one-third have severe pain2, 3. Post-SCI pain can increase with time and is often refractory to conventional treatment approaches4. Over the past decade, ...
Acrolein as a novel therapeutic target for motor and sensory deficits in spinal cord injury
2014-08-01
Acrolein, a highly reactive unsaturated aldehyde, has been shown to play a major role in the secondary injury by contributing significantly to both motor and sensory deficits. Prof. Riyi Shi, who comes from University of Purdue in USA will highlight the recent developments in the understanding of the mechanisms of acrolein in motor and sensory dysfunction in animal models of spinal cord injury, and will also discuss the therapeutic benefits of using acrolein scavengers to attenuate acrolein-mediated neuronal damage following spinal cord injury. The relevant study has been ...
Recent advances in stem cell biology
2014-08-01
Advances in stem cell research will provide enormous opportunities for both biological and future clinical applications. Basically, stem cells could replicate any other cells in the body, offering immense hope of curing Alzheimer's disease, repairing damaged spinal cords, treating kidney, liver and lung diseases and making damaged hearts whole. The potential for profit is staggering. Prof. Jinhui Chen from Indiana University in USA considered that this field of research still faces myriad biological, ethical, legal, political, and financial challenges. The eventual resolution ...
Developmental regulation of important plant phloem components discovered
2014-08-01
Sieve elements are a key component of phloem, the conductive tissue through which plants transport carbohydrates and a wide range of signalling molecules. Elongated cylindrical cells are capped at one end by a sieve plate and arranged end-to-end to form sieve tubes which in turn form a network throughout a plant's body.
"Sieve elements are very special cells which play an important role in carbon sequestration, yet so far very little has been known about their differentiation," says Professor Ykä Helariutta from the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, ...
Plastic surgeons or nurses: Who are the better injectors?
2014-08-01
In recent years, minimally invasive aesthetic injectable procedures have grown in popularity as more and more men and women are seeking age-defying treatments. As Botulinum toxin – generally known as BOTOX® – use has increased, a growing number of nonaesthetic health professionals have emerged to perform procedures utilizing this and other injectables. Kevin Small, MD and Henry M. Spinelli, MD from the Division of Plastic Surgery Presbyterian Hospital in New York and Kathleen M. Kelly, MD from Columbia University in New York have assessed the capability of various providers ...
'Active' surfaces control what's on them
2014-08-01
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Researchers at MIT and in Saudi Arabia have developed a new way of making surfaces that can actively control how fluids or particles move across them. The work might enable new kinds of biomedical or microfluidic devices, or solar panels that could automatically clean themselves of dust and grit.
"Most surfaces are passive," says Kripa Varanasi, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, and senior author of a paper describing the new system in the journal Applied Physics Letters. "They rely on gravity, or other forces, to move fluids or ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
[Press-News.org] Potential treatment and prevention of Parkinson's diseaseMax Planck researchers show that 2 products of the gene DJ-1 can increase the survival of neurons