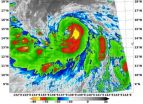
(Press-News.org) NASA satellite data showed Tropical Storm Halong's "best side" or most powerful side was east of its center. That's where the coldest cloud top temperatures and strongest thunderstorms appeared on satellite imagery.
On August 1 at 13:30 UTC (9:30 a.m. EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an infrared picture of Tropical Storm Halong. The infrared data showed the coldest, strongest thunderstorm cloud-top temperatures east of the center of circulation. Cloud tops were as cold as -80F/-62C. Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate thunderstorm cloud tops are near the top of the troposphere, and have the potential to drop very heavy rainfall.
At 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Halong had maximum sustained winds near 60 knots (69.0 mph/111.1 kph). It was centered near 14.9 north latitude and 137.9 east longitude, about 324 nautical miles (600 miles/372.9 km) north of Yap. It was moving to the west-northwest at 7 knots (8.0 mph/12.9 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Halong to continue intensifying for the next three days before it begins a weakening trend. Halong is expected to pass near Okinawa sometime on August 6. For forecast updates from the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, visit: http://www.usno.navy.mil/JTWC/.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees Tropical Storm Halong's 'best side'
2014-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advances in assisted reproduction create more options & new legal issues for LGBT couples
2014-08-01
New Rochelle, NY, August 1, 2014—Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals who want to conceive a child may face the same problems as some of their heterosexual and cisgendered peers, such as reduced fertility, but in addition they often face additional physiological and legal challenges to become parents. A comprehensive review of the most recent advances in assisted reproduction options is presented in the article "LGBT Assisted Reproduction: Current Practice and Future Possibilities," published in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
Scientists name new species of cetacean: The Australian humpback dolphin
2014-08-01
Scientists examining a taxonomically confused group of marine mammals have officially named a species new to science: the Australian humpback dolphin, Sousa sahulensis, according to the Wildlife Conservation Society and Clymene Enterprises.
The study describing the newly named species is the culmination of a 17-year long systematic examination of all available historical records, physical descriptions, and genetic data of humpback dolphins—a widespread group of coastal cetaceans ranging from the coast of West Africa to the northern coast of Australia. The Australian ...
Electronic reminders can help patients prevent surgical site infections
2014-08-01
CHICAGO (August 1, 2014)—The use of electronic reminders such as text messages, emails or voicemails is highly effective at getting surgical patients to adhere to a preadmission antiseptic showering regimen known to help reduce risk of surgical site infections (SSIs), according to a first-of-its-kind study published in the August issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Each year approximately 400,000 SSIs occur and lead to a death rate approaching nearly 100,000 according to data sources cited by study authors. To help reduce the risk of these dangerous ...
Potential treatment and prevention of Parkinson's disease
2014-08-01
This news release is available in German.
Parkinson's disease affects neurons in the Substantia nigra brain region – their mitochondrial activity ceases and the cells die. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics show that supplying D-lactate or glycolate, two products of the gene DJ-1, can stop and even counteract this process: Adding the substances to cultured HeLa cells and to cells of the nematode C. elegans restored the activity of mitochondria and prevented the degeneration of neurons. They also showed that the two substances ...
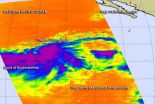
NASA eyes powerful bands of thunderstorms in newborn Tropical Storm Iselle
2014-08-01
Tropical Storm Iselle was born in the Eastern Pacific Ocean soon after NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared imagery on the storm that showed powerful thunderstorms wrapping into developing storm's center. Iselle is not close enough to land to cause any watches or warnings.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 95E on July 31 at 5:23 p.m. EDT from gathered infrared data before it became Tropical Storm Iselle. The data was made into a false-colored image at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. ...
Heavy metals and hydroelectricity
2014-08-01
Boulder, Colorado, USA – Hydraulic engineering is increasingly relied on for hydroelectricity generation. However, redirecting stream flow can yield unintended consequences. In the August 2014 issue of GSA Today, Donald Rodbell of Union College-Schenectady and coauthors from the U.S. and Peru document the wholesale contamination of the Lake Junín National Reserve by acid mine drainage from the Cerro de Pasco mining district.
According to the World Bank, about 60% of Peru's electricity is generated by hydropower, which during the dry season relies heavily on glacial meltwater ...
Scripps Research Institute scientists find new calorie-burning switch in brown fat
2014-08-01
LA JOLLA, CA—August 1, 2014—Biologists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have identified a signaling pathway that switches on a powerful calorie-burning process in brown fat cells.
The study, which is reported in this week's online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, sheds light on a process known as "brown fat thermogenesis," which is of great interest to medical researchers because it naturally stimulates weight loss and may also protect against diabetes.
"This finding offers new possibilities for the therapeutic activation ...
New mothers still excessively sleepy after 4 months: QUT study
2014-08-01
New mums are being urged to be cautious about returning to work too quickly, after a QUT study found one in two were still excessively sleepy four months after giving birth.
Dr Ashleigh Filtness, from QUT's Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS-Q), studied the sleep patterns and tiredness of postpartum mums and found despite new mums recording stable night sleep times at 18 weeks, they continued to report being excessively tired.
The CARRS-Q study, published in PLOS ONE, followed 33 healthy new mums who recorded their postpartum sleep patterns ...
Effect of microenvironment modulation on stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury pain
2014-08-01
Spinal cord injury (SCI) currently ranks second after mental retardation among neurological disorders in terms of cost to society. Pain is a debilitating consequence of SCI related to the nature of the lesion, neurological structures damaged, and secondary pathophysiological changes of surviving tissues1. Approximately two-thirds of persons who have sustained SCI experience clinically significant pain after injury, of whom one-third have severe pain2, 3. Post-SCI pain can increase with time and is often refractory to conventional treatment approaches4. Over the past decade, ...
Acrolein as a novel therapeutic target for motor and sensory deficits in spinal cord injury
2014-08-01
Acrolein, a highly reactive unsaturated aldehyde, has been shown to play a major role in the secondary injury by contributing significantly to both motor and sensory deficits. Prof. Riyi Shi, who comes from University of Purdue in USA will highlight the recent developments in the understanding of the mechanisms of acrolein in motor and sensory dysfunction in animal models of spinal cord injury, and will also discuss the therapeutic benefits of using acrolein scavengers to attenuate acrolein-mediated neuronal damage following spinal cord injury. The relevant study has been ...