(Press-News.org) A European Journal of Neuroscience study suggests that it is critical to treat lysosomal storage disorders early, before symptoms arise. These genetic disorders, which are caused by the malfunction of enzymes that normally degrade various substances within cells, lead to numerous ailments including neurological problems.
Although few therapeutic options are available, clinical trials of treatments including lysosomal enzyme replacement are underway. Researchers who used enzyme replacement to treat mice with early, mid- and later-stages of a lysosomal storage disease found that treatment was most effecting in mice with very early-stage disease. Once symptoms arose, treatment was ineffective.
"Until newborn screening is available world-wide for these conditions, and children are diagnosed prior to symptoms appearing, it is critical that we continue to gather information regarding the reversibility, or not, of disease-based degenerative changes," said senior author Dr. Kim Hemsley.
INFORMATION:
Very early treatment may be key to combatting inherited metabolic disorder
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Maternal singing during skin-to-skin contact benefits both preterm infants and their mothers
2014-08-04
A mother who sings to her preterm infant while providing 'kangaroo care,' or holding with direct skin-to-skin contact, may see improvements in both her child's and her own health. The finding comes from an Acta Paediatrica study of 86 mother-infant pairs in a neonatal intensive care unit in Meir Hospital in Israel.
Compared with preterm infants whose mothers just held them with direct skin-to-skin contact but did not sing, infants whose mothers both held them and sang to them had improved heart rate variability patterns. This combined effect of holding and singing also ...
Inadequately managed allergies cause significant economic burden in Europe
2014-08-04
New research indicates that avoidable indirect costs per patient insufficiently treated for allergy equal 2,405.00 Euros per year due to absence from work and reduced working capacity. On the other hand, appropriate therapy is available at an average cost of 125 Euros per patient annually, which represents only 5% of the cost of untreated disease.
"Between 55 and 151 billion Euros EU wide could be saved every year by better management of allergies," said Dr. Torsten Zuberbier, lead author of the Allergy study.
INFORMATION: END ...
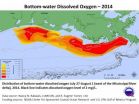
NOAA, EPA-supported scientists find average but large Gulf dead zone
2014-08-04
NOAA- and EPA-supported scientists have mapped the Gulf of Mexico dead zone, an area with low oxygen water, measuring 5,052 square miles this summer--approximately the size of the state of Connecticut. The measurements were taken during the 30th annual hypoxia survey cruise from July 27 to August 2.
This area falls within the predicted range of 4,633 to 5,708 square miles forecast by a suite of NOAA-sponsored models, and confirms the accuracy of the models and their utility for guiding management of nutrients in the Mississippi River watershed.
The size is smaller than ...
Eating baked or broiled fish weekly boosts brain health, Pitt study says
2014-08-04
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 4, 2014 – Eating baked or broiled fish once a week is good for the brain, regardless of how much omega-3 fatty acid it contains, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. The findings, published online recently in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, add to growing evidence that lifestyle factors contribute to brain health later in life.
Scientists estimate that more than 80 million people will have dementia by 2040, which could become a substantial burden to families and drive up health care costs, noted senior ...
Media exposure and sympathetic nervous system reactivity predict PTSD symptoms in adolescents
2014-08-04
In a Depression and Anxiety study that surveyed youth following the terrorist attack at the 2013 Boston marathon, adolescents with lower levels of sympathetic reactivity (the flight or fight response) before the attack developed posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms only following high exposure to media coverage of the attack. Adolescents with high levels of sympathetic reactivity developed higher levels of PTSD symptoms regardless of how much media coverage they saw.
"This study tells us more about which children are most vulnerable to symptoms of PTSD and emphasizes ...
Most gay and bisexual men in the United States have used lubricants during sexual activity
2014-08-04
More than 90% of gay and bisexual men in the United States have used lubricants to enhance a wide range of sexual activities, including but not limited to anal intercourse, researchers report in a Journal of Sexual Medicine study.
By minimizing potential skin tears, lubricants may help reduce the likelihood of HIV transmission between partners.
Public health practitioners and clinicians may find the study's results useful in their efforts to incorporate lubricant use into sexual health promotion efforts. "These findings show the need for a new generation of sexual health ...
Survival increases with clinical team debriefing after in-hospital cardiac arrest
2014-08-04
A new study found that staff members who joined structured team debriefings after emergency care for children suffering in-hospital cardiac arrests improved their CPR performance and substantially increased the rates of patients surviving with favorable neurological outcomes.
The study team, at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), said their research suggests that including all members of the intensive care unit (ICU) team, not just those immediately involved in the cardiac arrests, broadens learning and may improve compliance with standardized national guidelines ...
Study examines viewers' role in American death penalty films
2014-08-04
Over the course of the last 100 years or more, many scenes of execution in American film have offered intimate knowledge of executions, giving viewers a privileged 'backstage' gaze of an execution not available outside film, the chance to see what executioners see, and a chance to understand the condemned's experience as he awaits death.
These motifs are explored in a recent Law & Social Inquiry analysis, in which the authors conclude by asking whether and how scenes of execution in American film provoke an awareness of the political responsibility inherent in viewers' ...
Researchers identify potential gene that may increase risk of ad in African Americans
2014-08-04
(Boston)-- Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) report that two rare variants in the AKAP9 gene significantly increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in African-Americans.
This previously unknown association furthers the understanding of the role of genetic factors in the development of AD, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Alzheimer's & Dementia.
AD is the most frequent age-related dementia affecting 5.4 million Americans including 13 percent of people age 65 and older and more than 40 percent of people age 85 and ...
Patients with hypoventilation may need supplemental oxygen on-board flights
2014-08-04
Severely overweight people who suffer from hypoventilation can have abnormally low levels of oxygen (hypoxaemia) in their blood during air travel as a result of reduced atmospheric pressure in the cabin of aircrafts.
In a recent Respirology study, even patients diagnosed with obesity hypoventilation syndrome who were in the care of specialist and had normal daytime blood oxygen levels were still at risk of hypoxaemia when flying.
"The findings suggest that it is advisable for all hypoventilation syndrome patients to do a hypoxic challenge test before air travel to be ...