(Press-News.org) Each year, millions of birds migrate thousands of miles between the locations where they breed and raise young, and the areas where they spend the winter. Each migration is a trip fraught with danger—many birds die before they reach their final destination. To scientists, long distance migration still holds many mysteries, one of which is: where did migration begin and how did it evolve? This question has long been a debated topic among scientists, but thanks to new research from Field Museum scientists, we may have an answer for one of the largest groups of migratory birds. The scientists' research will be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Traditionally, there have been two schools of thought: one, that ancestors of migratory birds spent the whole year in North America and evolved migration by moving their winter range to the tropics. The other theory suggested that these ancestors were originally found in the tropics, and evolved migration by moving breeding grounds to more temperate locales like North America.
To uncover this mystery of migration Resident Graduate Student Ben Winger (University of Chicago) and Associate Curator of Botany Rick Ree created a model to infer how the breeding and winter ranges of migratory species changed through time. They applied the model to a large group of migratory birds that include warblers, cardinals, sparrows, tanagers, orioles, and others. The model uses a phylogeny (a "family tree" of species that depicts their evolutionary relationships), which was contributed by co-author Keith Barker, a former Field Museum graduate student now at the University of Minnesota.
"We named it the 'domino model' because the breeding and winter ranges of species were coded in 3x2 grids of binary values, like dots on domino pieces. The computational challenge was to reconstruct the most probable evolutionary shifts from one domino to another," explains Ree. Tracing back through time and examining common ancestors of migratory and non-migratory species, they were able to conclude that there was more evidence supporting the idea that birds lived year-round in North America and began migrating further and further south, resulting in today's birds migrating thousands of miles every year.
Another result of the study suggests that many tropical species of birds are descendants of migratory ancestors that lost migration and stayed in the tropics year-round. "This is an interesting result because species diversity in this group is much higher in the tropics. Previously, more species in the tropics led to the assumption that temperate, migratory species are derived from tropical, nonmigratory ancestors; however, the results of our phylogenetic study suggest that the opposite pattern happened often in this group."
INFORMATION:
The paper Temperate origins of long-distance seasonal migration in New World songbirds will be published by PNAS the week of August 4 and is available to media. Contact media@fieldmuseum.org for access to the paper, and to arrange interviews.
The evolution of migration
Ancestral songbirds headed south for the winter
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
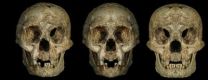
Flores bones show features of Down syndrome, not a new 'hobbit' human
2014-08-04
In October 2004, excavation of fragmentary skeletal remains from the island of Flores in Indonesia yielded what was called "the most important find in human evolution for 100 years." Its discoverers dubbed the find Homo floresiensis, a name suggesting a previously unknown species of human.
Now detailed reanalysis by an international team of researchers including Robert B. Eckhardt, professor of developmental genetics and evolution at Penn State, Maciej Henneberg, professor of anatomy and pathology at the University of Adelaide, and Kenneth Hsü, a Chinese geologist and ...
Triple therapy revs up immune system against common brain tumor
2014-08-04
A triple therapy for glioblastoma, including two types of immunotherapy and targeted radiation, has significantly prolonged the survival of mice with these brain cancers, according to a new report by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Mice with implanted, mouse-derived glioblastoma cells lived an average of 67 days after the triple therapy, compared with mice that lasted 24 days when they received only the two immunotherapies. Half of the mice who received the triple therapy lived 100 days or more and were protected against further tumors when new cancer ...
African American professional women positive on medical research
2014-08-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. — If a research survey of African American professional women is any indication, attitudes may be changing towards participation in medical research. Mayo Clinic and The Links, Incorporated researchers teamed up to survey members of the international women's organization, and found that a majority of African American women surveyed are willing to or have taken part in medical research. The results appear in the Journal of Women's Health.
"Our findings are highly encouraging," says Sharonne Hayes, M.D., Mayo Clinic cardiologist, co-author of the study, ...
Fires in California and Oregon
2014-08-04
The Little Deer fire in California began as a lightning strike on July 31, 2014. Currently it has burned 4,700 acres and is 43% contained however there has been increased humidity over the fire the last 24 hours with shifting wind conditions. The threat of thunder storms today (08/04) and tomorrow (08/05) may cause an increase in fire activity.
The Beaver Complex is comprised of the Salt Creek Fire (20 miles northwest of Medford) and the Oregon Gulch Fire (15 miles east of Ashland), which are lightning-started fires that started on July 30-31, 2014. After it was first ...
Eiler and Bald Fires in California
2014-08-04
The Eiler wildfire which began on July 31, 2014, has almost consumed 26,000 acres. It is currently unknown as to the cause of this fire. The weather patterns currently around this fire do not bode well for a quick containment. Maximum temperatures are in the mid- to high 80's with 10-20% relative humidity. There is an unstable atmosphere at work along with thunderstorm chances which are increasingly today (08/04) through Wednesday (08/06). A Red Flag Warning in effect for dry lightning on Monday (08/04).
The Bald Fire began with a lightning strike on July 30, 2014. ...
Smoke from Canadian wildfires over Baffin Bay
2014-08-04
Canadian wildfires have been raging this summer and some of the smoke from those fires already drifted downward into the U.S. over the Great Lakes (see the image feature from July 25 below). In this image collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on August 02, 2014 the large swath of smoke from these fires has taken a northward track and settled over the Bay of Baffin which borders Greenland.
To view the other Canadian fire images from July 2014:
Smoke from Canadian Fires Hovers Over Great Lakes - July 25, 2014
Smoke ...
Wildfires consume parts of eastern Russia
2014-08-04
Wildfires in far eastern Russia dot the landscape and what isn't covered by the fires is covered by the smoke that rises from these wildfires. This image taken by the Terra satellite shows the entire area covered with a blanket of heavy smoke coming off of dozens of wildfires that have broken out in the remote areas of Russia. Usually these fires are caused by lightning strikes that then consume the dry vegetation. With nothing to stop the spread, these fires take off and cover the landscape, especially during this time of year.INFORMATION:
NASA's Terra satellite collected ...
A hellacious two weeks on Jupiter's moon Io
2014-08-04
Three massive volcanic eruptions occurred on Jupiter's moon Io within a two-week period last August, leading astronomers to speculate that these presumed rare "outbursts," which can send material hundreds of miles above the surface, might be much more common than astronomers thought.
"We typically expect one huge outburst every one or two years, and they're usually not this bright," said Imke de Pater, professor and chair of astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and lead author of one of two papers describing the eruptions. "Here we had three extremely ...
Single-fraction RT as effective as multiple-fraction RT for palliation of bone metastases
2014-08-04
Fairfax, Va., August 4, 2014—Standardizing prescribing practices for single-fraction radiation therapy (SFRT) for palliation of bone metastases could lead to cost savings and improvement in patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the August 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Bone metastases are a common manifestation of distant spread of disease, occurring most frequently with prostate, breast ...
How long does it take to make a natural fracture?
2014-08-04
Boulder, Colo., USA – How long does it take for natural Earth processes to form hydraulic fractures? Is the formation driven by sediment compaction, oil and gas generation, or something else? What role do these natural fractures play in modern hydraulic fracturing production? A new GSA BULLETIN study by András Fall and colleagues from The University of Texas at Austin, Virginia Tech, and ExxonMobil addresses these questions, and the article is open-access online.
The process of fracture formation by a natural increase in pore-fluid pressure has previously been referred ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] The evolution of migrationAncestral songbirds headed south for the winter