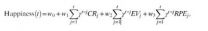(Press-News.org) Researchers from McGill University and the Génome Québec Innovation Centre have achieved a technical breakthrough that should result in speedier diagnosis of cancer and various pre-natal conditions.
The key discovery, which is described online this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), lies in a new tool developed by Professors Sabrina Leslie and Walter Reisner of McGill's Physics Department and their collaborator Dr. Rob Sladek of the Génome Québec Innovation Centre. It allows researchers to load long strands of DNA into a tunable nanoscale imaging chamber in ways that maintain their structural identity and under conditions that are similar to those found in the human body.
This newly developed "Convex Lens-Induced Confinement" (CLIC) will permit researchers to rapidly map large genomes while at the same time clearly identifying specific gene sequences from single cells with single-molecule resolution, a process that is critical to diagnosing diseases like cancer.
CLIC, the new tool, can sit on top of a standard inverted fluorescence microscope used in a university lab. The innovative aspect of CLIC lies in the fact that it allows strands of DNA to be loaded into the imaging chamber from above, a process which allows the strands of DNA to maintain their integrity. Existing tools used for genomic analysis rely on side-loading DNA under pressure into nanochannels in the imaging chamber, a practice that breaks the DNA molecules into small pieces, making it a challenge to reconstruct the genome.
"It's like squeezing many soft spaghetti noodles into long narrow tubes without breaking them," explains Prof. Leslie as she describes what it is like to use CLIC. "Once these long strands of DNA are gently squeezed down into nanochannels from a nanoscale bath above, they become effectively rigid which means that we can map positions along uniformly stretched strands of DNA, while holding them still. This means diagnostics can be performed quickly, one cell at a time, which is critical for diagnosing many pre-natal conditions and the onset of cancer."
"Current practices of genomic analysis typically require tens of thousands of cells worth of genomic material to obtain the information we need, but this new approach works with single cells," says Dr. Rob Sladek of the Génome Québec Innovation Centre. "CLIC will allow researchers to avoid having to spend time stitching together maps of entire genomes as we do under current techniques, and promises to make genomic analysis a much simpler and more efficient process."
"Nanoscale physics has so much to offer biomedicine and diagnostics," adds Prof. Leslie. "CLIC brings the nanoscale regime to the bench top, and genomics is just the beginning".
INFORMATION:
To read the full article "Convex Lens-Induced Nanoscale Templating" by Sabrina R. Leslie et al in PNAS: http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1321089111
To contact the researchers directly: sabrina.leslie@mcgill.ca
Speedier diagnosis of diseases such as cancer likely thanks to new DNA analysis technique
McGill researchers develop breakthrough technique for genomic analysis of long DNA molecules
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In defense of mouse models for studying human disorders
2014-08-04
Mouse models of human diseases are essential research tools that are widely used in the medical sciences to increase our understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of various diseases, and to search for cures. Despite the widespread use of mice as animal models of disease, in 2013, Seok et al. reported that mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases, such as severe burn injury, sepsis, and acute infection, in terms of gene expression (PNAS 2013, 110(9), 3507-3523), which has been cited more than 400 times since its publication only 18 months ago. Their ...
Sulfur signals in Antarctic snow reveal clues to climate, past and future
2014-08-04
Sulfur signals in the Antarctic snow have revealed the importance of overlooked atmospheric chemistry for understanding climate, past and future.
Eruptions of huge volcanoes, the disruptive weather pattern known as El Niño, and a fire season from hell each left distinctive chemical marks in layers of snow excavated near the South Pole, researchers from the University of California, San Diego and France report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of August 4.
Sorting out the chemical reactions that must have led to those traces revealed a process, ...
Overtreatment and undertreatment of patients with high blood pressure linked to kidney failure and death
2014-08-04
PASADENA, Calif., August 4, 2014 — The mantra for treatment for high blood pressure has been "the lower, the better," but that goal can potentially put patients at risk of kidney failure or death, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Researchers examined the electronic health records of nearly 400,000 Kaiser Permanente patients in Southern California who were taking medications to treat high blood pressure from January 2006 through December 2010. They found that:
patients within the range between ...
A polypill strategy to improve global secondary cardiovascular prevention
2014-08-04
WASHINGTON (Aug. 4, 2014) — The polypill, a combination pill taken just once a day that includes key medications for secondary prevention of heart disease, may be an effective low-cost strategy to improve adherence to medication recommendations and reduce costs, according to researchers from Spain and New York, who reviewed research on the polypill.
The review article, A Polypill Strategy to Improve Global Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention, was published online today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and will appear in the August 12, 2014 print issue. ...
Protective hinge process enables insulin to bind to cells
2014-08-04
CLEVELAND – August 4, 2014 – Since its landmark discovery in 1922, insulin has improved the health and extended the lives of more than 500 million people worldwide with diabetes mellitus. Yet the question of how this key hormone binds to its target cells in the body’s organs has posed an enduring scientific mystery. A global team of researchers from Cleveland, Australia, Chicago, India and Oregon has made a discovery about insulin and its structure that promises to enable design of new insulin products that will do a better job of regulating the metabolism of patients with ...
Blood-oxytocin levels in normal range in children with autism, study finds
2014-08-04
Autism does not appear to be solely caused by a deficiency of oxytocin, but the hormone's universal ability to boost social function may prove useful in treating a subset of children with the developmental disorder, according to new findings from the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford.
Low levels of oxytocin, a hormone involved in social functioning, have for years been suspected of causing autism. Prior research seeking a link has produced mixed results. Now, in the largest-ever study to test the purported connection, ...
Epidemic outbreaks caused by environment, not evolution
2014-08-04
Researchers have traced genetic changes in a bacterial pathogen over 450 years, and claim that epidemics of bacterial disease in human history may be caused by chance environmental changes rather than genetic mutations.
In a study published in PNAS, a team led by the University of Warwick analysed 149 genomes of Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A, which is a major cause of enteric fever. Enteric fever is currently estimated at 27 million clinical cases each year, resulting in 200,000 deaths.
Lead author, Zhemin Zhou from Warwick Medical School, said: "When epidemics ...
Study traces evolutionary origins of migration in New World birds
2014-08-04
Every year, millions of birds make the journey from North America to Central and South America for the winter. But the evolutionary origins of this long-distance migration have remained opaque due to the complex geographic distributions of modern and ancient bird ranges.
Now, a team of scientists from the University of Chicago have developed a new method to reveal the ancestral ranges of New World birds, and discovered that bird migration in the Americas evolved in species that resided in North America. Their work also offers evidence that many tropical bird species descended ...
Learning how things fall apart
2014-08-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Materials that are firmly bonded together with epoxy and other tough adhesives are ubiquitous in modern life — from crowns on teeth to modern composites used in construction. Yet it has proved remarkably difficult to study how these bonds fracture and fail, and how to make them more resistant to such failures.
Now researchers at MIT have found a way to study these bonding failures directly, revealing the crucial role of moisture in setting the stage for failure. Their findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science ...
Equation to predict happiness
2014-08-04
The happiness of over 18,000 people worldwide has been predicted by a mathematical equation developed by researchers at UCL, with results showing that moment-to-moment happiness reflects not just how well things are going, but whether things are going better than expected.
The new equation accurately predicts exactly how happy people will say they are from moment to moment based on recent events, such as the rewards they receive and the expectations they have during a decision-making task. Scientists found that overall wealth accumulated during the experiment was not ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Speedier diagnosis of diseases such as cancer likely thanks to new DNA analysis techniqueMcGill researchers develop breakthrough technique for genomic analysis of long DNA molecules