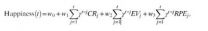(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Materials that are firmly bonded together with epoxy and other tough adhesives are ubiquitous in modern life — from crowns on teeth to modern composites used in construction. Yet it has proved remarkably difficult to study how these bonds fracture and fail, and how to make them more resistant to such failures.
Now researchers at MIT have found a way to study these bonding failures directly, revealing the crucial role of moisture in setting the stage for failure. Their findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science in a paper by MIT professors of civil and environmental engineering Oral Buyukozturk and Markus Buehler; research associate Kurt Broderick of MIT's Microsystems Technology Laboratories; and doctoral student Denvid Lau, who has since joined the faculty at the City University of Hong Kong.
"The bonding problem is a general problem that is encountered in many disciplines, especially in medicine and dentistry," says Buyukozturk, whose research has focused on infrastructure, where such problems are also of great importance. "The interface between a base material and epoxy, for example, really controls the properties. If the interface is weak, you lose the entire system."
"The composite may be made of a strong and durable material bonded to another strong and durable material," Buyukozturk adds, "but where you bond them doesn't necessarily have to be strong and durable."
Besides dental implants and joint replacements, such bonding is also critical in construction materials such as fiber-reinforced polymers and reinforced concrete. But while such materials are widespread, understanding how they fail is not simple.
There are standard methods for testing the strength of materials and how they may fail structurally, but bonded surfaces are more difficult to model. "When we are concerned with deterioration of this interface when it is degraded by moisture, classical methods can't handle that," Buyukozturk says. "The way to approach it is to look at the molecular level."
When such systems are exposed to moisture, "it initiates new molecules at the interface," Buyukozturk says, "and that interferes with the bonding mechanism. How do you assess how weak the interface becomes when it is affected? We came up with an innovative method to assess the interface weakening as a result of exposure to environmental effects."
The team used a combination of molecular simulations and laboratory tests in its assessment. The modeling was based on fundamental principles of molecular interactions, not on empirical data, Buyukozturk says.
In the laboratory tests, Buyukozturk and his colleagues controlled the residual stresses in a metal layer that was bonded and then forcibly removed. "We validated the method, and showed that moisture has a degrading effect," he says.
The findings could lead to exploration of new ways to prevent moisture from reaching into the bonded layer, perhaps using better sealants. "Moisture is the No. 1 enemy," Buyukozturk says.
"I think this is going to be an important step toward assessment of the bonding, and enable us to design more durable composites," he adds. "It gives a quantitative knowledge of the interface" — for example, predicting that under specific conditions, a given bonded material will lose 30 percent of its strength.
Interface problems are universal, Buyukozturk says, occurring in many areas besides biomedicine and construction. "They occur in mechanical devices, in aircraft, electrical equipment, in the packaging of electronic components," he says. "We feel this will have very broad applications."
Bonded composite materials are beginning to be widely used in airplane manufacturing; often these composites are then bonded to traditional materials, like aluminum. "We have not had enough experience to prove the durability of these composite systems is going to be there after 20 years," Buyukozturk says.
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by the National Science Foundation.
Written by David Chandler, MIT News Office
Learning how things fall apart
New research reveals how bonded materials, from airplane wings to dental crowns, lose their bonding
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Equation to predict happiness
2014-08-04
The happiness of over 18,000 people worldwide has been predicted by a mathematical equation developed by researchers at UCL, with results showing that moment-to-moment happiness reflects not just how well things are going, but whether things are going better than expected.
The new equation accurately predicts exactly how happy people will say they are from moment to moment based on recent events, such as the rewards they receive and the expectations they have during a decision-making task. Scientists found that overall wealth accumulated during the experiment was not ...
Model of viral lifecycle could help in finding a cure for hepatitis B
2014-08-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A new technique for studying the lifecycle of the hepatitis B virus could help researchers develop a cure for the disease.
In a paper published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Sangeeta Bhatia of MIT and Charles Rice of Rockefeller University describe using microfabricated cell cultures to sustain hepatitis B virus in human liver cells, allowing them to study immune responses and drug treatments.
Around 400 million people worldwide are infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV); of those, one-third will go on to develop ...
Weakness of leukemic stem cells discovered
2014-08-04
FRANKFURT. Despite improved therapy, only one out of every two adult patients survive acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The mean survival time for this disease, which predominantly occurs in the elderly, is less than a year for patients over 65 years. It is assumed that leukaemic stem cells, which cannot be completely eliminated during treatment, are the origin of relapse. However, as has been discovered by a team of Frankfurt-based researchers, these cells do have a weakness: In the current edition of the high impact journal "Cancer Research", they report that the enzyme ...
Minuscule chips for NMR spectroscopy promise portability, parallelization
2014-08-04
Cambridge, Mass. – August 4, 2014 – A team of engineers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Schlumberger-Doll Research Center in Cambridge, Mass., and the University of Texas, Austin, have created a truly portable device for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
NMR spectroscopy is a technique that perturbs protons within a molecule to glean important clues about its structure. It can identify unknown substances, detect very slight variations in chemical composition, and measure how molecules interact, making it an essential tool ...
The evolution of migration
2014-08-04
Each year, millions of birds migrate thousands of miles between the locations where they breed and raise young, and the areas where they spend the winter. Each migration is a trip fraught with danger—many birds die before they reach their final destination. To scientists, long distance migration still holds many mysteries, one of which is: where did migration begin and how did it evolve? This question has long been a debated topic among scientists, but thanks to new research from Field Museum scientists, we may have an answer for one of the largest groups of migratory birds. ...
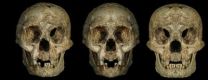
Flores bones show features of Down syndrome, not a new 'hobbit' human
2014-08-04
In October 2004, excavation of fragmentary skeletal remains from the island of Flores in Indonesia yielded what was called "the most important find in human evolution for 100 years." Its discoverers dubbed the find Homo floresiensis, a name suggesting a previously unknown species of human.
Now detailed reanalysis by an international team of researchers including Robert B. Eckhardt, professor of developmental genetics and evolution at Penn State, Maciej Henneberg, professor of anatomy and pathology at the University of Adelaide, and Kenneth Hsü, a Chinese geologist and ...
Triple therapy revs up immune system against common brain tumor
2014-08-04
A triple therapy for glioblastoma, including two types of immunotherapy and targeted radiation, has significantly prolonged the survival of mice with these brain cancers, according to a new report by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Mice with implanted, mouse-derived glioblastoma cells lived an average of 67 days after the triple therapy, compared with mice that lasted 24 days when they received only the two immunotherapies. Half of the mice who received the triple therapy lived 100 days or more and were protected against further tumors when new cancer ...
African American professional women positive on medical research
2014-08-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. — If a research survey of African American professional women is any indication, attitudes may be changing towards participation in medical research. Mayo Clinic and The Links, Incorporated researchers teamed up to survey members of the international women's organization, and found that a majority of African American women surveyed are willing to or have taken part in medical research. The results appear in the Journal of Women's Health.
"Our findings are highly encouraging," says Sharonne Hayes, M.D., Mayo Clinic cardiologist, co-author of the study, ...
Fires in California and Oregon
2014-08-04
The Little Deer fire in California began as a lightning strike on July 31, 2014. Currently it has burned 4,700 acres and is 43% contained however there has been increased humidity over the fire the last 24 hours with shifting wind conditions. The threat of thunder storms today (08/04) and tomorrow (08/05) may cause an increase in fire activity.
The Beaver Complex is comprised of the Salt Creek Fire (20 miles northwest of Medford) and the Oregon Gulch Fire (15 miles east of Ashland), which are lightning-started fires that started on July 30-31, 2014. After it was first ...
Eiler and Bald Fires in California
2014-08-04
The Eiler wildfire which began on July 31, 2014, has almost consumed 26,000 acres. It is currently unknown as to the cause of this fire. The weather patterns currently around this fire do not bode well for a quick containment. Maximum temperatures are in the mid- to high 80's with 10-20% relative humidity. There is an unstable atmosphere at work along with thunderstorm chances which are increasingly today (08/04) through Wednesday (08/06). A Red Flag Warning in effect for dry lightning on Monday (08/04).
The Bald Fire began with a lightning strike on July 30, 2014. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Learning how things fall apartNew research reveals how bonded materials, from airplane wings to dental crowns, lose their bonding