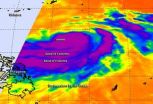
(Press-News.org) Infrared satellite imagery from NASA shows bands of powerful thunderstorms around Typhoon Halong's center, southern and eastern quadrants, while the northern quadrant is lacking in them. Typhoon Halong appears somewhat lopsided on satellite imagery because thunderstorm development in the northern side of the storm is being inhibited.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Halong on Aug. 4 at 12:47 a.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard provided infrared data on the cloud top temperatures of Typhoon Halong. AIRS data showed powerful thunderstorms with the highest, coldest cloud tops circled the center of the storm and were in two thick bands in the southern and eastern quadrants of the storm. Cloud top temperatures exceeded -63F/-52C indicating they were nearing the top of the troposphere. NASA research has shown that cloud top temperatures that cold, from storms that high, have the potential to produce heavy rainfall.
The other thing that the infrared imagery showed was a degradation of strong convection and thunderstorm development in the northern half of the storm. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that development is being inhibited because of subsidence, that is, the sinking of air (from above). In order for thunderstorms to form, air needs to rise and condense into clouds. When air is sinking from overhead, it prevents cloud formation from happening.
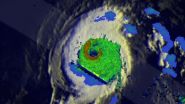
On Aug. 5 at 02:15 UTC, the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Typhoon Halong in the western Pacific Ocean that showed the strongest bands of thunderstorms continued to be in the southern and eastern quadrants of the storm.
At 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) Halong's center was located near 21.4 north latitude and 130.1 east longitude, about 351 nautical miles (403.9 miles/ 650.1 km) south-southeast of Kadena Air Base, Okinawa. Maximum sustained winds were near 85 knots (97.8 mph/157.4 kph). Halong continues to generate extremely rough seas with maximum significant wave heights at 35 feet (10.6 meters).
JTWC forecasters expect Halong to continue moving north-northeast over the next day or two before taking a more northerly track toward mainland Japan.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA satellite sees a somewhat lopsided Typhoon Halong
2014-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Butterflies could hold key to probes that repair genes
2014-08-05
CLEMSON, S.C. — New discoveries about how butterflies feed could help engineers develop tiny probes that siphon liquid out of single cells for a wide range of medical tests and treatments, according to Clemson University researchers.
The National Science Foundation recently awarded the project $696,514. It was the foundation's third grant to the project, bringing the total since 2009 to more than $3 million.
butterflyThe research has brought together Clemson's materials scientists and biologists who have been focusing on the proboscis, the mouthpart that many insects ...
PET/CT using FDG-labeled leucocytes may detect infection in acute pancreatitis patients
2014-08-05
Reston, Va. (August 5, 2014) – A new study diagnosing infection in patients with pancreatic fluid collections may swiftly and accurately rule out active infection in the body. As reported in the August issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, this treatment may assist in bringing nuclear medicine to the forefront of clinical management.
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment. While mild cases of AP are often successfully treated with conservative measures, such as nil per ...
Kaiser Permanente study finds shingles vaccine remains effective after chemotherapy
2014-08-05
PASADENA, Calif., August 5, 2014 — The herpes zoster vaccine continues to be effective in protecting older adults against shingles, even after they undergo chemotherapy, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published today in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Researchers examined the electronic health records of more than 21,000 Kaiser Permanente patients in Southern California who were 60 years of age and older and received chemotherapy between January 2007 and December 2012.
Researchers found that those patients who were previously vaccinated with zoster ...
Electronic cigarettes: many questions, limited research
2014-08-05
August 5, 2014 – Electronic cigarettes (ECIGs) are booming in popularity—but there's still only limited evidence on their potential health risks, or their advertised benefits in helping people to quit smoking, according to a research review in the July/August Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Based on their review, Alison B. Breland, PhD, of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues, write, "[V]ery ...
Genetic testing of tumor is recommended for colorectal cancer patients
2014-08-05
Bethesda, MD (Aug. 5, 2014) — Of the 143,000 patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer annually in the U.S., up to 25 percent have a familial risk of colorectal cancer. A new guideline from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer recommends genetic testing of tumors for all newly diagnosed colorectal cancer patients. The task force makes specific surveillance and management recommendations for those affected by a genetic condition called Lynch syndrome, the most common cause of inherited colorectal cancer, accounting for approximately 3 percent, or more than ...
NASA sees heavy rain in Hurricane Iselle as it heads toward Hawaii
2014-08-05
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM flew directly over the eye of powerful Hurricane Iselle and found extremely heavy rainfall rates occurring there.
On August 4, 2014 at 1037 UTC (6:37 a.m. EDT) when TRMM passed over the storm, Iselle had winds of about 120 knots (about 138 mph) at that time making it a dangerous category four hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale. Rainfall from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) instruments was overlaid on an enhanced infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite ...
A new 'whey' to control diabetes
2014-08-05
Blood sugar surges — after-meal glucose "spikes" — can be life threatening for the 29 million Americans with diabetes. Diabetic blood sugar spikes have been linked to cardiovascular disease, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, kidney failure, and retinal damage. Now a new Tel Aviv University study, published in Diabetologia, suggests a novel way to suppress these deadly post-meal glucose surges: the consumption of whey protein concentrate, found in the watery portion of milk separated from cheese curds, before breakfast.
According to TAU's Prof. Daniela Jakubowicz and Dr. Julio ...
Pump up the music -- especially the bass -- to make you feel powerful
2014-08-05
August 5, 2014 - It's the day of the big game – before heading out to the field, you put on your headphones and blast some music to pump you up. The music seemingly empowers you to do great things. This effect is not all in your head – according to new research, music truly does make us feel powerful. But not all songs have the same effect, researchers found, and the levels of bass are a key factor in their effectiveness.
"When watching major sports events, my coauthors and I frequently noticed athletes with their earphones on while entering the stadium and in the locker ...
Cancer fighter can help battle pneumonia
2014-08-05
AUGUSTA, Ga. – The tip of an immune molecule known for its skill at fighting cancer may also help patients survive pneumonia, scientists report.
A synthesized version of the tip of tumor necrosis factor appears to work like a doorstop to keep sodium channels open inside the air sacs of the lungs so excess fluid can be cleared, according to a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine.
This TIP peptide is attracted to the sugar coating at the mouth of the sodium channel. Once the two connect, they move inside the small but essential ...
Planet-like object may have spent its youth as hot as a star
2014-08-05
Washington, D.C.—Astronomers have discovered an extremely cool object that could have a particularly diverse history—although it is now as cool as a planet, it may have spent much of its youth as hot as a star.
The current temperature of the object is 200 to 300 degrees Fahrenheit (100 to 150 degrees Celsius), which is intermediate between that of the Earth and of Venus. However, the object shows evidence of a possible ancient origin, implying that a large change in temperature has taken place. In the past this object would have been as hot as a star for many millions ...