(Press-News.org) Scientists have known for a while that warming global temperatures are causing Arctic lakes to release methane, a potent greenhouse gas that leads to even more warming. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers including U of M researcher Jacques Finlay, found that Siberian lakes have actually pulled more greenhouse gasses from the atmosphere than they have released into it since the last Ice Age, causing an overall slight cooling effect.
Permafrost, especially that in the Siberian Arctic, contains significant amounts of all organic carbon found on Earth locked away in frozen soils. Warming global temperatures in the 15,000 years since the last Ice Age have begun to thaw the permafrost, leading to the widespread formation of lakes.
"As the lakes form, they thaw sediments that have been frozen for thousands of years," Finlay said. "Previous work by the lead author and others shows that this process accelerates methane production, leading to a large atmospheric flux of this greenhouse gas."
With this continued warming over thousands of years, however, the sediment destabilizes and the lakes fill and subsequently drain. Scientists had never studied the role of thaw, or thermokarst, in lakes in the global carbon cycle past the initial burst of greenhouse gas release.
"[The goal of our study] was to try to have an understanding of the long-term carbon dynamics of these lakes," Finlay said. He and his colleagues' work, published online July 24, shows that deep thermokarst lakes have taken more carbon and greenhouse gasses from the atmosphere than they have released since the last Ice Age.
However, Finlay cautions that the lakes have buried this carbon over a period of thousands of years. He says that scientists currently cannot predict if the "ice box" effect that rapidly freezes plant matter in the permafrost will continue to do so as atmospheric temperatures rise in the short term.
"If permafrost thaws rapidly, there is a large potential to release carbon back to the atmosphere from carbon rich soils and lake sediments," he said.
A key piece of the research was the identification of the source of the carbon collected in soil samples from these thermokarst lakes. One possibility was that all the carbon in lake sediments had been there since before the last Ice Age, indicating that soil carbon was simply moved around by the lake formation processes.
Finlay and colleagues instead found that much of the carbon had been buried there within the past 15,000 years. "The fossil data shows that a lot of the carbon that is there came there because of a burst of productivity that followed lake formation," Finlay said. "There were a lot of happy plants for a little while."
As the lakes drained, the plants and their sequestered carbon essentially were frozen into the permafrost. "The high rates of carbon burial exist because you have this ice box in the landscape that leads to a rapid transition back to a terrestrial environment with high rates of carbon burial," Finlay said. The study suggests that thermokarst lakes eventually compensate for their initial large release of greenhouse gases.
INFORMATION:
Finlay is an associate professor in the U of M's College of Biological Sciences and a resident fellow in the Institute on the Environment.
University of Minnesota researcher finds cooling effect in warming Arctic lakes
2014-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UH Case Medical Center study validates new approach to high blood pressure
2014-08-05
CLEVELAND – It truly could be mind over matter after all.
University Hospitals Case Medical Center's Richard Josephson, MD, recently released trial results in a study published in Psychosomatic Medicine that discusses mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) for hypertension.
Nearly 60 million adults in the United States have high blood pressure in the pre-hypertensive range. Current treatment guidelines recommend lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise and overall weight loss.
According to the new study, these changes can be dramatically augmented by MBSR as the ...
The interaction of climate change, fire, and forests in the US
2014-08-05
A special section of the September issue of Forest Ecology and Management, available online now, assesses the interactions among fire, climate change, and forests for five major regions of the United States.
The editors of the section—Drs. Chelcy Miniat from the U.S. Forest Service, Monique Rocca from Colorado State University, and Robert Mitchell (now deceased) from the Joseph W. Jones Ecological Research Center—started the project by organizing teams of scientists from the Forest Service and universities to provide scientific input into the third National Climate ...
NASA satellite sees a somewhat lopsided Typhoon Halong
2014-08-05
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA shows bands of powerful thunderstorms around Typhoon Halong's center, southern and eastern quadrants, while the northern quadrant is lacking in them. Typhoon Halong appears somewhat lopsided on satellite imagery because thunderstorm development in the northern side of the storm is being inhibited.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Halong on Aug. 4 at 12:47 a.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard provided infrared data on the cloud top temperatures of Typhoon Halong. AIRS data showed powerful ...
Butterflies could hold key to probes that repair genes
2014-08-05
CLEMSON, S.C. — New discoveries about how butterflies feed could help engineers develop tiny probes that siphon liquid out of single cells for a wide range of medical tests and treatments, according to Clemson University researchers.
The National Science Foundation recently awarded the project $696,514. It was the foundation's third grant to the project, bringing the total since 2009 to more than $3 million.
butterflyThe research has brought together Clemson's materials scientists and biologists who have been focusing on the proboscis, the mouthpart that many insects ...
PET/CT using FDG-labeled leucocytes may detect infection in acute pancreatitis patients
2014-08-05
Reston, Va. (August 5, 2014) – A new study diagnosing infection in patients with pancreatic fluid collections may swiftly and accurately rule out active infection in the body. As reported in the August issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, this treatment may assist in bringing nuclear medicine to the forefront of clinical management.
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment. While mild cases of AP are often successfully treated with conservative measures, such as nil per ...
Kaiser Permanente study finds shingles vaccine remains effective after chemotherapy
2014-08-05
PASADENA, Calif., August 5, 2014 — The herpes zoster vaccine continues to be effective in protecting older adults against shingles, even after they undergo chemotherapy, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published today in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Researchers examined the electronic health records of more than 21,000 Kaiser Permanente patients in Southern California who were 60 years of age and older and received chemotherapy between January 2007 and December 2012.
Researchers found that those patients who were previously vaccinated with zoster ...
Electronic cigarettes: many questions, limited research
2014-08-05
August 5, 2014 – Electronic cigarettes (ECIGs) are booming in popularity—but there's still only limited evidence on their potential health risks, or their advertised benefits in helping people to quit smoking, according to a research review in the July/August Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Based on their review, Alison B. Breland, PhD, of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues, write, "[V]ery ...
Genetic testing of tumor is recommended for colorectal cancer patients
2014-08-05
Bethesda, MD (Aug. 5, 2014) — Of the 143,000 patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer annually in the U.S., up to 25 percent have a familial risk of colorectal cancer. A new guideline from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer recommends genetic testing of tumors for all newly diagnosed colorectal cancer patients. The task force makes specific surveillance and management recommendations for those affected by a genetic condition called Lynch syndrome, the most common cause of inherited colorectal cancer, accounting for approximately 3 percent, or more than ...
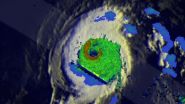
NASA sees heavy rain in Hurricane Iselle as it heads toward Hawaii
2014-08-05
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM flew directly over the eye of powerful Hurricane Iselle and found extremely heavy rainfall rates occurring there.
On August 4, 2014 at 1037 UTC (6:37 a.m. EDT) when TRMM passed over the storm, Iselle had winds of about 120 knots (about 138 mph) at that time making it a dangerous category four hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale. Rainfall from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) instruments was overlaid on an enhanced infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite ...
A new 'whey' to control diabetes
2014-08-05
Blood sugar surges — after-meal glucose "spikes" — can be life threatening for the 29 million Americans with diabetes. Diabetic blood sugar spikes have been linked to cardiovascular disease, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, kidney failure, and retinal damage. Now a new Tel Aviv University study, published in Diabetologia, suggests a novel way to suppress these deadly post-meal glucose surges: the consumption of whey protein concentrate, found in the watery portion of milk separated from cheese curds, before breakfast.
According to TAU's Prof. Daniela Jakubowicz and Dr. Julio ...