(Press-News.org) Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition that causes painful inflammation of several joints in the body. The joint capsule becomes swollen, and the disease can also destroy cartilage and bone as it progresses. Rheumatoid arthritis affects 0.5% to 1% of the world's population. Up to this point, doctors have used various drugs to slow or stop the progression of the disease. But now, ETH Zurich researchers have developed a therapy that takes the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in mice to a new level: after receiving the medication, researchers consider the animals to be fully cured.
The drug is a biotechnologically produced active substance consisting of two fused components. One component is the body's own immune messenger interleukin 4 (IL-4); previous studies have shown that this messenger protects mice with rheumatoid arthritis against cartilage and bone damage. ETH scientists have coupled an antibody to IL-4 that, based on the key-lock principle, binds to a form of a protein that is found only in inflamed tissue in certain diseases (and in tumour tissue).
Localised drug delivery
"As a result of combination with the antibody, IL-4 reaches the site of the disease when the fusion molecule is injected into the body," says pharmacist Teresa Hemmerle, who has just completed her dissertation in the group of Dario Neri, a professor at the Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Together with Fabia Doll, also a PhD pharmacist at ETH, she is the lead author of the study. "It allows us to concentrate the active substance at the site of the disease. The concentration in the rest of the body is minimal, which reduces side-effects," she says.
The researchers tested the new fusion molecule, which they refer to as an 'armed antibody', in a CTI project together with the ETH spin-off Philochem. They used a mouse model in which the animals developed swollen, inflamed toes and paws within a few days. Among other things, the researchers studied the fusion molecule in combination with dexamethasone, a cortisone-like anti-inflammatory drug that is already used to treat rheumatoid arthritis in humans. The researchers started treating each mouse as soon as they began showing signs of the disease in the form of swollen extremities.
Clinical trials in the next year
When used separately, the new fusion molecule and dexamethasone managed only to slow the progression of the disease in the affected animals. In contrast, the typical signs of arthritis, such as swollen toes and paws, disappeared completely within a few days when both medications were administered at the same time. Concentrations of a whole range of immune messengers in blood and inflamed tissue, which are changed in rheumatoid arthritis, returned to their normal levels. "In our mouse model, this combined treatment creates a long-term cure," says Hemmerle, who, since completing her dissertation, has been working at Philochem, where she continues the project.
Based on the promising results from the animal model, Philochem is currently preparing to test the new drug in clinical trials on people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. According to the researchers, these tests will begin in the next year.
INFORMATION:
Literature reference
Hemmerle T, Doll F, Neri D: Antibody-based delivery of IL4 to the neovasculature cures mice with arthritis. PNAS, online publication 4 August 2014, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402783111 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1402783111]
Curing arthritis in mice
2014-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Job insecurity in academia harms the mental wellbeing of non-tenure track faculty
2014-08-06
Non-tenure-track academics experience stress, anxiety, and depression due to their insecure job situation, according to the first survey of its kind published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Psychology.
There were 1.4 contingent faculty workers in the USA, according to a report by the American Association of University Professors. These faculty members, such as research adjunct faculty, lecturers and instructors, are off the so-called "tenure track". They work under short-term contracts with limited health and retirement benefits, often part-time and at different ...
Preparing for a changing climate: Ecologists unwrap the science in the National Climate Change Assessment
2014-08-06
Two Ignite sessions focusing on findings in the United States National Climate Assesment5 (NCA) will take place on Monday, August 11th during the Ecological Society of America's 99th Annual Meeting, held this year in Sacramento, California.
The first session, Ignite 1: From Plains to Oceans to Islands: Regional Findings from the Third National Climate Assessment will highlight major findings from the report about the regional effects of climate change, discuss impacts to the ecosystems of the region, and explore how changes in those ecosystems can moderate or exacerbate ...
Triangulum galaxy snapped by VST
2014-08-06
Messier 33, otherwise known as NGC 598, is located about three million light-years away in the small northern constellation of Triangulum (The Triangle). Often known as the Triangulum Galaxy it was observed by the French comet hunter Charles Messier in August 1764, who listed it as number 33 in his famous list of prominent nebulae and star clusters. However, he was not the first to record the spiral galaxy; it was probably first documented by the Sicilian astronomer Giovanni Battista Hodierna around 100 years earlier.
Although the Triangulum Galaxy lies in the northern ...
Study: Many cancer survivors smoke years after diagnosis
2014-08-06
ATLANTA – August 6, 2014–Nearly one in ten cancer survivors reports smoking many years after a diagnosis, according to a new study by American Cancer Society researchers. Further, among ten cancer sites included in the analysis, the highest rates of smoking were in bladder and lung cancers, two sites strongly associated with smoking. The study appears early online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
Cigarette smoking decreases the effectiveness of cancer treatments, increases the probability of recurrence, and reduces survival time. Nonetheless, some studies ...
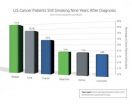
Nearly 10 percent of patients with cancer still smoke
2014-08-06
PHILADELPHIA — Nine years after diagnosis, 9.3 percent of U.S. cancer survivors were current smokers and 83 percent of these individuals were daily smokers who averaged 14.7 cigarettes per day, according to a report in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
"We need to follow up with cancer survivors long after their diagnoses to see whether they are still smoking and offer appropriate counseling, interventions, and possible medications to help them quit," said Lee Westmaas, PhD, director of tobacco ...
Healthy diet set early in life
2014-08-06
Promoting a healthy diet from infancy is important to prevent childhood obesity and the onset of chronic disease.
This is the finding from a study published in the latest issue of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.
Led by Rebecca Byrne from QUT, the study described quantity and diversity of food and drinks consumed by children aged 12-16 months.
"The toddler years are a critical age in the development of long-term food preferences, but this is also the age that autonomy, independence and food fussiness begins," Ms Byrne said.
"Childhood obesity in ...
Nutrition an issue for Indigenous Australians
2014-08-06
Nutrition has not been given enough priority in national Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health policy in recent years.
This is the finding from a study published in the latest issue of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.
Led by Jennifer Browne from La Trobe University, the study examined Aboriginal-specific health policies and strategies developed between 2000 and 2012.
"Increased inclusion of nutrition in Aboriginal health policy was identified during the first half of this period, but less during the second where a much greater emphasis was ...
Crime Victims' Institute tracks the state of stalking in Texas
2014-08-06
HUNTVILLE (8/6/14) -- According to a 2010 survey by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 1.4 million women in Texas experience stalking during their lifetimes. Despite recent laws adopted in the state to protect stalking victims, little information is available about the crime or policies and procedures to aid the criminal justice system, according to a report from the Crime Victims' Institute (CVI).
According to CDC estimates, 15.6 percent of the female population in Texas will experience stalking, slightly less than the 16.2 percent national ...
Vanderbilt finding may aid recovery from spinal cord injury
2014-08-05
Researchers in the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) have achieved the first conclusive non-invasive measurement of neural signaling in the spinal cords of healthy human volunteers.
Their technique, described today in the journal eLife, may aid efforts to help patients recover from spinal cord injuries and other disorders affecting spinal cord function, including multiple sclerosis.
"We definitely hope that this work can be translated to address many neurological disorders," said the paper's first author, Robert Barry, Ph.D., a postdoctoral ...
Researchers boost insect aggression by altering brain metabolism
2014-08-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists report they can crank up insect aggression simply by interfering with a basic metabolic pathway in the insect brain. Their study, of fruit flies and honey bees, shows a direct, causal link between brain metabolism (how the brain generates the energy it needs to function) and aggression.
The team reports its findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The new research follows up on previous work from the laboratory of University of Illinois entomology professor and Institute for Genomic Biology director Gene Robinson, ...