(Press-News.org) A major study of all penguin species suggests the birds are at continuing risk from habitat degradation. Writing in the journal, Conservation Biology, a group of internationally renowned scientists recommends the adoption of measures to mitigate against a range of effects including; food scarcity (where fisheries compete for the same resources), being caught in fishing nets, oil pollution and climate change. This could include the establishment of marine protected areas, although the authors acknowledge this might not always be practical. A number of other ecologically based management methods could also be implemented.
Populations of many penguin species have declined substantially over the past two decades. In 2013, eleven species were listed as 'threatened' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), two as 'near threatened' and five as 'of least concern'. In order to understand how they might respond to further human impacts on the world's oceans the scientists examined all eighteen species, looking at different factors where human activity might interfere with their populations. Forty-nine scientists contributed to the overall process.
They considered all the main issues affecting penguin populations including; terrestrial habitat degradation, marine pollution, fisheries bycatch and resource competition, environmental variability, climate change and toxic algal poisoning and disease. The group concludes that habitat loss, pollution, and fishing remain the primary concerns. They report that the future resilience of penguin populations to climate change impacts will almost certainly depend upon addressing current threats to existing habitat degradation on land and at sea.
The group of scientists recommends that the protection of penguin habitats is crucial for their future survival. This could be in the form of appropriately scaled marine reserves, including some in the High Seas, in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
Dr Phil Trathan, Head of Conservation Biology at the British Antarctic Survey and the lead author of the study, said:
"Penguins and humans often compete for the same food, and some of our other actions also impinge upon penguins. Our research highlights some of the issues of conservation and how we might protect biodiversity and the functioning of marine ecosystems.
"Whilst it is possible to design and implement large-scale marine conservation reserves it is not always practical or politically feasible. However, there are other ecosystem-based management methods that can help maintain biodiversity and a healthy ecosystem. For example, the use of spatial zoning to reduce the overlap of fisheries, oil rigs and shipping lanes with areas of the ocean used by penguins; the use of appropriate fishing methods to reduce the accidental bycatch of penguins and other species; and, the use of ecologically based fisheries harvesting rules to limit the allowable catches taken by fishermen, particularly where they target species that are also food for penguins."
The scientists believe their work will be of benefit to other studies of animal species, not just in the southern hemisphere, but the northern one too, where human impacts on the environment is even greater.
INFORMATION:
Issued by the British Antarctic Survey Press Office.
Contact: Paul Seagrove, Tel: +44 (0)1223 221414; +44 (0)7736 921693 email: psea@bas.ac.uk
Photos of some penguin species are available from the BAS Press Office.
Phil Trathan, British Antarctic Survey, Tel: +44 (0) 1223 221602; email: pnt@bas.ac.uk
Notes for editors
The paper: Pollution, Habitat Loss, Fishing and Climate Change as Critical Threats to Penguins by Phil Trathan, Pablo García-Borboroglu, Dee Boersma, Charles-André Bost, Robert Crawford, Glenn Crossin, Richard Cuthbert, Peter Dann, Lloyd Spencer Davis, Santiago De La Puente, Ursula Ellenberg, Heather Lynch, Thomas Mattern, Klemens Pϋtz, Philip Seddon, Wayne Trivelpiece and Barbara Wienecke is published in Conservation Biology this week.
Full details of the reviews for each species can be found in García-Borboroglu, P., and P.D. Boersma, [Editors]. 2013. Penguins: natural history and conservation, University of Washington Press, Seattle and London, the preparation of which was supported by the Global Penguin Society.
All 18 species of penguin were studied;
Emperor and Adelie (Antarctica), King, Chinstrap, Gentoo, Macaroni, Royal, Southern Rockhopper, Northern Rockhopper (Sub-Antarctic), Little, Fiordland, Snares, Erect-crested, Yellow-eyed (Oceania), and African, Magellanic, Humboldt and Galapágos (Africa and South America).
Each assessment of a species' status was subjected to independent peer review. The scientists then developed a scale for estimating risk factors.
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are zones of the sea or ocean where wildlife is protected from damage or disturbance. They can be established along coastlines or in the open ocean.
Phil Trathan's work was supported by funding from the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC).
British Antarctic Survey (BAS), an institute of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), delivers and enables world-leading interdisciplinary research in the Polar Regions. Its skilled science and support staff based in Cambridge, Antarctica and the Arctic, work together to deliver research that uses the Polar Regions to advance our understanding of Earth as a sustainable planet. Through its extensive logistic capability and know-how BAS facilitates access for the British and international science community to the UK polar research operation. Numerous national and international collaborations, combined with an excellent infrastructure help sustain a world leading position for the UK in Antarctic affairs. For more information visit http://www.antarctica.ac.uk.
Risks to penguin populations analysed
A major study of all penguin populations
2014-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
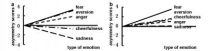
Frontal EEG lateralization as an objective indicator of emotional flexibility was found
2014-08-06
Emotional flexibility has become a widely discussed topic in emotional psychology, clinical psychology, health psychology and other fields. Professor Zhou Renlai and his group from Beijing Key Lab of Applied Experimental Psychology, School of Psychology, Beijing Normal University (BNU) explored whether frontal electroencephalogram (EEG) lateralization can predict emotional flexibility. Frontal EEG activation during different emotion stimuli was measured. They identified the difference of frontal EEG lateralization could predict difference in emotional flexibility. Relative ...
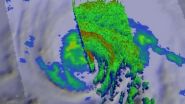
Typhoon Halong opens its eye again for NASA
2014-08-06
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Halong on its northern journey through the western North Pacific Ocean, it became wide-eyed again after going through eyewall replacement.
Eyewall replacement happens when the thunderstorms that circle the eye of a powerful hurricane are replaced by other thunderstorms. Basically, a new eye begins to develop around the old eye and it usually indicates a weakening trend.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Halong on August 6 at 04:30 UTC (12:30 a.m. ...
Older adults have morning brains!
2014-08-06
Toronto, Canada – Older adults who are tested at their optimal time of day (the morning), not only perform better on demanding cognitive tasks but also activate the same brain networks responsible for paying attention and suppressing distraction as younger adults, according to Canadian researchers.
The study, published online July 7th in the journal Psychology and Aging (ahead of print publication), has yielded some of the strongest evidence yet that there are noticeable differences in brain function across the day for older adults.
"Time of day really does matter when ...
New hand-held device uses lasers, sound waves for deeper melanoma imaging
2014-08-06
WASHINGTON, Aug. 6, 2014—A new hand-held device that uses lasers and sound waves may change the way doctors treat and diagnose melanoma, according to a team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis. The instrument, described in a paper published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Optics Letters, is the first that can be used directly on a patient and accurately measure how deep a melanoma tumor extends into the skin, providing valuable information for treatment, diagnosis or prognosis.
Melanoma is the fifth most common cancer type in the United ...
Trapped: Cell-invading piece of virus captured in lab by SLU scientists
2014-08-06
ST. LOUIS – In recent research published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Saint Louis University investigators report catching integrase, the part of retroviruses like HIV that is responsible for insertion of the viral DNA into human cell DNA, in the presence of a drug designed to thwart it.
This achievement sets the stage to use x-ray crystallography to develop complete images of HIV that include integrase, which in turn will help scientists develop new treatments for the illness.
Duane Grandgenett, Ph.D., professor at SLU's Institute of Molecular Virology ...
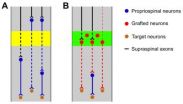
Transplanting neural progenitors to build a neuronal relay across the injured spinal cord
2014-08-06
Cellular transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury is a promising therapeutic strategy that includes the use of a variety of neural and non-neural cells isolated or derived from embryonic and adult tissue as well as embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. In particular, transplants of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) have been shown to limit secondary injury and scar formation and create a permissive environment in the injured spinal cord through the provision of neurotrophic molecules and growth supporting matrices that promote growth of injured host ...
Relay strategies combined with axon regeneration: A promising approach to restore spinal cord injury
2014-08-06
For decades, numerous investigations have only focused on axon regeneration to restore function after traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI), as interrupted neuronal pathways have to be reconnected for sensorimotor and autonomic recovery to occur. Experimental approaches have ranged from drug delivery and cell transplantation to genetic manipulations. Certainly, it would be an extraordinary achievement for injured axons to regenerate over long distances, to form synapses with target neurons, and to result in dramatic functional improvement. Dr. Shaoping Hou from Drexel University ...
Exposure to inflammatory bowel disease drugs could increase leukemia risk
2014-08-06
Bethesda, MD (August 6, 2014) – Immunosuppressive drugs called thiopurines have been found to increase the risk of myeloid disorders, such as acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome, a rare bone marrow disorder, seven-fold among inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. These data were reported in a new study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA). Thiopurines are an established treatment for IBD patients, used to reduce inflammation and provide symptom ...
Burrowing animals may have been key to stabilizing Earth's oxygen
2014-08-06
Evolution of the first burrowing animals may have played a major role in stabilizing the Earth's oxygen reservoir, according to a new study in Nature Geoscience.
Around 540 million years ago, the first burrowing animals evolved. When these worms began to mix up the ocean floor's sediments (a process known as bioturbation), their activity came to significantly influence the ocean's phosphorus cycle and as a result, the amount of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere.
"Our research is an attempt to place the spread of animal life in the context of wider biogeochemical cycles, ...
Skull shape risk factors could help in the welfare of toy dog breeds
2014-08-06
New research has identified two significant risk factors associated with painful neurological diseases in the skull shape of the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS). The findings could help in tackling these conditions in toy dog breeds and could be used in breeding guidelines.
The study conducted by undergraduate student, Thomas Mitchell, from the University of Bristol's School of Veterinary Sciences, and supervised by Dr Clare Rusbridge, is published online in the journal Canine Genetics and Epidemiology.
Syringomyelia (SM) is a painful condition in dogs and is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] Risks to penguin populations analysedA major study of all penguin populations