(Press-News.org) Rochester, MN, August 12, 2014 – There is strong epidemiological evidence of the importance of regular physical activity, such as brisk walking and jogging, in the management and rehabilitation of cardiovascular disease and in lowering the risk of death from other diseases such as hypertension, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommends about 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise or about 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. But there is clear evidence of an increase in cardiovascular deaths in heart attack survivors who exercise to excess, according to a new study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Paul T. Williams, PhD, of the Life Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, and Paul D. Thompson, MD, of the Department of Cardiology, Hartford Hospital, Hartford, CT, studied the relationship between exercise and cardiovascular disease-related deaths in about 2,400 physically active heart attack survivors. They conducted a prospective long-term study using the National Walkers' and Runners' Health Studies databases. This study confirmed previous reports indicating that the cardiovascular benefits for walking and running were equivalent, as long as the energy expenditures were the same (although when walking, as compared to running, it will take about twice as long to burn the same number of calories).
Remarkable dose-dependent reductions in deaths from cardiovascular events of up to 65% were seen among patients who were running less than 30 miles or walking less than 46 miles per week. Beyond this point however much of the benefit of exercise was lost, in what is described as a reverse J-curve pattern.
"These analyses provide what is to our knowledge the first data in humans demonstrating a statistically significant increase in cardiovascular risk with the highest levels of exercise," say Williams and Thompson. "Results suggest that the benefits of running or walking do not accrue indefinitely and that above some level, perhaps 30 miles per week of running, there is a significant increase in risk. Competitive running events also appear to increase the risk of an acute event." However, they point out that "our study population consisted of heart attack survivors and so the findings cannot be readily generalized to the entire population of heavy exercisers."
In the same issue, investigators in Spain report on a meta-analysis of ten cohort studies aimed at providing an accurate overview of mortality in elite athletes. The studies included over 42,000 top athletes (707 women) who had participated in a range of sports including football, baseball, track and field, and cycling, including Olympic level athletes and participants in the Tour de France.
"What we found on the evidence available was that elite athletes (mostly men) live longer than the general population, which suggests that the beneficial health effects of exercise, particularly in decreasing cardiovascular disease and cancer risk, are not necessarily confined to moderate doses," comments senior investigator Alejandro Lucia, MD, PhD, of the European University Madrid, Spain. "More research is needed however, using more homogeneous cohorts and a more proportional representation of both sexes."
"Extrapolation of the data from the current Williams and Thompson study to the general population would suggest that approximately one out of twenty people is overdoing exercise," comments James H. O'Keefe, MD, from the Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, MO, and first author of an editorial on "Exercising for Health and Longevity versus Peak Performance: Different Regimens for Different Goals," which appears in the same issue. Along with co-authors Carl "Chip" Lavie, MD, and Barry Franklin, PhD, he explains that "we have suggested the term 'cardiac overuse injury' for this increasingly common consequence of the 'more exercise is better' strategy." Even so, these authors state that about 10 out of every twenty people are not getting the minimum recommended amount of physical activity (>150 minutes/week of moderate exercise).
O'Keefe, Franklin and Lavie point out that a weekly cumulative dose of vigorous exercise of not more than about five hours has been identified in several studies to be the safe upper range for long-term cardiovascular health and life expectancy, and that it may also be beneficial to take one or two days a week off from vigorous exercise, and to refrain from high-intensity exercise on an everyday basis. They propose that individuals from either end of the exercise spectrum (sedentary people and over-exercisers) would probably reap long-term health benefits by changing their physical activity levels to be in the moderate range.
"For patients with heart disease, almost all should be exercising, and generally most should be exercising 30-40 minutes most days, but from a health stand-point, there is no reason to exercise much longer than that and especially not more than 60 minutes on most days," says Lavie, who is a cardiologist at the John Ochsner Heart and Vascular Institute, New Orleans, LA. "As Hippocrates said more than 2,000 years ago, 'if we could give every individual the right amount of nourishment and exercise, not too little and not too much, we would have found the safest way to health.' I and my co-authors believe this assessment continues to provide wise guidance," he concludes.
INFORMATION: END
Contrary to popular belief, more exercise is not always better
1 in 20 people may be overdoing exercise, reports Mayo Clinic Proceedings
2014-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate relicts may help researchers understand climate change
2014-08-12
While hiking through the Ozarks' characteristic oak and hickory forests as a teenager, ecologist Scott Woolbright discovered something decidedly uncharacteristic for the region: prickly pear cacti growing on an exposed, rocky ledge.
In a recent paper published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, Woolbright describes how populations and communities like these, known as climate relicts, can help scientists understand how ecological communities are affected by climate change.
Rocky, well-drained slopes in the Ozarks often create habitat "islands" within the surrounding ...
NASA sees the end of Tropical Depression Genevieve
2014-08-12
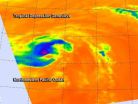
Cloud tops were warming and precipitation was waning in Tropical Depression Genevieve when NASA's Aqua satellite flew overhead. Genevieve moved through all three Pacific Ocean regions (eastern, central and western) in its two week lifetime and met its end today.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Genevieve on Aug. 11 at 01:29 UTC and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) captured infrared data on the storm. AIRS data showed a small area of the strongest thunderstorms were occurring over the northern quadrant, where temperatures approached -63F/-52C. ...
Roadside research from the pinelands and coast to coast
2014-08-12
PHILADELPHIA (August 12, 2014)— "Roads are essentially the primary feature of human civilization at this point," according to Dane Ward, a doctoral student in environmental science at Drexel University who is presenting research at the Ecological Society of America (ESA) meeting.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Ward, along with fellow doctoral students Ryan Rebozo and Kevin P.W. Smith from the Laboratory of Pinelands Research led by Walter Bien, PhD in Drexel's College of Arts and Sciences, took advantage of a cross-country roadtrip from Philadelphia to the meeting in Sacramento ...
UMN and NYBC research finds potential MERS transmission mechanism between bats and humans
2014-08-12
Researchers have identified the mechanism used by the deadly MERS virus to transmit from bats to humans. Bats are a native reservoir for MERS and the finding could be critical for understanding the animal origins of the virus, as well as preventing and controlling the spread of MERS and related viruses in humans.
The findings were published in the most recent edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Leading the research was Fang Li, Ph.D., associate professor of Pharmacology at the University of Minnesota Medical School. Graduate students Yang ...
Notre Dame paper offers insights into a new class of semiconducting materials
2014-08-12
A new paper by University of Notre Dame researchers describes their investigations of the fundamental optical properties of a new class of semiconducting materials known as organic-inorganic "hybrid" perovskites.
The research was conducted at the Notre Dame Radiation Laboratory by Joseph Manser, a doctoral student in chemical and biomolecular engineering, under the direction of Prashant Kamat, Rev. John A. Zahm Professor of Science. The findings appear in a paper in the August 10 edition of the journal Nature Photonics.
The term "perovskites" refers to the structural ...
New analysis reveals tumor weaknesses
2014-08-12
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Scientists have known for decades that cancer can be caused by genetic mutations, but more recently they have discovered that chemical modifications of a gene can also contribute to cancer. These alterations, known as epigenetic modifications, control whether a gene is turned on or off.
Analyzing these modifications can provide important clues to the type of tumor a patient has, and how it will respond to different drugs. For example, patients with glioblastoma, a type of brain tumor, respond well to a certain class of drugs known as alkylating agents ...
Federal Drug Discount Program faces challenges, report finds
2014-08-12
A federal program that provides billions in drug discounts to safety net hospitals and other health care providers is expanding under health care reform, but divergent views on the purpose and future scope of the program creates uncertainty for safety net providers and drug manufacturers, according to new report from the RAND Corporation.
The so-called 340B program faces a number of critical issues, such as whether to change and better define eligibility, strengthen compliance efforts and provide greater transparency about the discounts provided through the program, according ...
Digital literacy reduces cognitive decline in older adults, experts find
2014-08-12
Researchers have found a link between digital literacy and a reduction in cognitive decline, according to a study published in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Medical Sciences on July 8th.
Led by Andre Junqueira Xavier at the Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina, this is the first major study to show that digital literacy, or the ability to engage, plan and execute digital actions such as web browsing and exchanging emails, can improve memory.
Drawn from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing, the study followed 6442 participants in the UK between the ages ...
Regional anesthesia for pediatric knee surgery reduces pain, speeds recovery
2014-08-12
VIDEO:
As many as 98 percent of all pediatric knee surgeries performed at Nationwide Children's Hospital were done in an outpatient setting, as a result of this method that reduces...
Click here for more information.
A recent study of an ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia technique, called femoral nerve block, shows that it leads to less opioid use and allows the majority of patients to go home within hours of surgery. As many as 98 percent of all pediatric knee surgeries ...
Oxidative stress is significant predictor for hip fracture, research shows
2014-08-12
CINCINNATI—Oxidative stress is a significant predictor for hip fracture in postmenopausal women, according to new research led by University of Cincinnati (UC) epidemiologists.
The research, appearing online ahead of print in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, was led by Tianying Wu, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the UC College of Medicine Department of Environmental Health, and Shuman Yang, a postdoctoral fellow in the department. They collaborated with researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health and Harvard Medical School.
"To our knowledge, this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Contrary to popular belief, more exercise is not always better1 in 20 people may be overdoing exercise, reports Mayo Clinic Proceedings