(Press-News.org) Laser physicists have found a way to make atomic-force microscope probes 20 times more sensitive and capable of detecting forces as small as the weight of an individual virus.
The technique, developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU), hinges on using laser beams to cool a nanowire probe to minus 265 degrees Celsius.
"The level of sensitivity achieved after cooling is accurate enough for us to sense the weight of a large virus that is 100 billion times lighter than a mosquito," said Dr Ben Buchler from the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
The development could be used to improve the resolution of atomic-force microscopes, which are the state-of-the-art tool for measuring nanoscopic structures and the tiny forces between molecules.
Atomic force microscopes achieve extraordinarily sensitivity measurements of microscopic features by scanning a wire probe over a surface.
However, the probes, around 500 times finer than a human hair, are prone to vibration.
"At room temperature the probe vibrates, just because it is warm, and this can make your measurements noisy," said Professor Ping Koy Lam, a co-author of the research that is published in Nature Communications.
"We can stop this motion by shining lasers at the probe," he said.
The force sensor used by the ANU team was a 200 nm-wide silver gallium nanowire coated with gold.
"The laser makes the probe warp and move due to heat. But we have learned to control this warping effect and were able to use the effect to counter the thermal vibration of the probe," said Giovanni Guccione, a PhD student on the team.
However, the probe cannot be used while the laser is on as the laser effect overwhelms the sensitive probe. So the laser has to be turned off and any measurements quickly made before the probe heats up within a few milliseconds. By making measurements over a number of cycles of heating and cooling, an accurate value can be found.
"We now understand this cooling effect really well," says PhD student Harry Slatyer. "With clever data processing we might be able to improve the sensitivity, and even eliminate the need for a cooling laser."
INFORMATION:
Laser makes microscopes way cooler
Cooling a nanowire probe with a laser could lead to substantial improvements in the sensitivity of atomic force probe microscopes
2014-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adipose-derived stem cells and nerve regeneration
2014-08-15
Stem cell researchers at the Blond McIndoe Laboratory, University of Manchester, UK, led by Dr Adam Reid, present a review of the current literature on the suitability of adipose-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve repair.
Injuries to peripheral nerves are common and cause life-changing problems for patients alongside high social and health care costs for society. Current clinical treatment relies on sacrificing a nerve from elsewhere in the body to provide a nerve graft at the injury site, but much work has been done to develop a bioengineered nerve graft that would ...
Politicians need to address transport taboos, not just new technology, to meet carbon targets
2014-08-15
Transport accounts for 30% of CO2 emissions in the EU, with emissions rising 36% between 1990 and 2007. The research, carried out by Lund University and the University of Surrey a found a need to dissect the widely-held view that new technologies, such as biofuel and improved aircraft design, will result in carbon reduction targets being met.
In the paper, researchers highlight the fact that policy makers are turning to the perceived benefits of such technologies to drive decarbonisation policy, despite contrary evidence. They argue that in order to cut damaging carbon ...
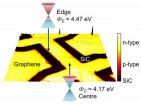
On the edge of graphene
2014-08-15
Researchers at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) have discovered that the conductivity at the edges of graphene devices is different to that of the central material.
Local scanning electrical techniques were used to examine the local nanoscale electronic properties of epitaxial graphene, in particular the differences between the edges and central parts of graphene Hall bar devices. The research was published in Scientific Reports, an open access publication from Nature Publishing Group.
The researchers found that the central part of the graphene channel demonstrated ...
TUM researchers develop defense against cyberattacks
2014-08-15
Port scanners are programs that search the Internet for systems that exhibit potential vulnerabilities. According to the report published today by journalists at Heise Online, Hacienda is one such port scanning program. The report says that this program is being put into service by the "Five Eyes," a federation of the secret services of the USA, Canada, the UK, Australia and New Zealand. "The goal is to identify as many servers as possible in other countries that can be remotely controlled," explains Dr. Christian Grothoff, Emmy Noether research group leader at the TUM ...
Experts close to perfect in determining truth in interrogations using active question methods
2014-08-15
Washington, DC (August 12, 2014) – Determining deception is a tool of the trade for law enforcement. The Good Cop/Bad Cop routine is etched in our minds as an effective method of finding out the truth. But prior research has shown that lie detecting is a 50/50 shot for experts and non-experts alike. So what exactly can we do to find out the truth? A recent study published in Human Communication Research by researchers at Korea University, Michigan State University, and Texas State University - San Marcos found that using active questioning of individuals yielded near-perfect ...
The beetle's white album
2014-08-15
The physical properties of the ultra-white scales on certain species of beetle could be used to make whiter paper, plastics and paints, while using far less material than is used in current manufacturing methods.
The Cyphochilus beetle, which is native to South-East Asia, is whiter than paper, thanks to ultra-thin scales which cover its body. A new investigation of the optical properties of these scales has shown that they are able to scatter light more efficiently than any other biological tissue known, which is how they are able to achieve such a bright whiteness. ...
Personal, public costs of scientific misconduct calculated
2014-08-15
Much has been assumed about the private and public damage of scientific misconduct. Yet few have tried to measure the costs to perpetrators and to society.
A recent study calculated some of the career impacts, as well as federal funding wasted, when biomedical research papers are retracted. The results appear in the Aug. 15 issue of the journal eLife.
In questioning common assumptions, the study authors determined that scientific misconduct typically, but not always, exacts a personal toll in derailing careers. On the public side, the cost to federal funding sources ...
Previous pulmonary disease linked to increased lung cancer risk in large study
2014-08-15
Links between a number of common respiratory diseases and an increased risk of developing lung cancer have been found in a large pooled analysis of seven studies involving more than 25,000 individuals.
"Associations between various respiratory diseases and lung cancer have been shown in earlier studies, but few of these studies considered multiple respiratory diseases simultaneously," said researcher Ann Olsson, PhD, of the International Agency for Research in Cancer in Lyon, France. "In our pooled analysis of seven case-control studies involving more than 12,500 cases ...
Human milk fat improves growth in premature infants
2014-08-15
HOUSTON – (August 15, 2014) – For premature infants, adequate growth while in the neonatal intensive care unit is an indicator of better long-term health and developmental outcomes. Researchers at the USDA/ARS Children's Nutrition Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children's Hospital have now successfully incorporated a cream supplement into premature infants' diets that improved their growth outcomes in the NICU. The report appears today in the Journal of Pediatrics.
"For premature babies who weigh less than 1,000 grams (about 2 pounds, 2 ounces), ...
Woodrats' genes help them to win the arms race against their food
2014-08-15
A handful of genes arm the woodrat against the toxic chemicals in its foodstuff, the creosote plant, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology.
It's long been a mystery exactly how the woodrat developed the ability to handle the chemicals in the creosote plant, which are toxic to other rodents. Previous research has suggested that they are protected by factors such as gut bacteria. But the new study identifies the genes switched on in two species of woodrat with resistance to the plant poisons, showing that the genes that they are born with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Laser makes microscopes way coolerCooling a nanowire probe with a laser could lead to substantial improvements in the sensitivity of atomic force probe microscopes