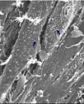
(Press-News.org) Tissue engineering technologies offer new treatment strategies for the repair of peripheral nerve injury, but cell loss between seeding and adhesion to the scaffold remains inevitable. In a study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014), a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel remained as a liquid when kept at temperatures below 10°C and gelled when the temperature was increased to 37°C in an incubator for 30 minutes, which was used as an extracellular matrix and combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered peripheral nerve composites in vitro. Results from DNA analysis and scanning electron microscope indicate that tissue-engineered composites formed with thermosensitive collagen hydrogel in dynamic culture can maintain larger numbers of seeded cells by avoiding cell loss during the initial adhesion stage; moreover, seeded cells are well-distributed throughout the material, which is of great significance for in vitro construction of tissue-engineered peripheral nerve composites.
INFORMATION:
Article: " Dynamic culture of a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel as an extracellular matrix improves the construction of tissue-engineered peripheral nerve," by Lanfeng Huang1, Rui Li2, Wanguo Liu3, Jin Dai1, Zhenwu Du4, Xiaonan Wang1, Jianchao Ma1, Jinsong Zhao5 (1 Department of Joint Surgery, Orthopedics Hospital of the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China; 2 Centre of Hand & Foot Surgery and Reparative & Reconstructive Surgery, Orthopedics Hospital of the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China; 3 Department of Orthopedics Surgery, the Third Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China; 4 Institute of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China; 5 Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin Province, China)
Huang LF, Li R, Liu WG, Dai J, Du ZW, Wang XN, Ma JC, Zhao JS. Dynamic culture of a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel as an extracellular matrix improves the construction of tissue-engineered peripheral nerve. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(14):1371-1378.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Dynamic culture of a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel improves tissue-engineered peripheral nerve
2014-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Incentives, innovation and growth
2014-08-15
Over the past decades, the economic sciences have seen fundamental breakthroughs in our understanding of human responses to incentives in the face of uncertainty and strategic interactions. But what is the scope and what are the limits for applying these models in the design of better institutions and better policies? And to what extent can they teach us what is needed to encourage the innovation that drives economic growth and social wellbeing? These are among the questions to be debated among 17 Nobel Laureates in Economic Sciences and approximately 450 aspiring young ...
New ways to treat solid tumors
2014-08-15
An international team of scientists has shown that an antibody against the protein EphA3, found in the micro-environment of solid cancers, has anti-tumour effects.
As EphA3 is present in normal organs only during embryonic development but is expressed in blood cancers and in solid tumours, this antibody-based approach may be a suitable candidate treatment for solid tumours.
The researchers from Monash University and Ludwig Cancer Research, in Australia, and KaloBios Pharmaceuticals, in the US, have had their findings published in the journal Cancer Research.
The ...
Guidelines can predict early menopause in child cancer survivors
2014-08-15
Girls with cancer who are most likely to become infertile after treatment can be identified using guidelines developed almost 20 years ago, new research shows.
The criteria – developed in Edinburgh – will help to select which girls should be offered the opportunity to freeze some tissue from their ovaries for use in the future.
Doctors are optimistic that the frozen tissue could one day help young cancer survivors to have children of their own.
Some cancer treatments can affect female fertility by bringing on early menopause. Freezing samples of ovary tissue before ...
Bats bolster brain hypothesis, maybe technology, too
2014-08-15
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Amid a neuroscience debate about how people and animals focus on distinct objects within cluttered scenes, some of the newest and best evidence comes from the way bats "see" with their ears, according to a new paper in the Journal of Experimental Biology. In fact, the perception process in question could improve sonar and radar technology.
Bats demonstrate remarkable skill in tracking targets such as bugs through the trees in the dark of night. Brown University neuroscience Professor James Simmons, the review paper's author, has long ...
A study of possible extended symmetries of field theoretic systems
2014-08-15
There has been much recent interest, especially among cosmologists, in theories known as galileons. Galileons are an interesting and novel, though still hypothetical, class of effective scalar fields which are extremely universal and have attracted much recent attention. They arise generically in describing the short distance behavior of the new degrees of freedom introduced during the process of modifying gravity, and in describing the dynamics of extra dimensional brane worlds. Modified gravity and brane worlds are just some of the ideas that have been studied as possible ...
Low vitamin D levels linked to increased risks after noncardiac surgery
2014-08-15
August 15, 2014 – Patients with low blood levels of vitamin D are at increased risk of death and serious complications after noncardiac surgery, suggests a study in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
"Vitamin D concentrations were associated with a composite of in-hospital death, serious infections, and serious cardiovascular events," according to the new research by Dr Alparslan Turan and colleagues of the Cleveland Clinic. They believe their results warrant further study to see if giving vitamin D supplementation before surgery can reduce the risk of these adverse outcomes.
Lower ...
Study: Brain imaging shows brain differences in risk-taking teens
2014-08-15
According to the CDC, unintentional injuries are the leading cause of death for adolescents. Compared to the two leading causes of death for all Americans, heart disease and cancer, a pattern of questionable decision-making in dire situations comes to light in teen mortality. New research from the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas investigating brain differences associated with risk-taking teens found that connections between certain brain regions are amplified in teens more prone to risk.
"Our brains have an emotional-regulation network that ...
Laser makes microscopes way cooler
2014-08-15
Laser physicists have found a way to make atomic-force microscope probes 20 times more sensitive and capable of detecting forces as small as the weight of an individual virus.
The technique, developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU), hinges on using laser beams to cool a nanowire probe to minus 265 degrees Celsius.
"The level of sensitivity achieved after cooling is accurate enough for us to sense the weight of a large virus that is 100 billion times lighter than a mosquito," said Dr Ben Buchler from the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
The ...
Adipose-derived stem cells and nerve regeneration
2014-08-15
Stem cell researchers at the Blond McIndoe Laboratory, University of Manchester, UK, led by Dr Adam Reid, present a review of the current literature on the suitability of adipose-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve repair.
Injuries to peripheral nerves are common and cause life-changing problems for patients alongside high social and health care costs for society. Current clinical treatment relies on sacrificing a nerve from elsewhere in the body to provide a nerve graft at the injury site, but much work has been done to develop a bioengineered nerve graft that would ...
Politicians need to address transport taboos, not just new technology, to meet carbon targets
2014-08-15
Transport accounts for 30% of CO2 emissions in the EU, with emissions rising 36% between 1990 and 2007. The research, carried out by Lund University and the University of Surrey a found a need to dissect the widely-held view that new technologies, such as biofuel and improved aircraft design, will result in carbon reduction targets being met.
In the paper, researchers highlight the fact that policy makers are turning to the perceived benefits of such technologies to drive decarbonisation policy, despite contrary evidence. They argue that in order to cut damaging carbon ...