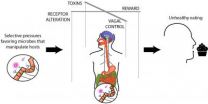
(Press-News.org) It sounds like science fiction, but it seems that bacteria within us — which outnumber our own cells about 100-fold — may very well be affecting both our cravings and moods to get us to eat what they want, and often are driving us toward obesity.
In an article published this week in the journal BioEssays, researchers from UC San Francisco, Arizona State University and University of New Mexico concluded from a review of the recent scientific literature that microbes influence human eating behavior and dietary choices to favor consumption of the particular nutrients they grow best on, rather than simply passively living off whatever nutrients we choose to send their way.
Bacterial species vary in the nutrients they need. Some prefer fat, and others sugar, for instance. But they not only vie with each other for food and to retain a niche within their ecosystem — our digestive tracts — they also often have different aims than we do when it comes to our own actions, according to senior author Athena Aktipis, PhD, co-founder of the Center for Evolution and Cancer with the Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at UCSF.
While it is unclear exactly how this occurs, the authors believe this diverse community of microbes, collectively known as the gut microbiome, may influence our decisions by releasing signaling molecules into our gut. Because the gut is linked to the immune system, the endocrine system and the nervous system, those signals could influence our physiologic and behavioral responses.
"Bacteria within the gut are manipulative," said Carlo Maley, PhD, director of the UCSF Center for Evolution and Cancer and corresponding author on the paper." "There is a diversity of interests represented in the microbiome, some aligned with our own dietary goals, and others not."
Fortunately, it's a two-way street. We can influence the compatibility of these microscopic, single-celled houseguests by deliberating altering what we ingest, Maley said, with measurable changes in the microbiome within 24 hours of diet change.
"Our diets have a huge impact on microbial populations in the gut," Maley said. "It's a whole ecosystem, and it's evolving on the time scale of minutes."
There are even specialized bacteria that digest seaweed, found in humans in Japan, where seaweed is popular in the diet.
Research suggests that gut bacteria may be affecting our eating decisions in part by acting through the vagus nerve, which connects 100 million nerve cells from the digestive tract to the base of the brain.
"Microbes have the capacity to manipulate behavior and mood through altering the neural signals in the vagus nerve, changing taste receptors, producing toxins to make us feel bad, and releasing chemical rewards to make us feel good," said Aktipis, who is currently in the Arizona State University Department of Psychology.
In mice, certain strains of bacteria increase anxious behavior. In humans, one clinical trial found that drinking a probiotic containing Lactobacillus casei improved mood in those who were feeling the lowest.
Maley, Aktipis and first author Joe Alcock, MD, from the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of New Mexico, proposed further research to test the sway microbes hold over us. For example, would transplantation into the gut of the bacteria requiring a nutrient from seaweed lead the human host to eat more seaweed?
The speed with which the microbiome can change may be encouraging to those who seek to improve health by altering microbial populations. This may be accomplished through food and supplement choices, by ingesting specific bacterial species in the form of probiotics, or by killing targeted species with antibiotics. Optimizing the balance of power among bacterial species in our gut might allow us to lead less obese and healthier lives, according to the authors.
"Because microbiota are easily manipulatable by prebiotics, probiotics, antibiotics, fecal transplants, and dietary changes, altering our microbiota offers a tractable approach to otherwise intractable problems of obesity and unhealthy eating," the authors wrote.
The authors met and first discussed the ideas in the BioEssays paper at a summer school conference on evolutionary medicine two years ago. Aktipis, who is an evolutionary biologist and a psychologist, was drawn to the opportunity to investigate the complex interaction of the different fitness interests of microbes and their hosts and how those play out in our daily lives. Maley, a computer scientist and evolutionary biologist, had established a career studying how tumor cells arise from normal cells and evolve over time through natural selection within the body as cancer progresses.
In fact, the evolution of tumors and of bacterial communities are linked, points out Aktipis, who said some of the bacteria that normally live within us cause stomach cancer and perhaps other cancers.
"Targeting the microbiome could open up possibilities for preventing a variety of disease from obesity and diabetes to cancers of the gastro-intestinal tract. We are only beginning to scratch the surface of the importance of the microbiome for human health," she said.
INFORMATION:
The co-authors' BioEssays study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the American Cancer Society, the Bonnie D. Addario Lung Cancer Foundation and the Institute for Advanced Study, in Berlin.
UC San Francisco (UCSF), now celebrating the 150th anniversary of its founding, is a leading university dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. It includes top-ranked graduate schools of dentistry, medicine, nursing and pharmacy, a graduate division with nationally renowned programs in basic, biomedical, translational and population sciences, as well as a preeminent biomedical research enterprise and two top-ranked hospitals, UCSF Medical Center and UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital San Francisco. Please visit http://www.ucsf.edu.
Do gut bacteria rule our minds?
In an ecosystem within us, microbes evolved to sway food choices
2014-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stroke researchers link ability to self-administer medication with memory loss
2014-08-15
West Orange, NJ. August 15, 2014. Kessler stroke researchers and colleagues have identified an association between over-optimistic estimation of one's own ability to take medications accurately, and memory loss among stroke survivors. Results indicate that assessing patients for their ability to estimate medication skills accurately may predict memory disorder. The article, "Stroke survivors over-estimate their medication self-administration ability (MSA), predicting memory loss," was epublished ahead of print on May 28 by Brain Injury (doi:10.3109/02699052.2014.915984). ...
Visual exposure predicts infants' ability to follow another's gaze
2014-08-15
Following another person's gaze can reveal a wealth of information critical to social interactions and also to safety. Gaze following typically emerges in infancy, and new research looking at preterm infants suggests that it's visual experience, not maturational age, that underlies this critical ability.
The research is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study showing that some aspects of the early development of social cognition is influenced by experience, even ...
NASA satellite spots a weakening Karina, now a tropical storm
2014-08-15
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Hurricane Karina before it weakened to a tropical storm early on August 15 and imagery showed the vertical wind shear was already taking its toll.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Karina on August 14 at 2:40 p.m. EDT when it was still clinging to hurricane status and noticed that wind shear was already having an effect on the storm's structure. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured an image that showed that the bulk of Karina's clouds were being pushed to the western side of the storm. That ...
NASA sees no punch left in Tropical Storm Julio
2014-08-15
Tropical Storm Julio doesn't have any strong thunderstorms or strong convection left in it according to infrared satellite imagery from NASA.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Julio on August 14 at 12:23 UTC (8:23 a.m. EDT), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder known as AIRS analyzed the clouds and temperatures of the storm. The AIRS data showed that cloud tops had warmed and dropped lower in the atmosphere. That indicates that the strength behind rising air had weakened and was not forming strong, high thunderstorms with cold cloud tops.
There was a ...
Bigger government makes for more satisfied people, international Baylor study finds
2014-08-15
People living in countries with governments that spend more on social services report being more contented, according to a Baylor University study.
"The effect of state intervention into the economy equals or exceeds marriage or employment status — two traditional predictors of happiness — when it comes to satisfaction," said Patrick Flavin, Ph.D., assistant professor of political science in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences.
The study — "Assessing the Impact of the Size and Scope of Government on Human Well-Being" — is published in the journal Social Forces. The researchers ...
Dynamic culture of a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel improves tissue-engineered peripheral nerve
2014-08-15
Tissue engineering technologies offer new treatment strategies for the repair of peripheral nerve injury, but cell loss between seeding and adhesion to the scaffold remains inevitable. In a study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014), a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel remained as a liquid when kept at temperatures below 10°C and gelled when the temperature was increased to 37°C in an incubator for 30 minutes, which was used as an extracellular matrix and combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered peripheral ...
Incentives, innovation and growth
2014-08-15
Over the past decades, the economic sciences have seen fundamental breakthroughs in our understanding of human responses to incentives in the face of uncertainty and strategic interactions. But what is the scope and what are the limits for applying these models in the design of better institutions and better policies? And to what extent can they teach us what is needed to encourage the innovation that drives economic growth and social wellbeing? These are among the questions to be debated among 17 Nobel Laureates in Economic Sciences and approximately 450 aspiring young ...
New ways to treat solid tumors
2014-08-15
An international team of scientists has shown that an antibody against the protein EphA3, found in the micro-environment of solid cancers, has anti-tumour effects.
As EphA3 is present in normal organs only during embryonic development but is expressed in blood cancers and in solid tumours, this antibody-based approach may be a suitable candidate treatment for solid tumours.
The researchers from Monash University and Ludwig Cancer Research, in Australia, and KaloBios Pharmaceuticals, in the US, have had their findings published in the journal Cancer Research.
The ...
Guidelines can predict early menopause in child cancer survivors
2014-08-15
Girls with cancer who are most likely to become infertile after treatment can be identified using guidelines developed almost 20 years ago, new research shows.
The criteria – developed in Edinburgh – will help to select which girls should be offered the opportunity to freeze some tissue from their ovaries for use in the future.
Doctors are optimistic that the frozen tissue could one day help young cancer survivors to have children of their own.
Some cancer treatments can affect female fertility by bringing on early menopause. Freezing samples of ovary tissue before ...
Bats bolster brain hypothesis, maybe technology, too
2014-08-15
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Amid a neuroscience debate about how people and animals focus on distinct objects within cluttered scenes, some of the newest and best evidence comes from the way bats "see" with their ears, according to a new paper in the Journal of Experimental Biology. In fact, the perception process in question could improve sonar and radar technology.
Bats demonstrate remarkable skill in tracking targets such as bugs through the trees in the dark of night. Brown University neuroscience Professor James Simmons, the review paper's author, has long ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
[Press-News.org] Do gut bacteria rule our minds?In an ecosystem within us, microbes evolved to sway food choices