(Press-News.org) AMES, Iowa – Sticking to a general rule of pouring just a half glass of wine limits the likelihood of overconsumption, even for men with a higher body mass index. That's the finding of a new Iowa State and Cornell University study to be published in a forthcoming issue of the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Laura Smarandescu, lead author and an assistant professor of marketing at Iowa State, says the research team looked at a variety of factors to understand and control over pouring. Researchers found BMI affected how much men poured, but had no influence on women. However, people who used a "rule of thumb," such as a half-glass rule or a two-fingers-from-the-top rule when pouring wine, poured less regardless of BMI or gender.
"About 70 percent of the people in the sample used the half-glass rule, and they poured significantly less by about 20 percent," Smarandescu said. "It's a big difference. We would suggest using a rule of thumb with pouring because it makes a big difference in how much people pour and prevents them from overdrinking."
Men with a higher BMI, who did not use a rule of thumb, poured more – 31 percent more for men considered overweight or obese and 26 percent more for men at the midpoint of the normal BMI range. While BMI did not affect how much women poured, those at the midpoint of the normal BMI poured 27 percent less when using the half-glass rule than those who did not.
Researchers were not surprised to find men poured more than women, which is consistent with other studies of alcohol consumption. However, they did not expect the half glass rule would be an exception to men pouring more.
"In this study, we had every expectation that men would always pour more than women, no matter what. But what we found is that the rule of thumb effect is so strong that men using a rule of thumb at all levels of BMI actually poured less than women who were not using a rule of thumb," said Doug Walker, an assistant professor of marketing at Iowa State.
Researchers asked 74 college students and staff to pour wine in a variety of settings so that they could control for the size, shape and color of the glass, as well as if wine is poured with a meal. They poured both red and white wine from bottles with different levels of fullness. Participants were told to pour as much as wine as they normally would in one setting.
Impact of social norms
Drinking is more socially acceptable for men than women, which is one explanation for why BMI did not have the same effect on women, researchers said. Women are often more conscious of how much they are pouring and will pour less.
"Women are more likely to socially compare with other women. They're aware that drinking is not as socially acceptable for women as it is for men, although it is becoming more acceptable than it has been in the past. But for men there is still more of a culture of drinking and pouring more," Smarandescu said.
The study looked only at pours, not consumption. However, researchers point to previous studies that show serving size is linked with overeating. Free pouring wine increases the tendency to over consume because it is not as easily measured as other types of beer or spirits.
"It is essential for all drinkers, especially men of higher BMIs, to have a rule of thumb for self-serving, because eye-balling a serving size is a difficult task and will often lead people to pour too much," said Brian Wansink, a professor of marketing at Cornell. "Next time you open a bottle, serve yourself a half glass – regardless of the size of your glass—and you will be less likely to accidentally drink too much."
INFORMATION: END
Use a rule of thumb to control how much you drink
2014-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
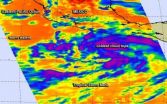
NASA sees massive Tropical Storm Lowell close enough to trouble Baja California
2014-08-22
Although Tropical Storm Lowell is not over land the storm is large enough to cause strong ocean swells in Baja California. NASA's Terra satellite passed over Lowell and captured an image that shows how it dwarfed Tropical Storm Karina.
The National Hurricane Center noted that swells generated by Lowell will affect the west coast of the Baja California, Mexico, peninsula and portions of the coast of southern California through the weekend of August 23 and 24. These swells are likely to cause life-threatening surf and rip current conditions.
NASA's Terra satellite passed ...
NASA's infrared data shows newborn Tropical Storm Marie came together
2014-08-22
Powerful thunderstorms in newborn Tropical Storm Marie were seen stretching toward the top of the troposphere in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Marie on Aug. 21 at 20:05 UTC when it was still classified as a low pressure area. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua read cloud top temperatures in the storm, and showed cloud tops as cold as -63F/-52C around the storm's center and in bands of thunderstorms east and south of the center. AIRS data showed that Marie is located in very warm ...
Women with severe, chronic health issues are screened for breast cancer less often
2014-08-22
TORONTO, Aug. 22, 2014 — Women with severe disabilities and multiple chronic conditions are screened for breast cancer less often than women with no disabilities or no chronic conditions, a new study has found.
They are also screened less often than women with moderate disabilities or women with only one chronic condition, according to Dr. Sara Guilcher, an affiliate scientist with the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael's Hospital.
Dr. Guilcher said women with disabilities often have other measures of social vulnerability, such as low income and low education ...
Many patients are discharged without a diagnosis
2014-08-22
Chest pain, breathing difficulties, fainting. Each year approx. 265,000 Danes are acutely admitted to medical departments with symptoms of serious illness. New research from Aarhus University and Aarhus University Hospital now shows that many of them – as many as every fourth patient – are sent home again without receiving a diagnosis of the severe symptoms that led to the acute hospitalisation.
"Naturally, there is no need for a diagnosis if the examinations at the hospital disprove that there is a serious illness. So some patients will always be discharged without a ...
Study shows epigenetic changes in children with Crohn's disease
2014-08-22
August 22, 2014 – A new study finds a wide range of epigenetic changes—alterations in DNA across the genome that may be related to key environmental exposures—in children with Crohn's disease (CD), reports Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, official journal of the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation of America (CCFA). The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The study provides "compelling evidence" of alterations of DNA in several regions of the genome in children with CD, according to Professor Jack Satsangi of University of ...
A breakthrough in imaging gold nanoparticles to atomic resolution by electron microscopy
2014-08-22
Nanometre-scale gold particles are intensively investigated for application as catalysts, sensors, drug delivery devices, biological contrast agents and components in photonics and molecular electronics. Gaining knowledge of their atomic-scale structures, fundamental for understanding physical and chemical properties, has been challenging. Now, researchers at Stanford University, USA, have demonstrated that high-resolution electron microscopy can be used to reveal a three-dimensional structure in which all gold atoms are observed. The results are in close agreement with ...
The striatum acts as hub for multisensory integration
2014-08-22
A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden provides insight on how the brain processes external input such as touch, vision or sound from different sources and sides of the body, in order to select and generate adequate movements. The findings, which are presented in the journal Neuron, show that the striatum acts as a sensory 'hub' integrating various types of sensory information, with specialised functional roles for the different neuron types.
"The striatum is the main input structure in the basal ganglia, and is typically associated with motor function", says ...
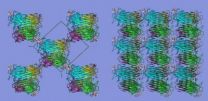
Proteins: New class of materials discovered
2014-08-22
This news release is available in German.
Thanks to certain helper substances, in PCFs proteins are fixated in a way so as to align themselves symmetrically, forming highly stable crystals. Next, the HZB and Fudan University researchers are planning on looking into how PCFs may be used as functional materials. Their findings are being published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5634).
Proteins are sensitive molecules. Everyone knows that – at least from having boiled eggs. Under certain circumstances – like immersion in ...
Research underway to create pomegranate drug to stem Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
2014-08-22
THE onset of Alzheimer's disease can be slowed and some of its symptoms curbed by a natural compound that is found in pomegranate. Also, the painful inflammation that accompanies illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and Parkinson's disease could be reduced, according to the findings of a two-year project headed by University of Huddersfield scientist Dr Olumayokun Olajide, who specialises in the anti-inflammatory properties of natural products.
Now, a new phase of research can explore the development of drugs that will stem the development of dementias such as Alzheimer's, ...
Scientists uncover why major cow milk allergen is actually allergenic
2014-08-22
Milk allergy is frequently confused with lactose intolerance. However, these are two entirely different mechanisms that occur in the body. People with lactose intolerance do not digest lactose properly because they lack an enzyme known as lactase. In the case of the potentially much more dangerous cow milk allergy, however, the body's immune system attacks milk proteins with its own IgE antibodies.
According to statistics, about two to three percent of children in Europe suffer from a genuine milk allergy. Less adults are diagnosed with the disease. The formation of so-called ...