(Press-News.org) Glass has many applications that call for different properties, such as resistance to thermal shock or to chemically harsh environments. Glassmakers commonly use additives such as boron oxide to tweak these properties by changing the atomic structure of glass. Now researchers at the University of California, Davis, have for the first time captured atoms in borosilicate glass flipping from one structure to another as it is placed under high pressure.
The findings may have implications for understanding how glasses and similar "amorphous" materials respond at the atomic scale under stress, said Sabyasachi Sen, professor of materials science at UC Davis. Sen is senior author on a paper describing the work published Aug. 29 in the journal Science.
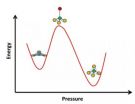
Boron oxide is often added to glass to control a range of properties, including chemical durability, flow resistance, optical transparency and thermal expansion. Material scientists know that the structure around the boron atoms in borosilicate glass changes with pressure and temperature, switching from a flat triangular configuration with three oxygen atoms surrounding one boron atom to a four-sided tetrahedron, with four oxygen atoms surrounding one boron.
Until know, material scientists have only been able to study these structures in one state or the other, but not in transition. Sen and graduate student Trenton Edwards developed a probe that enabled them to make nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements of the environment of boron atoms in glass under pressures up to 2.5 Gigapascal.
They found that under pressure, the flat triangles of boron and three oxygen atoms first deform into a pyramid shape, with the boron atom pushed up. That may bring it close to another oxygen atom, and let the structure turn into a tetrahedron, with four oxygen atoms surrounding one boron.
Intriguingly, although glass is structurally isotropic and the stress on the glass is the same in all directions, the boron atoms respond by moving in one direction in relation to the rest of the structure.
"This is an unexpected finding that may have far-reaching implications for understanding a wide range of stress-induced phenomena in amorphous materials," Sen said.
INFORMATION:
The work was done in collaboration with Jeffrey Walton, project scientist with the UC Davis NMR Facility. It was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
Watching the structure of glass under pressure
2014-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bradley Hospital collaborative study identifies genetic change in autism-related gene
2014-08-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – A new study from Bradley Hospital has identified a genetic change in a recently identified autism-associated gene, which may provide further insight into the causes of autism. The study, now published online in the Journal of Medical Genetics, presents findings that likely represent a definitive clinical marker for some patients' developmental disabilities.
Using whole-exome sequencing – a method that examines the parts of genes that regulate protein, called exons - the team identified a genetic change in a newly recognized autism-associated gene, Activity-Dependent ...
Yale study identifies possible bacterial drivers of IBD
2014-08-28
Yale University researchers have identified a handful of bacterial culprits that may drive inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, using patients' own intestinal immune responses as a guide.
The findings are published Aug. 28 in the journal Cell.
Trillions of bacteria exist within the human intestinal microbiota, which plays a critical role in the development and progression of IBD. Yet it's thought that only a small number of bacterial species affect a person's susceptibility to IBD and its potential severity.
"A handful ...
Drug shows promise against Sudan strain of Ebola in mice
2014-08-28
August 28, 2014 — (BRONX, NY) — Researchers from Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and other institutions have developed a potential antibody therapy for Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV), one of the two most lethal strains of Ebola. A different strain, the Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV), is now devastating West Africa. First identified in 1976, SUDV has caused numerous Ebola outbreaks (most recently in 2012) that have killed more than 400 people in total. The findings were reported in ACS Chemical Biology.
Between 30 and 90 percent of people infected with Ebola ...
NASA sees a weaker Tropical Storm Marie
2014-08-28
When NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of what is now Tropical Storm Marie, weakened from hurricane status on August 28, the strongest thunderstorms were located in the southern quadrant of the storm.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of Marie on August 28 at 11 a.m. EDT. Bands of thunderstorms circled the storm especially to the north. The National Hurricane Center noted that Marie has continued to produce a small area of convection (rising air that forms the thunderstorms that make up Marie) south and east of the center during some hours on the ...
DeVincenzo study breakthrough in RSV research
2014-08-28
MEMPHIS, Tenn. – The New England Journal of Medicine published research results on Aug. 21 from a clinical trial of a drug shown to safely reduce the viral load and clinical illness of healthy adult volunteers intranasally infected with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Le Bonheur Children's Hospital and the University of Tennessee Health Science Center researcher Infectious Disease Specialist John DeVincenzo, MD, is lead author of this study.
RSV is the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infections in young children in the United States and worldwide. ...
Small molecule acts as on-off switch for nature's antibiotic factory
2014-08-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Scientists have identified the developmental on-off switch for Streptomyces, a group of soil microbes that produce more than two-thirds of the world's naturally derived antibiotic medicines.
Their hope now would be to see whether it is possible to manipulate this switch to make nature's antibiotic factory more efficient.
The study, appearing August 28 in Cell, found that a unique interaction between a small molecule called cyclic-di-GMP and a larger protein called BldD ultimately controls whether a bacterium spends its time in a vegetative state or ...
Second-hand e-cig smoke compared to regular cigarette smoke
2014-08-28
E-cigarettes are healthier for your neighbors than traditional cigarettes, but still release toxins into the air, according to a new study from USC.
Scientists studying secondhand smoke from e-cigarettes discovered an overall 10-fold decrease in exposure to harmful particles, with close-to-zero exposure to organic carcinogens. However, levels of exposure to some harmful metals in second-hand e-cigarette smoke were found to be significantly higher.
While tobacco smoke contains high levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons – cancer-causing organic compounds – the level ...
Healthy Moms program helps women who are obese limit weight gain during pregnancy
2014-08-28
PORTLAND, Ore., August 28, 2014 — A new study finds that women who are obese can limit their weight gain during pregnancy using conventional weight loss techniques including attending weekly group support meetings, seeking advice about nutrition and diet, and keeping food and exercise journals.
Results of the Healthy Moms study, published in Obesity, also show that obese women who limit their weight gain during pregnancy are less likely to have large-for-gestational age babies which can complicate delivery and increase the baby's risk of becoming obese later in life.
"Most ...
University of Montana cicada study discovers 2 genomes that function as 1
2014-08-28
MISSOULA, Mont. – Two is company, three is a crowd. But in the case of the cicada, that's a good thing.
Until a recent discovery by a University of Montana research lab, it was thought that cicadas had a symbiotic relationship with two important bacteria that live within the cells of its body. Since the insect eats a simple diet consisting solely of plant sap, it relies on these bacteria to produce the nutrients it needs for survival.
In exchange, those two bacteria, Hodgkinia and Sulcia, live comfortably inside the cicada. Since all three divvy up the nutritional roles, ...
Non-adaptive evolution in a cicada's gut
2014-08-28
Organisms in a symbiotic relationship will often shed genes as they come to rely on the other organism for crucial functions. But now researchers have uncovered an unusual event in which a bacterium that lives in a type of cicada split into two species, doubling the number of organisms required for the symbiosis to survive.
Cicadas of the genus Tettigades feed only on sap they suck out of plants. To create some of the essential amino acids they rely on two bacterial helpers — Candidatus Hodgkinia cicadicola and Candidatus Sulcia muelleri — with which they have lived in ...