(Press-News.org) The brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys) is an invasive, herbivorous insect species that was accidentally introduced to the United States from Asia. First discovered in Allentown, Pennsylvania in 1996, it has since been found in at least 40 states in the U.S. as well as Canada, Switzerland, France, Germany, Italy, and Lichtenstein.
In North America, it has become a major agricultural pest across a wide range of commodities. The insect is capable of eating more than 100 different plant species, and in 2010 it caused $37 million worth of damage to apples alone.
Now a new, open-access article in the Journal of Integrated Pest Management describes available management options for this invasive pest species, as well as information about its origin and spread, its pest status in other invaded regions, descriptions of its life stages and biology, its chemical ecology, and the types of damage it does to various host plants. The authors of the article -- some of the best known experts on the BMSB in North America -- are from the the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, and a number of universities.
Nearly a dozen color photographs of the BMSB and the damage it does to crops are included in the article, along with a list of natural insect enemies that can potentially be used for biological control programs.
"Ultimately, classical biological control using parasitoids native to Asia and conservation biological control to enhance the effectiveness of introduced and indigenous natural enemies may provide the most promising long-term solutions for landscape-level reduction of H. halys populations," the authors wrote.
They also discuss different chemical control options that can be used successfully in integrated pest management programs.
"To return to an integrated approach to managing all pests in the crops affected by H. halys, growers require a more sustainable strategy for chemical control that combines efficient use of insecticides with a better understanding of its biology and behavior," according to the authors.
INFORMATION:
The full article is available at http://tinyurl.com/m3pnr6x.
The Journal of Integrated Pest Management is an open-access, peer-reviewed, extension journal covering the field of integrated pest management. The journal is multi-disciplinary in scope, publishing articles in all pest management disciplines, including entomology, nematology, plant pathology, weed science, and other subject areas. The intended readership for the journal is any professional who is engaged in any aspect of integrated pest management, including, but not limited to, crop producers, individuals working in crop protection, retailers, manufacturers and suppliers of pest management products, educators, and pest control operators.
The journal is published by the Entomological Society of America, the largest organization in the world serving the professional and scientific needs of entomologists and people in related disciplines. Founded in 1889, ESA today has nearly 7,000 members affiliated with educational institutions, health agencies, private industry, and government. Members are researchers, teachers, extension service personnel, administrators, marketing representatives, research technicians, consultants, students, and hobbyists. For more information, visit http://www.entsoc.org.
Brown marmorated stink bug biology and management options described in open-access article
2014-09-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cosmic forecast: Dark clouds will give way to sunshine
2014-09-03
Lupus 4 is located about 400 light-years away from Earth, straddling the constellations of Lupus (The Wolf) and Norma (The Carpenter's Square). The cloud is one of several affiliated dark clouds found in a loose star cluster called the Scorpius–Centaurus OB association. An OB association is a relatively young, yet widely dispersed grouping of stars [1]. The stars likely had a common origin in a gigantic cloud of material.
Because the association, and its Lupus clouds, form the closest such grouping to the Sun, they are a prime target for studying how stars grow up together ...
Scientists discover how to 'switch off' autoimmune diseases
2014-09-03
Scientists have made an important breakthrough in the fight against debilitating autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis by revealing how to stop cells attacking healthy body tissue.
Rather than the body's immune system destroying its own tissue by mistake, researchers at the University of Bristol have discovered how cells convert from being aggressive to actually protecting against disease.
The study, funded by the Wellcome Trust, is published today [03 September] in Nature Communications.
It's hoped this latest insight will lead to the widespread use of antigen-specific ...
Unplanned births out-of-hospital increases risk of infant mortality
2014-09-03
New research reveals that unplanned births out-of-hospital in Norway are associated with higher infant mortality. The findings published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, indicate that young women who have given birth at least once before (multiparous) and those living in remote areas are more likely to have unplanned deliveries, which may increase the risk of death in newborns.
In 2013, close to 60,000 babies were born in Norway according to the Statistics Norway. The country ...
Around 1 in 10 UK women has dry eye disease, requiring artificial tears
2014-09-03
The symptoms of dry eye disease include the sensation of grit in the eye, frequently accompanied by itching, burning and visual disturbance. The causes are poorly understood.
The researchers base their findings on almost 4000 women aged 20 to 87 (average age 57) from the TwinsUK cohort, drawn from the registry held at St Thomas' Hospital in London.
This cohort is widely regarded as representative of the UK general population, and has been used to look at a wide range of diseases and genetic traits over the years.
The prevalence of dry eye disease, and the frequency and ...
Stillbirth gap closing between indigenous and non-indigenous women, shows Australian study
2014-09-03
The gap in stillbirth rates between indigenous and non-indigenous women in Queensland, Australia, is closing, however indigenous women are still at risk of stillbirth due to preventable causes, find researchers in a new study published today (3 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
The Australian study used data from the Queensland Perinatal Data Collection and looked at 881,211 singleton births from 1995 to 2011. It aimed to assess the differences in stillbirth rates over time among indigenous (Australian Aboriginal and Torres ...
Estrogen increases cannabis sensitivity
2014-09-03
PULLMAN, Wash. - Smoking today's concentrated pot might be risky business for women, according to new research from Washington State University. The study is the first to demonstrate sex differences in the development of tolerance to THC.
Psychology professor Rebecca Craft showed that, thanks to their estrogen levels, female rats are at least 30 percent more sensitive than males to the pain-relieving qualities of THC—the key active ingredient in cannabis. Females also develop tolerance to THC more quickly. These sensitivities could increase vulnerability to negative ...
Discharged patients return to the ER because 'better safe than sorry'
2014-09-02
WASHINGTON – Patients who return to the emergency department within a few days of discharge do so principally because they are anxious about their symptoms and have lost trust in other parts of the health care system, according to the results of a study published online today in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("Return Visits to the Emergency Department: The Patient Perspective").
"When asked why they did not follow up as an outpatient, patients reported feeling that their symptoms were too severe to wait until their scheduled appointment or being instructed to return ...
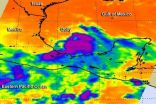
NASA satellites calling here you come again, Tropical Storm Dolly
2014-09-02
Tropical Storm Dolly visited Mexico six years ago, and NASA satellite data is calling "Here you come again," reminiscent of the famous country singer's hit song, as another storm named Dolly heads for a second landfall in Mexico.
In July of 2008, Tropical Storm Dolly made landfall on Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico before making a second and final landfall in south Texas. Now, six years later, Tropical Storm Dolly returns thanks to the six year list of revolving hurricane names, and once again Dolly is making landfall in eastern Mexico. NASA's Aqua satellite caught ...
Residency training predicts physicians' ability to practice conservatively
2014-09-02
LEBANON, NH – Doctors trained in locations with less intensive (and expensive) practice patterns appear to consistently be better at making clinical decisions that spare patients unnecessary and excessive medical care, according to a new study in JAMA Internal Medicine.
"Growing concern about the costs and harms of medical care has spurred interest in assessing physicians' ability to avoid the provision of unnecessary care," said lead author Brenda Sirovich of the VA Outcomes Group and The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice.
Sirovich and colleagues ...
Experiences make you happier than possessions -- Before and after
2014-09-02
To get the most enjoyment out of our dollar, science tells us to focus our discretionary spending on experiences such as travel over material goods. A new Cornell University study shows that the enjoyment we derive from experiential purchases may begin even before we buy.
This research offers important information for individual consumers who are trying to "decide on the right mix of material and experiential consumption for maximizing well-being," said psychology researcher and study author Thomas Gilovich of Cornell University.
Previously, Gilovich and colleagues ...