(Press-News.org) Tinnitus, migraine, epilepsy, depression, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's: all these are examples of diseases with neurological causes, the treatment and study of which is more and more frequently being carried out by means of magnetic stimulation of the brain. However, the method's precise mechanisms of action have not, as yet, been fully understood. The work group headed by PD Dr Dirk Jancke from the Institut für Neuroinformatik was the first to succeed in illustrating the neuronal effects of this treatment method with high-res images.
Painless Therapy
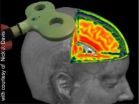
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a painless, non-invasive stimulation method, where an electromagnetic coil held above the head is used to generate a strong magnetic field. This method is deployed to activate or inhibit specific brain regions. Even though the number of its medical applications is constantly on the increase, TMS' precise neuronal mechanisms of action are not, as yet, very well understood. That is because imaging used for humans, such as fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging), do not possess the temporal resolution necessary for recording neural activities in milliseconds. More rapid measurement methods, such as EEG or MEG, on the other hand, are affected by the induced magnetic field, with the results that strong interferences are generated that cover important information regarding immediate TMS-based changes to brain activities.
Observing Effect on Neurons in Real Time
High-res images of TMS effects have now for the first time been successfully generated by RUB researchers in animal testing. The work group headed by PD Dr Dirk Jancke, Institut für Neuroinformatik, utilises voltage-sensitive dyes which, anchored in cell membranes, send out fluorescent light signals once neurons get activated or inhibited. By using light, the researchers avoided the problem of measurement of artefacts occurring due to magnetic fields. "We can now demonstrate in real time how one single TMS pulse suppresses brain activity across a considerable region, most likely through mass activation of inhibiting brain cells," says Dr Jancke. With higher TMS frequencies, each additional TMS pulse generates an incremental increase in brain activity. "This results in a higher cortical activation state, which opens up a time window for plastic changes," explains Dr Vladislav Kozyrev, the first author of the study.
Chances for Patients
The increased neuronal excitability may be utilised to effect specific reorganisation of cell connections by means of targeted learning processes. For example, through visual training after TMS, the ability to identify image contours improves; moreover, a combination of these methods enhances contrast perception in patients with amblyopia - a disorder of sight acquired during child development.
For many neurological diseases of the brain, such as epilepsy, depression and stroke, specific models have been developed. "Deployed in animal testing, our technology has delivered high spatiotemporal resolution imaging data of cortical activity changes," says Dirk Jancke. "We are hoping that these data will enable us to optimise TMS parameters and learning processes in a targeted manner, which are going to be used in future to adapt this technology for medical treatment of humans."
INFORMATION:
Funding
The German Research Foundation has financed the study, e.g. under the framework of Bochum's SFB 874 "Integration and Representation of Sensory Processes (Project A2, Eysel/Jancke)".
Title Catalogue
V. Kozyrev, U.T. Eysel, D. Jancke (2014): Voltage-sensitive dye imaging of transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced intracortical dynamics, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1405508111
Visualizing plastic changes to the brain
Effects of novel treatment method demonstrated
2014-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harvard and Cornell researchers develop untethered, autonomous soft robot
2014-09-05
New Rochelle, NY, September 4, 2014--Imagine a non-rigid, shape-changing robot that walks on four "legs," can operate without the constraints of a tether, and can function in a snowstorm, move through puddles of water, and even withstand limited exposure to flames. Harvard advanced materials chemist George Whitesides, PhD and colleagues describe the mobile, autonomous robot they have created in Soft Robotics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Soft Robotics website.
In "A Resilient, Untethered Soft Robot," ...
Study: Viral infection in nose can trigger middle ear infection
2014-09-05
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Sept. 5, 2014 – Middle ear infections, which affect more than 85 percent of children under the age of 3, can be triggered by a viral infection in the nose rather than solely by a bacterial infection, according to researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
By simultaneously infecting the nose with a flu virus and a bacterium that is one of the leading causes of ear infections in children, the researchers found that the flu virus inflamed the nasal tissue and significantly increased both the number of bacteria and their propensity to travel ...
NASA adds up heavy rainfall from Hurricane Norbert
2014-09-05
As Hurricane Norbert continued dropping heavy amounts of rainfall on Mexico's Baja California on September 5, NASA's TRMM satellite calculated the rain that had already fallen.
From its orbit in space, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite has the capability of determining how much rainfall has occurred over given areas. Data from TRMM was compiled into a rainfall map that showed the rainfall generated from Tropical Storm Dolly and Hurricane Norbert from August 28 through September 4, 2014.
Tropical storm Dolly dissipated quickly after coming ashore ...
It's the pits: Ancient peach stones offer clues to fruit's origins
2014-09-05
Anyone who enjoys biting into a sweet, fleshy peach can now give thanks to the people who first began domesticating this fruit: Chinese farmers who lived 7,500 years ago.
In a study published today in PLOS ONE, Gary Crawford, a U of T Mississauga anthropology professor, and two Chinese colleagues propose that the domestic peaches enjoyed worldwide today can trace their ancestry back at least 7,500 years ago to the lower Yangtze River Valley in Southern China, not far from Shanghai. The study, headed by Yunfei Zheng from the Zhejiang Institute of Archeology in China's ...
Like weeds of the sea, 'brown tide' algae exploit nutrient-rich coastlines
2014-09-05
The sea-grass beds of Long Island's Great South Bay once teemed with shellfish. Clams, scallops and oysters filtered nutrients from the water and flushed money through the local economy. But three decades after the algae that cause brown tides first appeared here, much of the sea grass and the bounty it used to provide is gone.
Spring on eastern Long Island is now marked by dense blooms of Aureococcus anophagefferens, which turn estuaries like Great South Bay the color of mud and crowd out native sea grass and stunt or poison shellfish. For years, researchers have puzzled ...
Past sexual assault triples risk of future assault for college women
2014-09-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Disturbing news for women on college campuses: a new study from the University at Buffalo Research Institute on Addictions (RIA) indicates that female college students who are victims of sexual assault are at a much higher risk of becoming victims again.
In fact, researchers found that college women who experienced severe sexual victimization were three times more likely than their peers to experience severe sexual victimization the following year.
RIA researchers followed nearly 1,000 college women, most age 18 to 21, over a five-year period, studying ...
Breast cancer specialist reports advance in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
2014-09-05
William M. Sikov, a medical oncologist in the Breast Health Center and associate director for clinical research in the Program in Women's Oncology at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, served as study chair and lead author for a recently-published major national study that could lead to improvements in outcomes for women with triple-negative breast cancer, an aggressive form of the disease that disproportionately affects younger women.
"Impact of the Addition of Carboplatin and/or Bevacizumab to Neoadjuvant Once-Per-Week Paclitaxel Followed by Dose-Dense Doxorubicin ...
Syracuse University physicists explore biomimetic clocks
2014-09-05
Working with a team of scientists from the Technical University of Munich (TU Munich), Brandeis University, and Leiden University in the Netherlands, M. Cristina Marchetti and Mark Bowick, professors in the Soft Matter Program in the Syracuse University College of Arts and Sciences, have engineered and studied "active vesicles." These purely synthetic, molecularly thin sacs are capable of transforming energy, injected at the microscopic level, into organized, self-sustained motion.
Their findings are the subject of a cover-story in the Sept. 5 issue of Science magazine.
The ...
Thousands of nuclear loci via target enrichment and genome skimming
2014-09-05
The use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies in phylogenetic studies is in a state of continual development and improvement. Though the botanically-inclined have historically focused on markers from the chloroplast genome, the importance of incorporating nuclear data is becoming increasingly evident. Nuclear genes provide not only the potential to resolve relationships between closely related taxa, but also the means to disentangle hybridization and better understand incongruences caused by incomplete lineage sorting and introgression.
By harnessing the power ...
Social support: How to thrive through close relationships
2014-09-05
PITTSBURGH—Close and caring relationships are undeniably linked to health and well-being for all ages. Previous research has shown that individuals with supportive and rewarding relationships have better physical and mental health and lower mortality rates. However, exactly how meaningful relationships affect health has remained less clear.
In a new paper, Carnegie Mellon University's Brooke Feeney and University of California, Santa Barbara's Nancy L. Collins detail specific interpersonal processes that explain how close relationships help individuals thrive. Published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Visualizing plastic changes to the brainEffects of novel treatment method demonstrated