(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Contrary to popular opinion, unruly students are not driving out teachers in droves from America's urban school districts. Instead, teachers are quitting due to frustration with standardized testing, declining pay and benefits and lack of voice in what they teach.
So finds a Michigan State University education scholar – and former high school teacher – in her latest research on teacher turnover, which costs the nation an estimated $2.2 billion a year.
Alyssa Hadley Dunn, assistant professor of teacher education, conducted in-depth interviews with urban secondary teachers before they quit successful careers in teaching. In a pair of studies, Dunn found that despite working in a profession they love, the teachers became demoralized by a culture of high-stakes testing in which their evaluations are tied to student scores and teachers have little say in the curriculum.
Many policymakers say the dominant emphasis on standardized testing is needed to make U.S. students more globally competitive. But "preparing students to answer multiple choice questions," Dunn argues, is not true learning.
"Those are not the skills that created Silicon Valley and Facebook," Dunn said, "and I don't believe the child who will eventually cure cancer will achieve that by learning to choose between A and B."
Frustration with high-stakes testing and top-down educational policies is part of what led Dunn, in 2009, to leave her job as an urban high school English teacher in Atlanta. According to the Alliance for Excellent Education, the teacher turnover rate in poor schools is about 20 percent per year – roughly 50 percent higher than the rate in affluent schools.
While previous research has examined why teachers quit after the fact, Dunn wanted to explore the issue while teachers are wrestling with the decision, to get a real-time take on the problem. In one of her studies, which appears in the Urban Review, the teachers she interviewed said the factors that made them want to continue teaching included their students, colleagues, commitment to the profession and worry about pursuing a new career in hard economic times.
"As previous research has shown, it is not, contrary to popular opinion, students who drive teachers out of the classroom," Dunn said.
But the negative factors – including lack of quality instruction time and low salaries – outweighed the positive aspects of teaching and led the teachers to quit. The average U.S. teacher salary decreased 1.3 percent between 2000 and 2013 – to $56,383, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. Further, the United States ranked 22 out of 27 participating countries in a 2011 study of teacher salaries by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
In addition, lack of support contributed to teachers' decision to quit. Dunn said teachers need more than professional development – they also need personal support, even if that's a colleague or an organized group to talk to about the pressures they face.
"How can teachers and administrators support each other in having courageous conversations about what teaching is doing to them," Dunn said, "and how can they work together to ease some of the common stressors?"
In the other study, which appears in Teachers College Record, Dunn interviewed one of her brightest former teaching candidates, Samantha Durrance, who went on to become an urban middle school teacher – only to quit after just two years in the classroom.
Like Dunn, Durrance found the high-pressure environment of standardized testing to be detrimental to both her and her students.
"The reality I found was one in which there are far too many standards and far too little time to teach," Durrance said. "I have given all of myself to this for too short a time to already be so drained. Fighting against the myriad of forces that drag our students down is just too much for me."
INFORMATION: END
High-stakes testing, lack of voice driving teachers out
2014-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
RT and concurrent chemotherapy after surgery is effective treatment for high-risk endometrial cancer
2014-09-09
Fairfax, Va., September 9, 2014—Radiation therapy with concurrent paclitaxel chemotherapy following surgery is an effective treatment for patients with high-risk endometrial cancer, according to a study published in the September 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology ● Biology ● Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy. Patients with early-stage disease are typically treated with surgery alone; however, ...
PP&AR sets national agenda for long-term care
2014-09-09
The number of Americans needing long-term care — also called long-term services and supports (LTSS) — is projected to more than double to 27 million by 2050. Approximately 70 percent of people over the age of 65 will rely on some form of LTSS for an average of three years. The latest issue of Public Policy & Aging Report (PP&AR) lays down a policy prescription for a sustainable system of LTSS in the U.S., using the Federal Commission on Long-Term Care's 2013 final report as its foundation.
With support from The SCAN Foundation, the issue presents nine articles under ...
Why do mushrooms turn brown?
2014-09-09
This news release is available in German.
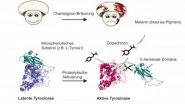
The research team of Annette Rompel from the Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, University of Vienna explore the mechanisms behind the "browning reaction" during the spoilage of mushrooms. The researchers were able to demonstrate that the enzyme responsible is already formed prior to fungal spoiling. The detailed study is published online in the well renowned journals, Phytochemistry and Acta Crystallographica.
Understanding the mechanism of enzyme tyrosinase pigmentation is currently of both medical as well as technological ...
Growth factors found in breast milk may protect against necrotizing enterocolitis
2014-09-09
Philadelphia, PA, September 9, 2014 – Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating gastrointestinal illness affecting up to 10% of premature infants, with a 30% mortality rate, and formula feeding has been identified as a risk factor for NEC. A study published in The American Journal of Pathology found that growth factors present in human breast milk, but not in formula, may explain the protection against intestinal damage. Further, supplementing the diet of newborn NEC-affected rodents with these growth factors promotes epithelial cell survival.
"NEC is a highly ...
A weekly text message could encourage healthier food choices, new study shows
2014-09-09
Many people are unaware that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's mandated nutrition labels are based on a 2,000-calorie-a-day diet, but a simple weekly text message reminder can greatly improve that awareness, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
While not an outright recommendation, the 2,000-calorie benchmark is what the FDA considers a reasonable daily calorie intake for many adults. More importantly, nutrition labels on food products sold in the U.S. are based on it.
The key to translating nutrition labels and ...
The saplings go their own way
2014-09-09
This news release is available in German. Leipzig. In tropical rainforests, most young trees grow spatially independent from their parent trees. This means that it is not possible to predict where seedlings will take root, and less specialised species therefore have an advantage even in the species-rich rainforests of the tropics. This is the finding of a study, conducted by researchers at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), the University of California and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, the results of which were published recently in ...
Study sheds light on asthma and respiratory viruses
2014-09-09
People with asthma often have a hard time dealing with respiratory viruses such as the flu or the common cold, and researchers have struggled to explain why.
In a new study that compared people with and without asthma, the answer is becoming clearer. The researchers found no difference in the key immune response to viruses in the lungs and breathing passages. The work, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, suggests that a fundamental antiviral defense mechanism is intact in asthma. This means that another aspect of the immune system must explain the ...
Weakness in malaria parasite fats could see new treatments
2014-09-09
A new study has revealed a weak spot in the complex life cycle of malaria, which could be exploited to prevent the spread of the deadly disease.
It found female malaria parasites put on fat differently to male ones.
"The study opens potential new ways to combat malaria," said Associate Professor Alexander Maier, from The Australian National University Research School of Biology.
"Malaria parasites show resistance to all current anti-malarial drugs. We are losing our weapons against this very important disease. But by studying lipid molecules – fats – rather than ...
Eating is addictive but sugar and fat are not like drugs, study says
2014-09-09
People can become addicted to eating for its own sake but not to consuming specific foods such as those high in sugar or fat, research suggests.
An international team of scientists has found no strong evidence for people being addicted to the chemical substances in certain foods.
The brain does not respond to nutrients in the same way as it does to addictive drugs such as heroin or cocaine, the researchers say.
Instead, people can develop a psychological compulsion to eat, driven by the positive feelings that the brain associates with eating.
This is a behavioural ...
New methods enhance the quality of myocardial perfusion imaging
2014-09-09
New methods that enhance the quality of myocardial perfusion imaging were developed in a recent study completed at the University of Eastern Finland. In her PhD study, Tuija Kangasmaa, Lic. Phil., invented a method which makes it possible to reduce the imaging time by up to 50%, making the scan session easier for the patient. Furthermore, the study also created two additional methods which correct errors resulting from patient movement during the scan. The methods were validated and they have already been taken into use in hospitals all over the world.
Coronary artery ...