(Press-News.org) Resilience, a person's ability to overcome adverse circumstances, is the main quality associated with pain tolerance among patients and their adjustment to chronic pain. This is the result of a new study carried out at the University of Málaga that shows that the effect of gender on this ability is not as significant as originally thought.
Over the years a number of clinical trials have shown important gender differences with regard to susceptibility to pain through illness, effectiveness of medications and recovery after anaesthetic. Furthermore, these results coincide with general lore where it is often said that women tolerate pain better than men.
However, a new study led by researchers at Malaga University with the aim of analysing the differences between men and women in terms of their experience with chronic pain has dispelled this theory, revealing that these differences are minimal.
Quite the opposite, it is a person's resilience -the ability to overcome adverse circumstances- that determines the high or low acceptance of pain, as it is related to a series of characteristics that provide the individual with resources to cope with chronic pain.
400 patients with chronic spinal pain (190 men and 210 women) treated in primary care centres took part in this study and the findings show more similarities than differences between the two sexes.
"More resilient individuals tend to accept their pain, that is, they tend to understand that their ailment is chronic and they stop focusing on trying to get the pain to disappear, to focus their energy on enhancing their quality of life, despite the pain," Carmen Ramírez-Maestre, the main author and researcher at the Andalusian institution, told SINC.
"In this regard," continued Ramírez-Maestre, "patients who are able to accept their pain feel less pain, they are more active on a daily basis and have a better mood".
Fear of pain
Also, the findings, which were published recently in 'The Journal of Pain', showed that patients that feared pain also experienced significantly more anxiety and depression.
"However, this fear was only related to a greater degree of pain in the samples of men and this was the only difference found between the sexes," concludes the author.
INFORMATION:
Citation:
Carmen Ramírez-Maestre, Rosa Esteve. "The role of sex/gender in the experience of pain. Resilience, fear and acceptance as central variables in the adjustment of men and women with chronic pain". The Journal of Pain.
Contact:
Carmen Ramírez-Maestre
Facultad de Psicología - Universidad de Málaga
Tel.: +34 95213 2430 - Email: cramirez@uma.es
Pain tolerance levels between men and women are similar
More resilient people tend to have a higher pain tolerance
2014-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UM study finds air pollution harmful to young brains
2014-09-10
MISSOULA, Mont. – Pollution in many cities threatens the brain development in children.
Findings by University of Montana Professor Dr. Lilian Calderón-Garcidueñas, MA, MD, Ph.D., and her team of researchers reveal that children living in megacities are at increased risk for brain inflammation and neurodegenerative changes, including Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease.
Calderón-Garcidueñas' findings are detailed in a paper titled "Air pollution and children: Neural and tight junction antibodies and combustion metals, the role of barrier breakdown and brain ...
Lady baboons with guy pals live longer
2014-09-10
DURHAM, N.C. –- Numerous studies have linked social interaction to improved health and survival in humans, and new research confirms that the same is true for baboons.
A long-term study of more than 200 wild female baboons from the plains of southern Kenya finds that the most sociable females –- measured by how often they engaged in social grooming relative to their peers -- live two to three years longer than their socially isolated counterparts.
Socializing with males gave females an even bigger longevity boost than socializing with other females, the researchers ...
New study reconstructs mega-earthquakes timeline in Indian Ocean
2014-09-10
MIAMI – A new study on the frequency of past giant earthquakes in the Indian Ocean region shows that Sri Lanka, and much of the Indian Ocean, is affected by large tsunamis at highly variable intervals, from a few hundred to more than one thousand years. The findings suggest that the accumulation of stress in the region could generate as large, or even larger tsunamis than the one that resulted from the 2004 magnitude-9.2 Sumatra earthquake.
Researchers from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science and the University of Peradeniya ...
Mystery solved: 'Sailing stones' of Death Valley seen in action for the first time
2014-09-10
Racetrack Playa is home to an enduring Death Valley mystery. Littered across the surface of this dry lake, also called a "playa," are hundreds of rocks – some weighing as much as 320 kilograms (700 pounds) – that seem to have been dragged across the ground, leaving synchronized trails that can stretch for hundreds of meters.
What powerful force could be moving them? Researchers have investigated this question since the 1940s, but no one has seen the process in action – until now.
In a paper published in the journal PLOS ONE on Aug. 27, a team led by Scripps Institution ...
UC San Diego researchers build first 500 GHz photon switch
2014-09-10
The work took nearly four years to complete and it opens a fundamentally new direction in photonics – with far-reaching potential consequences for the control of photons in optical fiber channels.
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have built the first 500 Gigahertz (GHz) photon switch. "Our switch is more than an order of magnitude faster than any previously published result to date," said UC San Diego electrical and computer engineering professor Stojan Radic. "That exceeds the speed of the fastest lightwave information channels in use today."
According ...
This star cluster is not what it seems
2014-09-10
The Milky Way galaxy is orbited by more than 150 globular star clusters, which are balls of hundreds of thousands of old stars dating back to the formation of the galaxy. One of these, along with several others in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), was found in the late eighteenth century by the French comet hunter Charles Messier and given the designation Messier 54.
For more than two hundred years after its discovery Messier 54 was thought to be similar to the other Milky Way globulars. But in 1994 it was discovered that it was actually associated with a ...
New method to detect prize particle for future quantum computing
2014-09-10
Quantum computing relies on the laws of quantum mechanics to process vast amounts of information and calculations simultaneously, with far more power than current computers. However, development of quantum computers has been limited as researchers have struggled to find a reliable way to increase the power of these systems, a power measured in Q-Bits.
Previous attempts to find the elusive Majorana particle have been very promising but have not yet provided definitive and conclusive evidence of its existence.
Now, researchers from the University of Surrey and the Ben-Gurion ...
Combining antibodies, iron nanoparticles and magnets steers stem cells to injured organs
2014-09-10
LOS ANGELES – Researchers at the Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute infused antibody-studded iron nanoparticles into the bloodstream to treat heart attack damage. The combined nanoparticle enabled precise localization of the body's own stem cells to the injured heart muscle.
The study, which focused on laboratory rats, was published today in the online peer reviewed journal Nature Communications. The study addresses a central challenge in stem cell therapeutics: how to achieve targeted interactions between stem cells and injured cells.
Although stem cells can be a potent ...
PPPL scientists take key step toward solving a major astrophysical mystery
2014-09-10
Magnetic reconnection can trigger geomagnetic storms that disrupt cell phone service, damage satellites and black out power grids. But how reconnection, in which the magnetic field lines in plasma snap apart and violently reconnect, transforms magnetic energy into explosive particle energy remains a major unsolved problem in plasma astrophysics. Magnetic field lines represent the direction, and indicate the shape, of magnetic fields.
Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have taken a key step toward a solution, ...
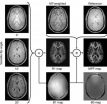
MRI shows gray matter myelin loss strongly related to MS disability
2014-09-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – People with multiple sclerosis (MS) lose myelin in the gray matter of their brains and the loss is closely correlated with the severity of the disease, according to a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study. Researchers said the findings could have important applications in clinical trials and treatment monitoring. The study appears online in the journal Radiology.
Loss of myelin, the fatty protective sheath around nerve fibers, is a characteristic of MS, an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that can lead to a variety of serious neurological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
[Press-News.org] Pain tolerance levels between men and women are similarMore resilient people tend to have a higher pain tolerance